Oceanography Overview Notes
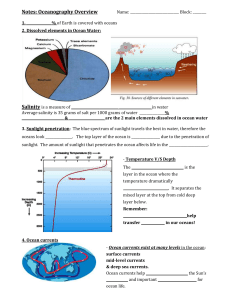
... Salinity is a measure of ____________________________ ___________________ in water Average salinity is 35 grams of salt per 1000 grams of water _______________% _________________________ & _____________________ are the 2 main elements dissolved in ocean water 3. Sunlight penetration: The blue spectr ...
... Salinity is a measure of ____________________________ ___________________ in water Average salinity is 35 grams of salt per 1000 grams of water _______________% _________________________ & _____________________ are the 2 main elements dissolved in ocean water 3. Sunlight penetration: The blue spectr ...
Glossary algae – Plant-like organisms that live mostly in water. Can
... natural history – Detailed description of a species and its lifestyle. operculum – Cover for the opening of the shells of gastropods (like snails), and a plate covering the gills of bony fish. overfishing – Taking too many fish and seriously depleting its numbers and potentially affecting the future ...
... natural history – Detailed description of a species and its lifestyle. operculum – Cover for the opening of the shells of gastropods (like snails), and a plate covering the gills of bony fish. overfishing – Taking too many fish and seriously depleting its numbers and potentially affecting the future ...
Answer Key
... sunlight always filtered, water level does not change drastically; intertidal zone: temperature and salinity may change, sunlight is sometimes direct and sometimes filtered, water level changes drastically. 2. Coral reef: built-up limestone deposits formed by large colonies of ant-sized organisms ca ...
... sunlight always filtered, water level does not change drastically; intertidal zone: temperature and salinity may change, sunlight is sometimes direct and sometimes filtered, water level changes drastically. 2. Coral reef: built-up limestone deposits formed by large colonies of ant-sized organisms ca ...
Slide 1
... Oceans vary in light, pressure, temperature and nutrients. lack of sediments in the water is a key factor for marine species= light ...
... Oceans vary in light, pressure, temperature and nutrients. lack of sediments in the water is a key factor for marine species= light ...
The Ocean
... Coral Reefs Continued… • They provide: – Surfaces under water that sunlight reaches easily – Shelter for animals: sea urchins, sponges, surgeon fish, parrot fish – Living space for algae and some plants (seaweed and plankton are the main food source) – Most corals are polyps: mouth at end of body w ...
... Coral Reefs Continued… • They provide: – Surfaces under water that sunlight reaches easily – Shelter for animals: sea urchins, sponges, surgeon fish, parrot fish – Living space for algae and some plants (seaweed and plankton are the main food source) – Most corals are polyps: mouth at end of body w ...
Ocean Water - Perry Local Schools
... Ocean Currents • Surface currents: stream-like movements of water that occur at or near the surface of the ocean ...
... Ocean Currents • Surface currents: stream-like movements of water that occur at or near the surface of the ocean ...
Chapter 1- Introduction to Castro Part 1
... • Learn nature of marine environment • Learn diversity of marine organisms • Learn ecosystems • Guide to issues in human-marine interactions • Provide info that can inform policy decisions ...
... • Learn nature of marine environment • Learn diversity of marine organisms • Learn ecosystems • Guide to issues in human-marine interactions • Provide info that can inform policy decisions ...
Ocean Water - Cloudfront.net
... Abyssal (dark): extends to 6,000m. Sponges, worms, sea cucumbers. Hadal (dark): below 6,000m, virtually unexplored, life is sparse and depends on food that falls from higher levels. ...
... Abyssal (dark): extends to 6,000m. Sponges, worms, sea cucumbers. Hadal (dark): below 6,000m, virtually unexplored, life is sparse and depends on food that falls from higher levels. ...
Upwelling - cloudfront.net
... Upwelled water is cooler and saltier than the original surface water, and typically has much greater concentrations of nutrients. Leatherbacks and Jellyfish in Monterey Bay ...
... Upwelled water is cooler and saltier than the original surface water, and typically has much greater concentrations of nutrients. Leatherbacks and Jellyfish in Monterey Bay ...
