Egyptian Language Report
... to the Coptic used in Coptic Christian church services today. Most of the language has been lost, frustrating both Egyptologists and linguists alike, although the basics of the language such as syllable structure, prosody, morphological typology, word classes and syntax are understood. This enjoyabl ...
... to the Coptic used in Coptic Christian church services today. Most of the language has been lost, frustrating both Egyptologists and linguists alike, although the basics of the language such as syllable structure, prosody, morphological typology, word classes and syntax are understood. This enjoyabl ...
the rise of river valley civilizations
... these settlements suggest a technologically advanced urban culture. Dockyards, granaries, warehouses, brick platforms and protective walls were present in many of their cities. They were also among the first "urban planners," with almost all their houses connected to public sewers and a water supply ...
... these settlements suggest a technologically advanced urban culture. Dockyards, granaries, warehouses, brick platforms and protective walls were present in many of their cities. They were also among the first "urban planners," with almost all their houses connected to public sewers and a water supply ...
A Rebirth for the Pharaoh* Reflections on the Classification of the
... while at the same time, it seems to be the general theme of any religious rituals: maintenance (the repelling of chaos) and renewal. According to Heliopolitan cosmogony, the creator god Atum (usually identified with the solar deity) begot the world by masturbation and ejaculation (see e.g. PT 600; S ...
... while at the same time, it seems to be the general theme of any religious rituals: maintenance (the repelling of chaos) and renewal. According to Heliopolitan cosmogony, the creator god Atum (usually identified with the solar deity) begot the world by masturbation and ejaculation (see e.g. PT 600; S ...
With an astounding length of 4,145 miles, the Nile River is the
... pelicans and herons all lived along the Nile. They ate the abundant fish that lived in the Nile. Egyptian people also ate fish from the river, but the Pharaoh never ate fish because it was considered “unclean” from the Nile waters. ...
... pelicans and herons all lived along the Nile. They ate the abundant fish that lived in the Nile. Egyptian people also ate fish from the river, but the Pharaoh never ate fish because it was considered “unclean” from the Nile waters. ...
Pharaoh Poster Project For this project you will create a large poster
... Where were the main cities during your pharaohs lifetime? Where were the political boundaries during your pharaoh’s lifetime? Where were other civilizations in relation to Egypt? ...
... Where were the main cities during your pharaohs lifetime? Where were the political boundaries during your pharaoh’s lifetime? Where were other civilizations in relation to Egypt? ...
Ancient Kush
... that Kush would grow even more powerful and attack Egypt. To prevent such an attack from occurring, the pharaoh Thutmose I sent an army to take control of Kush around 1500 BC. The pharaoh’s army conquered all of Nubia north of the Fifth Cataract. As a result, Kush became part of Egypt. After his arm ...
... that Kush would grow even more powerful and attack Egypt. To prevent such an attack from occurring, the pharaoh Thutmose I sent an army to take control of Kush around 1500 BC. The pharaoh’s army conquered all of Nubia north of the Fifth Cataract. As a result, Kush became part of Egypt. After his arm ...
Lesson 25 Theme Review and Vocabulary Builder
... Having a surplus of grain allowed farmers in some towns to use the surplus grain for trade. The Sinai Peninsula was a crossroads for the early Egyptians and traders from southwestern Asia. ...
... Having a surplus of grain allowed farmers in some towns to use the surplus grain for trade. The Sinai Peninsula was a crossroads for the early Egyptians and traders from southwestern Asia. ...
File
... B. each city had its own government / rulers, warriors, it’s own patron god, and functioned like an independent country C. includes within the city walls and also the surrounding farm land D. Examples include Sumerian cities of Ur, Uruk, Kish, Lagesh E. At center of each city was the walled temple w ...
... B. each city had its own government / rulers, warriors, it’s own patron god, and functioned like an independent country C. includes within the city walls and also the surrounding farm land D. Examples include Sumerian cities of Ur, Uruk, Kish, Lagesh E. At center of each city was the walled temple w ...
MOSES Study Guide
... Many generations before Moses was born, there was an Israelite living in Egypt, named Joseph. Joseph was born in Israel. He was the grandson of Abraham and the favorite of the seven sons of his father, Jacob. Joseph’s jealous brothers kidnapped him, sold him into slavery in Egypt and told their fath ...
