(GTP) specification for Gateway Location Register (GLR).
... In the network with the GLR, The optional Location Management messages are defined to support the case when Network-Requested PDP Context Activation procedures are used and an IM_GSN does not have a SS7 MAP interface. GTP is then used to transfer signalling messages between the IM_GSN and a GTP-MAP ...
... In the network with the GLR, The optional Location Management messages are defined to support the case when Network-Requested PDP Context Activation procedures are used and an IM_GSN does not have a SS7 MAP interface. GTP is then used to transfer signalling messages between the IM_GSN and a GTP-MAP ...
BROCADE NETIRON XMR 4000, 8000 16000, 32000
... packet’s source IP address against the routing table to ensure that the packet came from a valid, and expected, source network. ...
... packet’s source IP address against the routing table to ensure that the packet came from a valid, and expected, source network. ...
DSL-302T ADSL Modem User`s Manual
... shall be to replace the non-conforming Software (or defective media) with software that substantially conforms to D-Link’s functional specifications for the Software or to refund at D-Link’s sole discretion. Except as otherwise agreed by D-Link in writing, the replacement Software is provided only t ...
... shall be to replace the non-conforming Software (or defective media) with software that substantially conforms to D-Link’s functional specifications for the Software or to refund at D-Link’s sole discretion. Except as otherwise agreed by D-Link in writing, the replacement Software is provided only t ...
Interphase 4515 / 4525 / 4575 Manual
... This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15, Subpart B of the FCC Rules. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy. If not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, it may cause interf ...
... This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15, Subpart B of the FCC Rules. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy. If not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, it may cause interf ...
Alcatel-Lucent OmniSwitch 6900
... total cost of ownership (TCO) through the low power consumption. ...
... total cost of ownership (TCO) through the low power consumption. ...
ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1
... • If signals are then detected that show another device was transmitting at the same time, all devices stop sending and try again later • While Ethernet networks are designed with CSMA/CD technology, with today’s intermediate devices, collisions do not occur and the processes utilized by CSMA/CD are ...
... • If signals are then detected that show another device was transmitting at the same time, all devices stop sending and try again later • While Ethernet networks are designed with CSMA/CD technology, with today’s intermediate devices, collisions do not occur and the processes utilized by CSMA/CD are ...
Document
... IP lookup forms a major bottleneck in high performance routers. This is further made worse by the fact that IP forwarding requires complex lookup operation at every hop along the path. So, we could identify the FECs and associate each packet to certain FEC, we would be able to either avoid or simpli ...
... IP lookup forms a major bottleneck in high performance routers. This is further made worse by the fact that IP forwarding requires complex lookup operation at every hop along the path. So, we could identify the FECs and associate each packet to certain FEC, we would be able to either avoid or simpli ...
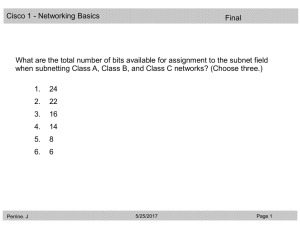
Q1 on FINAL
... What are the total number of bits available for assignment to the subnet field when subnetting Class A, Class B, and Class C networks? (Choose three.) ...
... What are the total number of bits available for assignment to the subnet field when subnetting Class A, Class B, and Class C networks? (Choose three.) ...
GlobeSurfer® II 1.8 - 7.2 - 7.2 S
... enter a PIN code. The PIN code is received from your ISP, but normally provided separately from the SIM card for security reasons. ...
... enter a PIN code. The PIN code is received from your ISP, but normally provided separately from the SIM card for security reasons. ...
- Lecturer
... – How to keep global state consistent? – Need for distributed coherency protocols. ...
... – How to keep global state consistent? – Need for distributed coherency protocols. ...
Model Answers Mid-Semester Test 2010
... d. Subnet 500: Note that the subnet 500 is not the last possible subnet, it is the last subnet used by the organization. To find the first address in subnet 500, we need to add 16,351,232 (499 x 32678) in base 256 (0. 249.128.0) to the first address in subnet 1. We have 16.0.0.0 + 0.249.128.0 = 16.2 ...
... d. Subnet 500: Note that the subnet 500 is not the last possible subnet, it is the last subnet used by the organization. To find the first address in subnet 500, we need to add 16,351,232 (499 x 32678) in base 256 (0. 249.128.0) to the first address in subnet 1. We have 16.0.0.0 + 0.249.128.0 = 16.2 ...
