A. Continental Slope Transition from the Cont. Shelf to the ocean
... Average depth is about 4-6 km. Covered by a layer of sediment, mostly <1 km thick. The flattest areas on the planet. ...
... Average depth is about 4-6 km. Covered by a layer of sediment, mostly <1 km thick. The flattest areas on the planet. ...
Deep sea: habitat profile
... - Average depth 4,000m – near freezing water and high -pressure - <10% of the deep sea has been explored - Whale falls and ‘marine snow’ key source of food as well as chemicals from hydrothermal vents ...
... - Average depth 4,000m – near freezing water and high -pressure - <10% of the deep sea has been explored - Whale falls and ‘marine snow’ key source of food as well as chemicals from hydrothermal vents ...
DEEP-SEA SUBMERSIBLE EXPEDITION TO AUSTRALIA AND
... Two-thirds of the earth’s surface is covered by sea, of which 90% lies beyond the relatively shallow waters of continental shelves. The Pacific, with an average depth of 4,200m, is the world’s largest ecological zone; yet the vast bulk of its deep-sea is unexplored, impractical for commercial fishin ...
... Two-thirds of the earth’s surface is covered by sea, of which 90% lies beyond the relatively shallow waters of continental shelves. The Pacific, with an average depth of 4,200m, is the world’s largest ecological zone; yet the vast bulk of its deep-sea is unexplored, impractical for commercial fishin ...
104 PAGES OF IDEAS TO FUTURE-PROOF YOURSELF &
... in2015,asoysterreefsbecomefront-line troops in the battle to reduce the effect of human activity on the natural world. Oyster reefs are examples of important coastal ecosystems – the group also includes coral reefs, mangroves, salt marshes and sea grasses – that provide disproportionately high level ...
... in2015,asoysterreefsbecomefront-line troops in the battle to reduce the effect of human activity on the natural world. Oyster reefs are examples of important coastal ecosystems – the group also includes coral reefs, mangroves, salt marshes and sea grasses – that provide disproportionately high level ...
1 - National Oceanography Centre
... Utilization of the marine environment, whether it be for scientific research or economic development requires significant cross-‐disciplinary collaboration. When focusing on the economic interests driving the exploitati ...
... Utilization of the marine environment, whether it be for scientific research or economic development requires significant cross-‐disciplinary collaboration. When focusing on the economic interests driving the exploitati ...
Chapter 21 Populations and Communities
... other and produce offspring that can also mate and reproduce. All the members of one species in a particular area are referred to as a population. Communities-All the different populations that live together in an area make up a community. In order to be considered a community, the different populat ...
... other and produce offspring that can also mate and reproduce. All the members of one species in a particular area are referred to as a population. Communities-All the different populations that live together in an area make up a community. In order to be considered a community, the different populat ...
Dr. R. Venkatesan
... He enjoys working on projects having direct relevance to the society such as real time data from moored buoys for cyclone and tsunami for coastal hazard warning and successfully executed societal programmes to support livelihood of coastal fishermen. He also organized Coastal cleanup campaign in Ind ...
... He enjoys working on projects having direct relevance to the society such as real time data from moored buoys for cyclone and tsunami for coastal hazard warning and successfully executed societal programmes to support livelihood of coastal fishermen. He also organized Coastal cleanup campaign in Ind ...
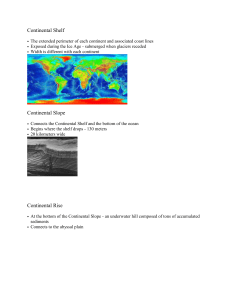
Continental Shelf • The extended perimeter of each continent and
... • At the bottom of the Continental Slope - an underwater hill composed of tons of accumulated sediments • Connects to the abyssal plain ...
... • At the bottom of the Continental Slope - an underwater hill composed of tons of accumulated sediments • Connects to the abyssal plain ...
Oceans: Chapters 19, 20, and 21
... 7. Gases dissolve most easily in water that is ____. 8. Ocean water temperature depends on two things: the solar energy an area receives and ____. 9. As deep ocean water becomes colder, it also becomes ____. 10. What two factors affect the salinity of ocean water? 11. How do marine organisms help ba ...
... 7. Gases dissolve most easily in water that is ____. 8. Ocean water temperature depends on two things: the solar energy an area receives and ____. 9. As deep ocean water becomes colder, it also becomes ____. 10. What two factors affect the salinity of ocean water? 11. How do marine organisms help ba ...
Zone
... Pelagic Creatures Plankton (drifters) • Microscopic organisms • Weak swimmers (at mercy of currents) • Primary Producers ...
... Pelagic Creatures Plankton (drifters) • Microscopic organisms • Weak swimmers (at mercy of currents) • Primary Producers ...
Dropping pH in the Oceans Causing a Rising Tide of...
... carbonate sands formed by reef ecosystem processes dwindle, and as reefs become less diverse and monochromatic. But we are not talking only of ruining the vacation plans of wealthy tourists. Many coastal economies are wholly dependent on coastal tourism and marine resources. And coral reefs provide ...
... carbonate sands formed by reef ecosystem processes dwindle, and as reefs become less diverse and monochromatic. But we are not talking only of ruining the vacation plans of wealthy tourists. Many coastal economies are wholly dependent on coastal tourism and marine resources. And coral reefs provide ...