... Many generations before Moses was born, there was an Israelite living in Egypt, named Joseph. Joseph was born in Israel. He was the grandson of Abraham and the favorite of the seven sons of his father, Jacob. Joseph’s jealous brothers kidnapped him, sold him into slavery in Egypt and told their fath ...
Map of Ancient Egypt ANCIENT EGYPT
... Art of Ancient Egypt The materials in this curriculum packet are designed to be used by students of all ages and their teachers. The curriculum packet contains • Posters of twelve artworks from the collection of the Saint Louis Art Museum. Each poster has information about the work of art and sugge ...
... Art of Ancient Egypt The materials in this curriculum packet are designed to be used by students of all ages and their teachers. The curriculum packet contains • Posters of twelve artworks from the collection of the Saint Louis Art Museum. Each poster has information about the work of art and sugge ...
Egyptian Gardens - BYU ScholarsArchive
... most comprehensive resource to date regarding their layout and symbolism. In 1994, Egyptologist C. J. Eyre contributed archeological explanations of the use of the gardens. In 1989, Salima Ikram extensively explored the gardens and garden shrines of Amarna with Barry J. Kemp, who is still currently ...
... most comprehensive resource to date regarding their layout and symbolism. In 1994, Egyptologist C. J. Eyre contributed archeological explanations of the use of the gardens. In 1989, Salima Ikram extensively explored the gardens and garden shrines of Amarna with Barry J. Kemp, who is still currently ...
The Great Pyramid of Giza
... he travels, the clothes he wears, the tasks he’s assigned. Nakht is conscripted along with his brother Deba from a tiny village near Aswan in about 2,500 BC. The two of them sail up the Nile to work at Giza, the great desert plateau of limestone where the Great Pyramid still stands today. “It's more ...
... he travels, the clothes he wears, the tasks he’s assigned. Nakht is conscripted along with his brother Deba from a tiny village near Aswan in about 2,500 BC. The two of them sail up the Nile to work at Giza, the great desert plateau of limestone where the Great Pyramid still stands today. “It's more ...
Document
... Large drainage project created arable farmland. created a large empire that reached the Euphrates River. Traders had contacts with Middle East and Hatshepsut Crete. encouraged trade. Corruption and Ramses II expanded rebellions were Egyptian rule to Syria. common. Hyksos invaded and occupied the del ...
... Large drainage project created arable farmland. created a large empire that reached the Euphrates River. Traders had contacts with Middle East and Hatshepsut Crete. encouraged trade. Corruption and Ramses II expanded rebellions were Egyptian rule to Syria. common. Hyksos invaded and occupied the del ...
Egypt, Nubia, and Kush
... must recognize causes and effects on our own. I notice on page 3 the author says we know a lot about ancient Egyptian culture because Egypt had a written language. The word because is a clue word that signals a causeand-effect relationship. Egypt’s written language is the cause, and our knowledge ab ...
... must recognize causes and effects on our own. I notice on page 3 the author says we know a lot about ancient Egyptian culture because Egypt had a written language. The word because is a clue word that signals a causeand-effect relationship. Egypt’s written language is the cause, and our knowledge ab ...
Calliope
... a less important wife, became king. His name was also Thutmose, like his father and grandfather, so we call him Thutmose III. Thutmose III was very young when he became king, so Hatshepsut, as the chief queen and most important royal woman, became the regent. During this period, she was still repres ...
... a less important wife, became king. His name was also Thutmose, like his father and grandfather, so we call him Thutmose III. Thutmose III was very young when he became king, so Hatshepsut, as the chief queen and most important royal woman, became the regent. During this period, she was still repres ...
File
... 3. Trade grew in Egypt and the Army grew stronger. 4. In 1963 BCE, The Rosetta Stone was created. This stone has Greek, Egyptian hieroglyphics, and Egyptian cursive which enabled historians to decipher hieroglyphics. ...
... 3. Trade grew in Egypt and the Army grew stronger. 4. In 1963 BCE, The Rosetta Stone was created. This stone has Greek, Egyptian hieroglyphics, and Egyptian cursive which enabled historians to decipher hieroglyphics. ...
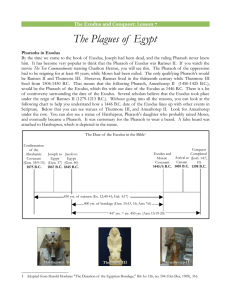
The Plagues of Egypt - Bible Classes for Students
... Up to this point, you can see how the plagues became more serious as they progressed. Fire was one of the two most feared things in the ancient world. Locusts Exodus 10:1-20 WARNING Isis was the god of life and as you know, Seth was the protector of the crops. The locusts blocked the sun, which kept ...
