Unit 6ана Classical Greece
... In which citystate would a person be more likely to conform to set rules and standards? Why? ...
... In which citystate would a person be more likely to conform to set rules and standards? Why? ...
Chapter 6
... ancient Greeks were all islanders? Some Greeks lived on actual islands. Others lived on land islands, or peninsulas, that were surrounded by water on all sides but the one that connected it to the land. These peninsulas gave the people the same feeling of being surrounded by water as the islands did ...
... ancient Greeks were all islanders? Some Greeks lived on actual islands. Others lived on land islands, or peninsulas, that were surrounded by water on all sides but the one that connected it to the land. These peninsulas gave the people the same feeling of being surrounded by water as the islands did ...
Ancient Greece: Geography and First Civilizations
... • Oldest Civilization from this part of the world—Developed around 2,000 BC on the island of Crete • Minoans were completely surrounded by water—so they took to the sea and eventually had a culture based on trade • They even established settlements in Asia Minor—all the way across the Aegean Sea ...
... • Oldest Civilization from this part of the world—Developed around 2,000 BC on the island of Crete • Minoans were completely surrounded by water—so they took to the sea and eventually had a culture based on trade • They even established settlements in Asia Minor—all the way across the Aegean Sea ...
Golden Age of Greece: 480-430 BC
... into regions and the rugged terrain made travel and communication difficult. (It could take a week to travel 60 miles – that’s about how far Seaside is). The land also was difficult to farm, so Greece’s food supply was not too great resulting in a small population. Land played a major role in the po ...
... into regions and the rugged terrain made travel and communication difficult. (It could take a week to travel 60 miles – that’s about how far Seaside is). The land also was difficult to farm, so Greece’s food supply was not too great resulting in a small population. Land played a major role in the po ...
File
... The Alexandria library was one of the largest of the time partially due to the practice of searching trader’s ships for _________ and making __________ of the books from all over the known world. ...
... The Alexandria library was one of the largest of the time partially due to the practice of searching trader’s ships for _________ and making __________ of the books from all over the known world. ...
Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle
... responsible for many cultural achievements. These influenced societies around them as well as future civilizations. ...
... responsible for many cultural achievements. These influenced societies around them as well as future civilizations. ...
Impact of Geography on Greece
... Identify 1 geographic feature & propose how it might impact the culture of Greece ...
... Identify 1 geographic feature & propose how it might impact the culture of Greece ...
The League of Corinth (Corinthian League)
... Importantly, Macedonia did not join the League so was not bound by these clauses ...
... Importantly, Macedonia did not join the League so was not bound by these clauses ...
The Greece Spot Wiki Webquest
... Children were given to the state at age 6 and educated for another 24 years before he could become a citizen. Foreign travel was encouraged so Spartans could share crops. Spartan women raised children for the purpose of serving the state. Even male babies could be left to die if they were not perfec ...
... Children were given to the state at age 6 and educated for another 24 years before he could become a citizen. Foreign travel was encouraged so Spartans could share crops. Spartan women raised children for the purpose of serving the state. Even male babies could be left to die if they were not perfec ...
Chapter 6
... ancient Greeks were all islanders? Some Greeks lived on actual islands. Others lived on land islands, or peninsulas, that were surrounded by water on all sides but the one that connected it to the land. These peninsulas gave the people the same feeling of being surrounded by water as the islands did ...
... ancient Greeks were all islanders? Some Greeks lived on actual islands. Others lived on land islands, or peninsulas, that were surrounded by water on all sides but the one that connected it to the land. These peninsulas gave the people the same feeling of being surrounded by water as the islands did ...
Greeks_QuestionSheet-UA - Digital Schoolhouse Resources
... The ancient greek civilization lived ________________________ . How was ancient Greece governed? The Greeks lived in ________________________ ________________________ , each one like a small town in the United States today, with no more than about ________________________ people in each city-state. ...
... The ancient greek civilization lived ________________________ . How was ancient Greece governed? The Greeks lived in ________________________ ________________________ , each one like a small town in the United States today, with no more than about ________________________ people in each city-state. ...
The Persian Wars - Orangefield ISD
... __________________________________—Indo-Europeans who settled on Greek mainland in 2000 B.C. ...
... __________________________________—Indo-Europeans who settled on Greek mainland in 2000 B.C. ...
Classical Greece
... with the Persian Empire 2. The Greeks helped an unsuccessful revolt in the Ionian States. 3. When the Persians invaded they came with in 26 miles of Athens before they were defeated. 2nd War 1. A new Persian leader (Xerxes) vowed revenge. 2. The Persian’s then invaded again. (150,000 troops, 700 nav ...
... with the Persian Empire 2. The Greeks helped an unsuccessful revolt in the Ionian States. 3. When the Persians invaded they came with in 26 miles of Athens before they were defeated. 2nd War 1. A new Persian leader (Xerxes) vowed revenge. 2. The Persian’s then invaded again. (150,000 troops, 700 nav ...
Greece Study Guide
... Greece is known as the birthplace of democracy. All citizens had an equal voice in running the country. Men were the only people allowed to vote. Direct Democracy – a government in which all people vote to make their own rules and laws. ...
... Greece is known as the birthplace of democracy. All citizens had an equal voice in running the country. Men were the only people allowed to vote. Direct Democracy – a government in which all people vote to make their own rules and laws. ...
Classical reading - GREEK help at LSU
... • Euripides wrote many turbulent tragedies and is reported to have lived a comparably turbulent life. During his career, he seems to have generated controversy with his plays, an artist both captivating and disturbing. • Reportedly, Euripides left his native Athens in his last years and took up resi ...
... • Euripides wrote many turbulent tragedies and is reported to have lived a comparably turbulent life. During his career, he seems to have generated controversy with his plays, an artist both captivating and disturbing. • Reportedly, Euripides left his native Athens in his last years and took up resi ...