Notes and Ocean Vocab Words
... Terrestrial food web is on land and aquatic food web is in water (aquatic animals). A bear eating a fish is an example of how terrestrial and aquatic food webs are connected. Many times they overlap and are affected by each other’s environment. ...
... Terrestrial food web is on land and aquatic food web is in water (aquatic animals). A bear eating a fish is an example of how terrestrial and aquatic food webs are connected. Many times they overlap and are affected by each other’s environment. ...
Chapter 23
... waves can not penetrate to the sea floor, but they still can create a high resolution sea floor map based on the height of the sea level. ...
... waves can not penetrate to the sea floor, but they still can create a high resolution sea floor map based on the height of the sea level. ...
File
... o Currents move in the ________ direction. (different in each _____________) Coriolis Effect – the movement of wind and water to the right or left that is caused by Earth’s rotation. o Causes air and water to _________ to the right in the ___________ hemisphere, in a ________________ direction. o In ...
... o Currents move in the ________ direction. (different in each _____________) Coriolis Effect – the movement of wind and water to the right or left that is caused by Earth’s rotation. o Causes air and water to _________ to the right in the ___________ hemisphere, in a ________________ direction. o In ...
Chapter 16: Marine and Costal Systems
... commonly fished in the past to prevent this, consumers can chose which product to buy according to fishing practices ...
... commonly fished in the past to prevent this, consumers can chose which product to buy according to fishing practices ...
Marine biologist - BrauerCaledonianProject
... biology helps us to understand the natural variability in marine ecosystems and to detect whether changes that occur are natural or induced by the actions of humans. Environmental management practices can then be adopted to limit the impact of human-induced changes,' says experimental scientist in c ...
... biology helps us to understand the natural variability in marine ecosystems and to detect whether changes that occur are natural or induced by the actions of humans. Environmental management practices can then be adopted to limit the impact of human-induced changes,' says experimental scientist in c ...
MARINE BIOLOGY Unit 5 Marine Classification, Autotrophs
... 2. Identify the 6 Kingdoms of living things & their general characteristics. 3. Identify the Kingdoms that include marine autotrophs. 4. Identify types of marine flowering plants, where they grow & their adaptations. 5. Describe the general characteristics (appearance, structure, habitats & adaptati ...
... 2. Identify the 6 Kingdoms of living things & their general characteristics. 3. Identify the Kingdoms that include marine autotrophs. 4. Identify types of marine flowering plants, where they grow & their adaptations. 5. Describe the general characteristics (appearance, structure, habitats & adaptati ...
INFO - Andalusian Stories
... SUMMARY: This research is being conducted by researchers from the Andalusian Centre for Marine Science and Technology and has been financially supported by the Andalusian Government and the European Union. Drugs get to marine environments through waste water because the human body excretes drug part ...
... SUMMARY: This research is being conducted by researchers from the Andalusian Centre for Marine Science and Technology and has been financially supported by the Andalusian Government and the European Union. Drugs get to marine environments through waste water because the human body excretes drug part ...
Exam 3
... 10. Speciation occurs because of gradual change and/or punctuated equilibrium. 11. All species in nature are "fixed" and do not change. 12. 99.9% of all species that ever evolved on earth are extinct today 13. Impacts from comets, asteroids & meteorites changed the course of evolution many times ove ...
... 10. Speciation occurs because of gradual change and/or punctuated equilibrium. 11. All species in nature are "fixed" and do not change. 12. 99.9% of all species that ever evolved on earth are extinct today 13. Impacts from comets, asteroids & meteorites changed the course of evolution many times ove ...
Inner-Space Speciation Project
... Why Explore the Deep Sea? • The deep ocean is the largest living space on Earth • It’s properties are radically different from shallow ocean environments • Some of the oldest life forms live in the deep sea • Less than 1% of its volume has been explored • There is a high probability of discovering ...
... Why Explore the Deep Sea? • The deep ocean is the largest living space on Earth • It’s properties are radically different from shallow ocean environments • Some of the oldest life forms live in the deep sea • Less than 1% of its volume has been explored • There is a high probability of discovering ...
Marine habitats
.jpg?width=300)
The marine environment supplies many kinds of habitats that support marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater that is in the sea (the term marine comes from the Latin mare, meaning sea or ocean). A habitat is an ecological or environmental area inhabited by one or more living species.Marine habitats can be divided into coastal and open ocean habitats. Coastal habitats are found in the area that extends from as far as the tide comes in on the shoreline out to the edge of the continental shelf. Most marine life is found in coastal habitats, even though the shelf area occupies only seven percent of the total ocean area. Open ocean habitats are found in the deep ocean beyond the edge of the continental shelf.Alternatively, marine habitats can be divided into pelagic and demersal habitats. Pelagic habitats are found near the surface or in the open water column, away from the bottom of the ocean. Demersal habitats are near or on the bottom of the ocean. An organism living in a pelagic habitat is said to be a pelagic organism, as in pelagic fish. Similarly, an organism living in a demersal habitat is said to be a demersal organism, as in demersal fish. Pelagic habitats are intrinsically shifting and ephemeral, depending on what ocean currents are doing.Marine habitats can be modified by their inhabitants. Some marine organisms, like corals, kelp, mangroves and seagrasses, are ecosystem engineers which reshape the marine environment to the point where they create further habitat for other organisms.