Leap From Space
... Many new species were found in hard-to-reach areas such as deep ocean trenches. Others were discovered in places like coral reefs, which scientists had studied for years. This siphonophore was observed at a depth of 300 to 1,500 meters (1,000 to 5,000 feet). Some of these creatures can reach 3 m (10 ...
... Many new species were found in hard-to-reach areas such as deep ocean trenches. Others were discovered in places like coral reefs, which scientists had studied for years. This siphonophore was observed at a depth of 300 to 1,500 meters (1,000 to 5,000 feet). Some of these creatures can reach 3 m (10 ...
marine ecosystem
... habitat on sandy beaches, but storms, tides and currents mean their habitat continually reinvents itself. ...
... habitat on sandy beaches, but storms, tides and currents mean their habitat continually reinvents itself. ...
Marine Life zones and biotic and abiotic factors chart information
... *Intertidal areas: the place where the ocean meets the land (shore); *organisms must be able to live underwater (high tide) and out of water (low tide) *must have adaptations that allow them to hold on during the crashing of the waves *crabs, clams, snails, worms, plankton, algae *Abundance of disso ...
... *Intertidal areas: the place where the ocean meets the land (shore); *organisms must be able to live underwater (high tide) and out of water (low tide) *must have adaptations that allow them to hold on during the crashing of the waves *crabs, clams, snails, worms, plankton, algae *Abundance of disso ...
4.1 & 4.2C Ocean Life PPt
... 2.)MANGROVE FORESTS ~ Coastal Wetlands in WARM AREAS Found closer to the EQUATOR (Southern US) Mangrove shrubs & trees with thick roots extending into water Human Harm to Wetlands: - clearing of land - pollution from industry/shipping ...
... 2.)MANGROVE FORESTS ~ Coastal Wetlands in WARM AREAS Found closer to the EQUATOR (Southern US) Mangrove shrubs & trees with thick roots extending into water Human Harm to Wetlands: - clearing of land - pollution from industry/shipping ...
Chapter 4.4
... A wetland is an ecosystem that either covers soil or is present at or near the surface of the soil for at least part of the year. This water may be flowing or standing and fresh, salty, or brackish (mix of fresh and salt water). ...
... A wetland is an ecosystem that either covers soil or is present at or near the surface of the soil for at least part of the year. This water may be flowing or standing and fresh, salty, or brackish (mix of fresh and salt water). ...
RAIN FORESTS - Cobb Learning
... Earth’s surface and holds both the largest animals and the smallest organisms on earth? ...
... Earth’s surface and holds both the largest animals and the smallest organisms on earth? ...
Marine Ecosystems Vocabulary
... A water environment, from pond to ocean, in which plants and animals interact with the chemical and physical features of the environment. They contain a large diversity of organisms and include oceans, salt marshes, estuaries, lagoons, mangroves and coral reefs ...
... A water environment, from pond to ocean, in which plants and animals interact with the chemical and physical features of the environment. They contain a large diversity of organisms and include oceans, salt marshes, estuaries, lagoons, mangroves and coral reefs ...
Marine habitats
.jpg?width=300)
The marine environment supplies many kinds of habitats that support marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater that is in the sea (the term marine comes from the Latin mare, meaning sea or ocean). A habitat is an ecological or environmental area inhabited by one or more living species.Marine habitats can be divided into coastal and open ocean habitats. Coastal habitats are found in the area that extends from as far as the tide comes in on the shoreline out to the edge of the continental shelf. Most marine life is found in coastal habitats, even though the shelf area occupies only seven percent of the total ocean area. Open ocean habitats are found in the deep ocean beyond the edge of the continental shelf.Alternatively, marine habitats can be divided into pelagic and demersal habitats. Pelagic habitats are found near the surface or in the open water column, away from the bottom of the ocean. Demersal habitats are near or on the bottom of the ocean. An organism living in a pelagic habitat is said to be a pelagic organism, as in pelagic fish. Similarly, an organism living in a demersal habitat is said to be a demersal organism, as in demersal fish. Pelagic habitats are intrinsically shifting and ephemeral, depending on what ocean currents are doing.Marine habitats can be modified by their inhabitants. Some marine organisms, like corals, kelp, mangroves and seagrasses, are ecosystem engineers which reshape the marine environment to the point where they create further habitat for other organisms.


















