ExamView Pro - oceanography review.tst
... 33. What causes a density current? 34. How do the sun’s rays strike the equator? 35. What is the relationship between elevation and precipitation? 36. Which of the two cities, located at the same latitude, would have the hotter summer: the one situated on the coast or the one situated farther inland ...
... 33. What causes a density current? 34. How do the sun’s rays strike the equator? 35. What is the relationship between elevation and precipitation? 36. Which of the two cities, located at the same latitude, would have the hotter summer: the one situated on the coast or the one situated farther inland ...
Marine Ecosystems
... vegetation also provides protection and food for fish, crab, and shrimp that use the ecosystem as a nursery. Mudflats often cover low-lying areas between salt marsh vegetation, mangroves, or seagrass meadows. They form when tides or rivers deposit layers of mud (silt, clay) and nutrients (detritus). ...
... vegetation also provides protection and food for fish, crab, and shrimp that use the ecosystem as a nursery. Mudflats often cover low-lying areas between salt marsh vegetation, mangroves, or seagrass meadows. They form when tides or rivers deposit layers of mud (silt, clay) and nutrients (detritus). ...
Chapter 10: Siliciclastic Marine Environments The Shelf
... generated by storms that originate far out to sea. Storm waves: stronger more energenic waves that accompany storm activity on the shelf. They erode the beachface and upper shoreface. Wind-forced currents: unidirectional currents generated by wind-shear stress as wind blows across the water surface, ...
... generated by storms that originate far out to sea. Storm waves: stronger more energenic waves that accompany storm activity on the shelf. They erode the beachface and upper shoreface. Wind-forced currents: unidirectional currents generated by wind-shear stress as wind blows across the water surface, ...
Chapter 11: The Early-to-Middle Paleozoic World
... o The rifting and continued movement of continents cause seafloor spreading centers to displace large amounts of water out of the ocean basins, producing epicontinental seas and decreasing Earth’s albedo o Rifting, subduction and volcanism produced large amounts of CO2; no plants yet existed on land ...
... o The rifting and continued movement of continents cause seafloor spreading centers to displace large amounts of water out of the ocean basins, producing epicontinental seas and decreasing Earth’s albedo o Rifting, subduction and volcanism produced large amounts of CO2; no plants yet existed on land ...
THE Neritic zone and open ocean
... They are called extremophiles because of their extreme living conditions. ...
... They are called extremophiles because of their extreme living conditions. ...
Water Quality Poster
... Pacific Islands Ocean Observing System (PacIOOS) is the Pacific Islands regional component of the U.S. Integrated Ocean Observing System (IOOS®). Based within the School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST) at the University of Hawai‘i at Mānoa, PacIOOS a partnership of data providers a ...
... Pacific Islands Ocean Observing System (PacIOOS) is the Pacific Islands regional component of the U.S. Integrated Ocean Observing System (IOOS®). Based within the School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST) at the University of Hawai‘i at Mānoa, PacIOOS a partnership of data providers a ...
Key Action 3: Sustainable Marine Ecosystems
... Main MAST III (FP4) projects with relevance to the new FP5, EESD KA3 topics. Important note: the projects below were not aimed specifically to nor funded under the headings of FP5. Therefore their association to those headings is only orientative and has no official character. For a search of the pr ...
... Main MAST III (FP4) projects with relevance to the new FP5, EESD KA3 topics. Important note: the projects below were not aimed specifically to nor funded under the headings of FP5. Therefore their association to those headings is only orientative and has no official character. For a search of the pr ...
SEMESTER AT SEA COURSE SYLLABUS
... COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course explores the biology of the oceans, which cover about 70% of the Earth’s surface. The course begins with an introduction to the oceans as physical habitats, including ocean currents, topographical structure, climate regimes, and ocean chemistry. The course then examin ...
... COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course explores the biology of the oceans, which cover about 70% of the Earth’s surface. The course begins with an introduction to the oceans as physical habitats, including ocean currents, topographical structure, climate regimes, and ocean chemistry. The course then examin ...
