File
... Large natural objects which revolve around a planet many planets have more than one moon Earth’s moon has no atmosphere and has hills/valleys/craters after the invention of the telescope Galileo saw 4 moons of Jupiter Moons can come in a variety of size and with a variety of surfaces ...
... Large natural objects which revolve around a planet many planets have more than one moon Earth’s moon has no atmosphere and has hills/valleys/craters after the invention of the telescope Galileo saw 4 moons of Jupiter Moons can come in a variety of size and with a variety of surfaces ...
BIO 10 Lecture 2
... – H is being converted to He in the core – 4 H → 1 He, so pressure drops with fusion and gravity squeezes harder – As gravity increases, temp increases, levels of radiation increase, and star is pushed outward, maintains size – When all the H is used up, the star will begin to convert He to C (carbo ...
... – H is being converted to He in the core – 4 H → 1 He, so pressure drops with fusion and gravity squeezes harder – As gravity increases, temp increases, levels of radiation increase, and star is pushed outward, maintains size – When all the H is used up, the star will begin to convert He to C (carbo ...
Chapter 19 I. The Sun, Earth and Moon A. Sun is our closest star B
... II. During this process small celestial bodies also formed A. Comets- long tails and icy centers 1. orbits around Sun usually very long B. Asteroids- made from different elements C. Meteorites- sometimes strike the Earth Chapter 20 I. The Life and Death of Stars A. What are stars? 1. Stars are huge ...
... II. During this process small celestial bodies also formed A. Comets- long tails and icy centers 1. orbits around Sun usually very long B. Asteroids- made from different elements C. Meteorites- sometimes strike the Earth Chapter 20 I. The Life and Death of Stars A. What are stars? 1. Stars are huge ...
Name: Astronomy Study Guide Part 1 Define Astronomy
... 1. Cosmic Background Radiation- left over energy from the big bang in space ...
... 1. Cosmic Background Radiation- left over energy from the big bang in space ...
PPT
... below? Do you think its’ orbit around the sun is more or Less elliptical as compared to Earth? ...
... below? Do you think its’ orbit around the sun is more or Less elliptical as compared to Earth? ...
astronomy final exam - Physics and Astronomy
... What does the term “encephalization” refer to? What is the characteristic molecule called which carries the code of LAWKI? What are it's properties? What would best be the best means of communication between other intelligent species in the galaxy and us? A cell's DNA molecules are constructed of wh ...
... What does the term “encephalization” refer to? What is the characteristic molecule called which carries the code of LAWKI? What are it's properties? What would best be the best means of communication between other intelligent species in the galaxy and us? A cell's DNA molecules are constructed of wh ...
Objects in the Sky Power Point
... energy moves from the core to the surface surface temperature 4 million degrees F energy travels through space as electromagnetic waves of light and heat Earth is 93 million miles from Sun, receives only tiny amount of Sun's energy harmful rays are filtered by atmosphere, ozone and Earth's surface S ...
... energy moves from the core to the surface surface temperature 4 million degrees F energy travels through space as electromagnetic waves of light and heat Earth is 93 million miles from Sun, receives only tiny amount of Sun's energy harmful rays are filtered by atmosphere, ozone and Earth's surface S ...
qwk9
... A. Accretion disks and bi-polar jets are features associated with both star formation and active galactic nuclei B. Hayashi tracks describe the evolution of a star on the HR diagram after it has started nuclear fusion C. New stars in the Milky Way are born as a result of the gravitational collapse o ...
... A. Accretion disks and bi-polar jets are features associated with both star formation and active galactic nuclei B. Hayashi tracks describe the evolution of a star on the HR diagram after it has started nuclear fusion C. New stars in the Milky Way are born as a result of the gravitational collapse o ...
Questions on Black Body radiation and Wien`s Law
... 1. Given the wavelength of maximum intensity observed in the spectrum of each of the stars below , calculate their surface temperature. ...
... 1. Given the wavelength of maximum intensity observed in the spectrum of each of the stars below , calculate their surface temperature. ...