... Up to this point, you can see how the plagues became more serious as they progressed. Fire was one of the two most feared things in the ancient world. Locusts Exodus 10:1-20 WARNING Isis was the god of life and as you know, Seth was the protector of the crops. The locusts blocked the sun, which kept ...
Teacher`s Manual
... presence of Carnarvon, his daughter Lady Evelyn Herbert and Carter’s colleague Arthur Callender. Carnarvon asked Carter whether he could see anything. Carter answered with the famous words: “Yes, wonderful things.” Soon the team was certain it had discovered the tomb of Tutankhamun. The first articl ...
... presence of Carnarvon, his daughter Lady Evelyn Herbert and Carter’s colleague Arthur Callender. Carnarvon asked Carter whether he could see anything. Carter answered with the famous words: “Yes, wonderful things.” Soon the team was certain it had discovered the tomb of Tutankhamun. The first articl ...
The Four Early River Valley Civilizations
... B. each city had its own government / rulers, warriors, it’s own patron god, and functioned like an independent country C. includes within the city walls and also the surrounding farm land D. Examples include Sumerian cities of Ur, Uruk, Kish, Lagesh E. At center of each city was the walled temple w ...
... B. each city had its own government / rulers, warriors, it’s own patron god, and functioned like an independent country C. includes within the city walls and also the surrounding farm land D. Examples include Sumerian cities of Ur, Uruk, Kish, Lagesh E. At center of each city was the walled temple w ...
illustrated by Nigel Owen
... some control of the Nile. At first, they built simple irrigation ditches to bring water to their fields. Later, they built dams and dikes to control the yearly flooding. They also learned to store water in ponds or pools for use during times when the river was low. As the Egyptians learned to benefi ...
... some control of the Nile. At first, they built simple irrigation ditches to bring water to their fields. Later, they built dams and dikes to control the yearly flooding. They also learned to store water in ponds or pools for use during times when the river was low. As the Egyptians learned to benefi ...
Select Reading List for Ancient Egypt and Sudan
... Many earlier publications (notably by Wallis Budge) have been superseded by recent work; although often reprinted, they are not included here. We have given precedence to works in English, but many of the best publications are in other languages, most notably German and French. Many older publicatio ...
... Many earlier publications (notably by Wallis Budge) have been superseded by recent work; although often reprinted, they are not included here. We have given precedence to works in English, but many of the best publications are in other languages, most notably German and French. Many older publicatio ...
Egyptian Medicine - More Light In Masonry
... The purpose-built workmen's town ofKahun was constructed to house the officials and workforce building the pyramid of Sesostris II at Lahun in about 1895 Be. The larger houses in Kahun generally included a reception hall or living room, women's quarters, a kitchen and a room with washing or bathing ...
... The purpose-built workmen's town ofKahun was constructed to house the officials and workforce building the pyramid of Sesostris II at Lahun in about 1895 Be. The larger houses in Kahun generally included a reception hall or living room, women's quarters, a kitchen and a room with washing or bathing ...
Ancient Egyptian Pyramids and History Webquest
... Click on Cairo 3. How is Cairo an important city in Egypt today? Click on Memphis 4. Who created Memphis? 5. Why was Memphis so important during the time period of the Old Kingdom? Click on Saqqara 6. How many pyramids are at Saqqara? 7. What pyramid is considered the oldest in Egypt? 8. Overtime, w ...
... Click on Cairo 3. How is Cairo an important city in Egypt today? Click on Memphis 4. Who created Memphis? 5. Why was Memphis so important during the time period of the Old Kingdom? Click on Saqqara 6. How many pyramids are at Saqqara? 7. What pyramid is considered the oldest in Egypt? 8. Overtime, w ...
Cultural Change in the Ancient Mediterranean and Near Eastern
... East. The multitude of cultural artifacts found in the archaeological record from the ancient Near East, from religious relics to everyday items to clay tablets with intercultural correspondences, provide valuable evidence that archaeologists use to both extract and construct the different types of ...
... East. The multitude of cultural artifacts found in the archaeological record from the ancient Near East, from religious relics to everyday items to clay tablets with intercultural correspondences, provide valuable evidence that archaeologists use to both extract and construct the different types of ...