Ancient Greek Games - ps1286-2
... the civilizations of the Minoan and Mycenaean kings. This was followed by a period of wars and invasions, known as the Dark Ages. In about 1100 BC, a people called the Dorians invaded from the north and spread down the west coast. In the period from 500-336 BC Greece was divided into small city stat ...
... the civilizations of the Minoan and Mycenaean kings. This was followed by a period of wars and invasions, known as the Dark Ages. In about 1100 BC, a people called the Dorians invaded from the north and spread down the west coast. In the period from 500-336 BC Greece was divided into small city stat ...
Where is Greece?
... • Vegetation is dependent on geographical regions. • Due to the variety of land, there a some 6,000 indigenous species in Greece. • In Ancient Greece, farmers grew olives, figs, grain, fruit and grapes in the fertile valleys. ...
... • Vegetation is dependent on geographical regions. • Due to the variety of land, there a some 6,000 indigenous species in Greece. • In Ancient Greece, farmers grew olives, figs, grain, fruit and grapes in the fertile valleys. ...
Achievements of Ancient Greece
... first university called the Academy in Greece which taught students for 900 years after Plato died. The ideas of both Plato and Socrates are still studied today around the world. Greek Government ...
... first university called the Academy in Greece which taught students for 900 years after Plato died. The ideas of both Plato and Socrates are still studied today around the world. Greek Government ...
Social Studies Study Guide: Chapter 6
... -Minoans gained power through _________ and the Mycenaeans gained power through _________. The Trojan War: p.171 -The Trojan War was fought between the _________ and the _________. -What did the Greeks give the Trojans as a gift that helped them win the war? -Who wrote about the Trojan War? -What t ...
... -Minoans gained power through _________ and the Mycenaeans gained power through _________. The Trojan War: p.171 -The Trojan War was fought between the _________ and the _________. -What did the Greeks give the Trojans as a gift that helped them win the war? -Who wrote about the Trojan War? -What t ...
1 Greece Notes 2016
... considered harsh and cruel, rather they were seen as leaders who would work for the interests of the ordinary people. ...
... considered harsh and cruel, rather they were seen as leaders who would work for the interests of the ordinary people. ...
16- Cultures of the Mountains and the Sea Geography Shapes
... Fertile Crescent, India, and China. In one sense, the Greeks did not live on a land but around a sea. Greeks rarely had to travel more than 85 miles to reach the coastline. The Aegean Sea, the Ionian Sea, and the neighboring Black Sea were important transportation routes for the Greek people. These ...
... Fertile Crescent, India, and China. In one sense, the Greeks did not live on a land but around a sea. Greeks rarely had to travel more than 85 miles to reach the coastline. The Aegean Sea, the Ionian Sea, and the neighboring Black Sea were important transportation routes for the Greek people. These ...
Chapter Three - MrVHistory.com
... 3. Collapse of Mycenae (probably due to internal conflict) was followed by the Dark Age (1100 B.C.800 B.C.). C. Homer, Hesiod, Gods, and Heroes (1100800 B.C.) 1. Homer’s Iliad and Odyssey a) The poems of Homer idealized the Greek past. b) The Iliad describes the expedition against the Trojans. c) ...
... 3. Collapse of Mycenae (probably due to internal conflict) was followed by the Dark Age (1100 B.C.800 B.C.). C. Homer, Hesiod, Gods, and Heroes (1100800 B.C.) 1. Homer’s Iliad and Odyssey a) The poems of Homer idealized the Greek past. b) The Iliad describes the expedition against the Trojans. c) ...
Greece: Geography and Culture
... Greece is located north of the Mediterranean Sea between the Ionian Sea and the Aegean Sea. Today, this region is called the Balkan Peninsula. Greece is very mountainous and most of its people live near major bodies of water. Greece has a temperate climate, which means hot and dry summers, and mild ...
... Greece is located north of the Mediterranean Sea between the Ionian Sea and the Aegean Sea. Today, this region is called the Balkan Peninsula. Greece is very mountainous and most of its people live near major bodies of water. Greece has a temperate climate, which means hot and dry summers, and mild ...
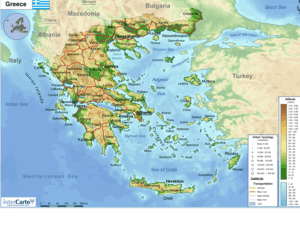
Regions of ancient Greece

The regions of ancient Greece were areas identified by the ancient Greeks as geographical sub-divisions of the Hellenic world. These regions are described in the works of ancient historians and geographers, and in the legends and myths of the ancient Greeks.Conceptually, there is no clear theme to the structure of these regions. Some, particularly in the Peloponnese, can be seen primarily as distinct geo-physical units, defined by physical boundaries such as mountain ranges and rivers. These regions retained their identity, even when the identity of the people living there changed during the Greek Dark Ages (or at least, was conceived by the Greeks to have changed). Conversely, the division of central Greece between Boeotia, Phocis, Doris and the three parts of Locris, cannot be understood as a logical division by physical boundaries, and instead seems to follow ancient tribal divisions. Nevertheless, these regions also survived the upheaval of the Greek Dark Ages, showing that they had acquired less political connotations. Outside the Peloponnese and central Greece, geographical divisions and identities did change over time suggesting a closer connection with tribal identity. Over time however, all the regions also acquired geo-political meanings, and political bodies uniting the cities of a region (such as the Arcadian League) became common in the Classical period.These traditional sub-divisions of Greece form the basis for the modern system of regional units of Greece. However, there are important differences, with many of the smaller ancient regions not represented in the current system. To fully understand the ancient history of Greece therefore requires more detailed description of the ancient regions.