Solar Nebula Theory
... Formation of the Moon Properties that need to be explained: - Overall composition is similar to Earth. - Moon’s density is similar to Earth’s crust - Orbital plane is close to Ecliptic - Lack of water on the Moon. ...
... Formation of the Moon Properties that need to be explained: - Overall composition is similar to Earth. - Moon’s density is similar to Earth’s crust - Orbital plane is close to Ecliptic - Lack of water on the Moon. ...
astrophysics 2009
... 4. The most distant star visible to the naked eye is epsilon Aurigi at 5000ly. How far is this in m? 5. The most distant galaxy visible to the naked eye is the Andromeda Galaxy M31 at 2.2 x 106 ly. How far is this I metres? ...
... 4. The most distant star visible to the naked eye is epsilon Aurigi at 5000ly. How far is this in m? 5. The most distant galaxy visible to the naked eye is the Andromeda Galaxy M31 at 2.2 x 106 ly. How far is this I metres? ...
Stars - Clover Sites
... 11. At what time of year is the constellation Orion best seen? Locate and idenify in the sky the three brightest stars of this constellation. 12. How are the letters of the Greek alphabet used to name stars in a constellation? Give five illustrations of the use of the letters of the Greek alphabet ...
... 11. At what time of year is the constellation Orion best seen? Locate and idenify in the sky the three brightest stars of this constellation. 12. How are the letters of the Greek alphabet used to name stars in a constellation? Give five illustrations of the use of the letters of the Greek alphabet ...
Stars and Moon Summative Review
... Identify the phases of the moon. How does the gravitational pull of the moon affect the Earth? (the side closest and the side farthest) What does a waxing moon indicate? Identify the cause of tides on Earth. Describe the effect that the elliptical orbit of the moon has on the Earth. ...
... Identify the phases of the moon. How does the gravitational pull of the moon affect the Earth? (the side closest and the side farthest) What does a waxing moon indicate? Identify the cause of tides on Earth. Describe the effect that the elliptical orbit of the moon has on the Earth. ...
Chapter 17 and 18 Vocabulary Quist
... 40. The source of all the energy in the solar system is the _____________________ ...
... 40. The source of all the energy in the solar system is the _____________________ ...
practice exam #1
... 38. Briefly explain why the surface temperature of a red giant star is cooler than that of a main sequence star, even though the temperature in a red giant’s core is much hotter than a main sequence star’s core. ...
... 38. Briefly explain why the surface temperature of a red giant star is cooler than that of a main sequence star, even though the temperature in a red giant’s core is much hotter than a main sequence star’s core. ...
Current Study Guide - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... What does the term “encephalization” refer to? What is the characteristic molecule called which carries the code of LAWKI? What are it's properties? What would best be the best means of communication between other intelligent species in the galaxy and us? What is the water hole? If our radio telesco ...
... What does the term “encephalization” refer to? What is the characteristic molecule called which carries the code of LAWKI? What are it's properties? What would best be the best means of communication between other intelligent species in the galaxy and us? What is the water hole? If our radio telesco ...
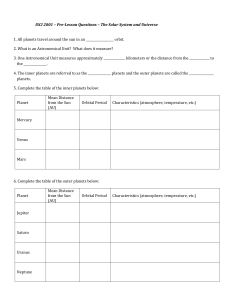
The Solar System and the Universe
... 8. Energy is released in the core of the Sun through a process called _____________________. When this process is accompanied by high temperature within the sun it is referred to as ___________________________. 9. During thermonuclear fusion, four ________________ nuclei fuse together to form one __ ...
... 8. Energy is released in the core of the Sun through a process called _____________________. When this process is accompanied by high temperature within the sun it is referred to as ___________________________. 9. During thermonuclear fusion, four ________________ nuclei fuse together to form one __ ...
R136a1

RMC 136a1 (usually abbreviated to R136a1) is a Wolf-Rayet star located at the center of R136, the central condensation of stars of the large NGC 2070 open cluster in the Tarantula Nebula. It lies at a distance of about 50 kiloparsecs (163,000 light-years) in the Large Magellanic Cloud. It has the highest mass and luminosity of any known star, at 265 M☉ and 8.7 million L☉, and also one of the hottest at over 50,000 K.