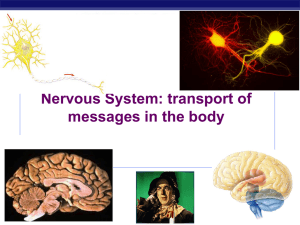
Knowledge Representation
... what is it ? what do we represent ? how is it represented ? Kn Repn strategies inferencing example tasks ...
... what is it ? what do we represent ? how is it represented ? Kn Repn strategies inferencing example tasks ...
Module 12 - Doral Academy Preparatory
... • memory files that contain related information organized around a specific topic or category – refers to the arrangement of nodes or memory files in a certain order or hierarchy – bottom of the hierarchy are nodes with very concrete information, which are connected to nodes with somewhat more speci ...
... • memory files that contain related information organized around a specific topic or category – refers to the arrangement of nodes or memory files in a certain order or hierarchy – bottom of the hierarchy are nodes with very concrete information, which are connected to nodes with somewhat more speci ...
Mental Imagery
... whether they be verbal or visual, rather than the imaginal components. – Anderson and Bower explain that concrete concepts are coded by a rich set of predicates that bind concepts together. ..."the only difference between the internal representation for a linguistic input and a memory image is detai ...
... whether they be verbal or visual, rather than the imaginal components. – Anderson and Bower explain that concrete concepts are coded by a rich set of predicates that bind concepts together. ..."the only difference between the internal representation for a linguistic input and a memory image is detai ...
Synapse
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
Long-term memory
... Strengthening of synapses • Long-term potentiation (LTP) is the long-lasting strengthening of the connection between two neurons • can last from hours to days, months, and years. ...
... Strengthening of synapses • Long-term potentiation (LTP) is the long-lasting strengthening of the connection between two neurons • can last from hours to days, months, and years. ...
Memory
... Figure 2.25 The cerebral cortex, dorsal and lateral views Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers ...
... Figure 2.25 The cerebral cortex, dorsal and lateral views Klein/Thorne: Biological Psychology © 2007 by Worth Publishers ...
Pubertal Influences on Sleep
... • Learning engages the whole person. (cognitive, affective and psychomotor domains) • The brain seeks patterns in its search for meaning. (making connections are essential) • Emotions affect all aspects of learning, retention, and recall. (novelty seeker) • Past experiences always affect new learni ...
... • Learning engages the whole person. (cognitive, affective and psychomotor domains) • The brain seeks patterns in its search for meaning. (making connections are essential) • Emotions affect all aspects of learning, retention, and recall. (novelty seeker) • Past experiences always affect new learni ...
... supramammillary nucleus. The results showed that spatial training in reference and working memory tasks increased the number of entorhinal cortex activated neurons (c-Fos positive neurons). No clear association was found between c-fos activation in the anterior cingulate gyrus and either spatial ref ...
Small System of Neurons
... In 1894, Santiago Ramon y Cajal suggested that memory is stored in the growth of new connections. Kandel’s research showed that although the connections are invariant, their specific strength is not. Homosynaptic changes occur in a synapse because of activity in that synapse, while heterosynaptic ch ...
... In 1894, Santiago Ramon y Cajal suggested that memory is stored in the growth of new connections. Kandel’s research showed that although the connections are invariant, their specific strength is not. Homosynaptic changes occur in a synapse because of activity in that synapse, while heterosynaptic ch ...
Intellectual Functions of the Brain
... • Related to: Gene expression, protein synthesis and hypertrophy of synaptic plates. ...
... • Related to: Gene expression, protein synthesis and hypertrophy of synaptic plates. ...
Memory Systems
... • Anterograde – Cannot form any new types of memories so always live at time of injury ...
... • Anterograde – Cannot form any new types of memories so always live at time of injury ...
memory drsidra
... Number of Neurons and Their Connectivities Often Change Significantly During Learning • Learning” is achieved in adult human beings and animals by modification of numbers of neurons in the memory circuits • Use it or lose it! ...
... Number of Neurons and Their Connectivities Often Change Significantly During Learning • Learning” is achieved in adult human beings and animals by modification of numbers of neurons in the memory circuits • Use it or lose it! ...
a PowerPoint Presentation of Module 24
... The brain is NOT like a hard drive. Memories are NOT in isolated files, but are in overlapping neural networks. The brain’s long-term memory storage does not get full; it gets more elaborately rewired and interconnected. Parts of each memory can be distributed throughout the brain. Memory of ...
... The brain is NOT like a hard drive. Memories are NOT in isolated files, but are in overlapping neural networks. The brain’s long-term memory storage does not get full; it gets more elaborately rewired and interconnected. Parts of each memory can be distributed throughout the brain. Memory of ...
中原大學 95 學年度 碩士班入學考試
... 20. Transfer of information from WORKING to LTM may require rehearsal; however a. rehearsal does not necessarily transfer information to long-term memory. b. words presented first and last in a long list are most likely to be recalled. c. serial searches take longer as the list of items to be search ...