Chapter 4
... Obtaining IP Addresses • Typically an ISP gets a block of IP addresses, and assigns them to customers – E.g. the ISP might get 200.23.16.0/20, which it breaks down into smaller subnets for each customer – 200.23.16.0/23 for one, 200.23.18.0/23 for another, etc. – That way, routing knows anything st ...
... Obtaining IP Addresses • Typically an ISP gets a block of IP addresses, and assigns them to customers – E.g. the ISP might get 200.23.16.0/20, which it breaks down into smaller subnets for each customer – 200.23.16.0/23 for one, 200.23.18.0/23 for another, etc. – That way, routing knows anything st ...
Heile
... • Bluetooth would either : – keep a counter running so that it could predict which hop frequency the light would have reached or – use the inquiry procedure to find the light each time the switch was operated. ...
... • Bluetooth would either : – keep a counter running so that it could predict which hop frequency the light would have reached or – use the inquiry procedure to find the light each time the switch was operated. ...
A Survey of BGP Security Issues and Solutions
... interception attack, where the AS inspects the packets (compromising the user’s privacy) before forwarding them along to the legitimate destination [9]. To ensure that virtually all ASes direct traffic to the wrong place, the offending AS may advertise more-specific prefixes (e.g., 12.34.128.0/17 an ...
... interception attack, where the AS inspects the packets (compromising the user’s privacy) before forwarding them along to the legitimate destination [9]. To ensure that virtually all ASes direct traffic to the wrong place, the offending AS may advertise more-specific prefixes (e.g., 12.34.128.0/17 an ...
5 – Network Layer
... • IPv6 host dynamically determine packet size • using path MTU discovery • packet too large? router discard, send error msg • only source can fragment packets Checksum field removed • calculation reduces performance • networks are now reliable • data link, transport layers do own checksums ...
... • IPv6 host dynamically determine packet size • using path MTU discovery • packet too large? router discard, send error msg • only source can fragment packets Checksum field removed • calculation reduces performance • networks are now reliable • data link, transport layers do own checksums ...
Multicast_I
... •A unicast address identifies a single IP interface •A broadcast address identifies all IP interfaces on the subnet •A multicast address identifies a set of IP interfaces •A multicast datagram is received only by those interfaces interested in the datagram (applications wishing to participate in the ...
... •A unicast address identifies a single IP interface •A broadcast address identifies all IP interfaces on the subnet •A multicast address identifies a set of IP interfaces •A multicast datagram is received only by those interfaces interested in the datagram (applications wishing to participate in the ...
85 Kyung Hee University BGP (cont`d)
... Link State Routing OSPF uses Link State Routing to update the routing tables in an area Each router shares its knowledge about its neighborhood with every router in the area. Kyung Hee University ...
... Link State Routing OSPF uses Link State Routing to update the routing tables in an area Each router shares its knowledge about its neighborhood with every router in the area. Kyung Hee University ...
Evolution of P2P file sharing
... A host protected in this way cannot easily function as server Outgoing connections may be restricted to certain applications we block traffic to certain ports at the firewall e.g., only HTTP (ports 80 and 8080) and FTP (ports 20 and 21) ...
... A host protected in this way cannot easily function as server Outgoing connections may be restricted to certain applications we block traffic to certain ports at the firewall e.g., only HTTP (ports 80 and 8080) and FTP (ports 20 and 21) ...
Internet protocol suite

The Internet protocol suite is the computer networking model and set of communications protocols used on the Internet and similar computer networks. It is commonly known as TCP/IP, because among many protocols, the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP) is the accepted and most widely used protocol in Internet. Often also called the Internet model, it was originally also known as the DoD model, because the development of the networking model was funded by DARPA, an agency of the United States Department of Defense.TCP/IP provides end-to-end connectivity specifying how data should be packetized, addressed, transmitted, routed and received at the destination. This functionality is organized into four abstraction layers which are used to sort all related protocols according to the scope of networking involved. From lowest to highest, the layers are the link layer, containing communication technologies for a single network segment (link); the internet layer, connecting hosts across independent networks, thus establishing internetworking; the transport layer handling host-to-host communication; and the application layer, which provides process-to-process application data exchange.The TCP/IP model and related protocol models are maintained by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).