... 20. Transfer of information from WORKING to LTM may require rehearsal; however a. rehearsal does not necessarily transfer information to long-term memory. b. words presented first and last in a long list are most likely to be recalled. c. serial searches take longer as the list of items to be search ...
(Early Period) - Connectionism
... numbers of units (the analogs of neurons) together with weights that measure the strength of connections between the units. A glance at its history: ● The 1940s: it was pioneered by neurophysiologist Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts. They noted that neurons are either ‘firing’ electrochemical impul ...
... numbers of units (the analogs of neurons) together with weights that measure the strength of connections between the units. A glance at its history: ● The 1940s: it was pioneered by neurophysiologist Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts. They noted that neurons are either ‘firing’ electrochemical impul ...
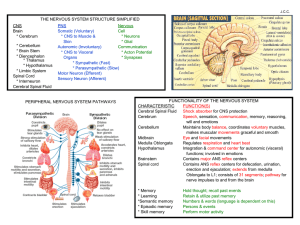
CNS Brain * Cerebrum * Cerebellum * Brain Stem * Diencephalon
... Speech, sensation, communication, memory, reasoning, will and emotions Cerebellum Maintains body balance, coordinates voluntary muscles, makes muscular movements graceful and smooth Midbrain Eye and facial movements Medulla Oblongata Regulates respiration and heart beat Hypothalamus Integration & co ...
... Speech, sensation, communication, memory, reasoning, will and emotions Cerebellum Maintains body balance, coordinates voluntary muscles, makes muscular movements graceful and smooth Midbrain Eye and facial movements Medulla Oblongata Regulates respiration and heart beat Hypothalamus Integration & co ...
Optical Stimulation of Engram-bearing Cells
... Five sessions of light-induced fear memory recall elicit a decrease in freezing to the original training context. ...
... Five sessions of light-induced fear memory recall elicit a decrease in freezing to the original training context. ...
Module_12vs9_Final
... • according to Sigmund Freud, repression is a mental process that automatically hides emotionally threatening or anxiety-producing information in the unconscious (from which repressed memories can’t be recalled voluntarily, but something may cause them to enter consciousness at a later time) ...
... • according to Sigmund Freud, repression is a mental process that automatically hides emotionally threatening or anxiety-producing information in the unconscious (from which repressed memories can’t be recalled voluntarily, but something may cause them to enter consciousness at a later time) ...
Memory and Law
... •Smell: Since the olfactory bulb and olfactory cortex (where smells are processed) are physically very close to the hippocampus and amygdala (where memory is processed) smells may be more quickly and strongly associated with memories and emotions. •Andy Warhol wore different scents for different pha ...
... •Smell: Since the olfactory bulb and olfactory cortex (where smells are processed) are physically very close to the hippocampus and amygdala (where memory is processed) smells may be more quickly and strongly associated with memories and emotions. •Andy Warhol wore different scents for different pha ...
Nervous System Exam Review
... Be able to diagram how the nervous system is organized (refer to concept map). What is the fundamental unit of the nervous system? Distinguish between a neuron and a neuroglia cell. Know the 5 types of neuroglia cell --- where are they found, what do they do. Identify neurons by structural classific ...
... Be able to diagram how the nervous system is organized (refer to concept map). What is the fundamental unit of the nervous system? Distinguish between a neuron and a neuroglia cell. Know the 5 types of neuroglia cell --- where are they found, what do they do. Identify neurons by structural classific ...
Midterm Review Project
... Memory- learning that has persisted over time; it has been acquired, stored, and can be retrieved In order to remember something it must be: ● Encoded- perceived by the brain ● Stored- retained in the brain for a long period of time ● Retrieved- come back out of storage and into conscious thought Pa ...
... Memory- learning that has persisted over time; it has been acquired, stored, and can be retrieved In order to remember something it must be: ● Encoded- perceived by the brain ● Stored- retained in the brain for a long period of time ● Retrieved- come back out of storage and into conscious thought Pa ...
Answers to Test Your Knowledge questions for
... change has to reflect environmental experience of the animal in question. Any learning experience is associated with a memory as its base. (Additional note: It used to be argued that learning can be characterized by the fact that any change can be reversed but even that is being called into question ...
... change has to reflect environmental experience of the animal in question. Any learning experience is associated with a memory as its base. (Additional note: It used to be argued that learning can be characterized by the fact that any change can be reversed but even that is being called into question ...
Flash Card Fever!
... approved answers to questions about oneself on a survey or questionnaire. experimenter control ...
... approved answers to questions about oneself on a survey or questionnaire. experimenter control ...
INTRODUCTION TO FUNCTIONAL NEUROBIOLOGY Tamás
... function only in mutual relationship with other cortical areas. The elements of the thalamocorticalcorticothalamic circuit and the generation of different oscillations within the circuit will also be explained. The second part of the presentation will focus on the “less known part”, the higher order ...
... function only in mutual relationship with other cortical areas. The elements of the thalamocorticalcorticothalamic circuit and the generation of different oscillations within the circuit will also be explained. The second part of the presentation will focus on the “less known part”, the higher order ...