Chapter 23 The Ocean Floor
... • Sediment • Long, hollow Sampling…Core cylindrical Sampling instrument removes a long core of sediments from the ocean floor ...
... • Sediment • Long, hollow Sampling…Core cylindrical Sampling instrument removes a long core of sediments from the ocean floor ...
MARINE SCIENCES
... MARINE SCIENCE PROGRAM LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon completion of the COM-FSM Marine Sciences requirements, students will be sufficiently skilled in or be able to do the following: ...
... MARINE SCIENCE PROGRAM LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon completion of the COM-FSM Marine Sciences requirements, students will be sufficiently skilled in or be able to do the following: ...
Chapter 15 - Life Near the Surface
... of the seas - away from _________________________________________. ...
... of the seas - away from _________________________________________. ...
Marine Ecosystems - National Geographic
... vegetation also provides protection and food for fish, crab, and shrimp that use the ecosystem as a nursery. Mudflats often cover low-lying areas between salt marsh vegetation, mangroves, or seagrass meadows. They form when tides or rivers deposit layers of mud (silt, clay) and nutrients (detritus). ...
... vegetation also provides protection and food for fish, crab, and shrimp that use the ecosystem as a nursery. Mudflats often cover low-lying areas between salt marsh vegetation, mangroves, or seagrass meadows. They form when tides or rivers deposit layers of mud (silt, clay) and nutrients (detritus). ...
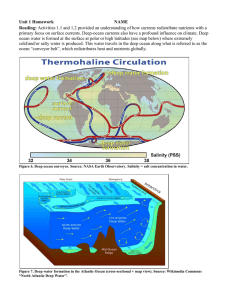
2.36 Deep Ocean Currents
... • In order for sea level to remain constant, if water sinks in one area, it must rise somewhere else • Areas where deep water rises to the surface are called areas of upwelling ...
... • In order for sea level to remain constant, if water sinks in one area, it must rise somewhere else • Areas where deep water rises to the surface are called areas of upwelling ...
Unit 1_homework (.doc)
... the atmosphere. The Southern Ocean takes up approximately 60 percent of the anthropogenic heat produced on Earth and 40 to 50 percent of the anthropogenic carbon dioxide.” Here’s what the article says about how atmospheric CO2 is taken up: “In conducting photosynthesis, the phytoplankton take up car ...
... the atmosphere. The Southern Ocean takes up approximately 60 percent of the anthropogenic heat produced on Earth and 40 to 50 percent of the anthropogenic carbon dioxide.” Here’s what the article says about how atmospheric CO2 is taken up: “In conducting photosynthesis, the phytoplankton take up car ...
Chapter 1
... To solve the problems marine organisms create Predict the effects of human activities on the life of the sea Marine organisms provide clues to earth’s past and the history of life and our own bodies ...
... To solve the problems marine organisms create Predict the effects of human activities on the life of the sea Marine organisms provide clues to earth’s past and the history of life and our own bodies ...
Slide 1 - OnCourse
... • Upon striking shore, a tsunami creates a number of waves with a period between waves of 10 to 30 minutes • Most originate along the Ring of Fire • Area of volcanoes & seismic activity 24K mi long encircling the Pacific Ocean • Since 1819, more than 40 tsunamis have struck the Hawaiian Islands ...
... • Upon striking shore, a tsunami creates a number of waves with a period between waves of 10 to 30 minutes • Most originate along the Ring of Fire • Area of volcanoes & seismic activity 24K mi long encircling the Pacific Ocean • Since 1819, more than 40 tsunamis have struck the Hawaiian Islands ...
Glossary
... hydrogen sulfide: a compound toxic to many life forms but utilized by some bacteria as an energy source to fix carbon through oxidation and can support specialized chemosynthesisbased communities. The most prevalent chemical dissolved in the sea water of vents, it smells like rotten eggs and is pro ...
... hydrogen sulfide: a compound toxic to many life forms but utilized by some bacteria as an energy source to fix carbon through oxidation and can support specialized chemosynthesisbased communities. The most prevalent chemical dissolved in the sea water of vents, it smells like rotten eggs and is pro ...
Marine Freshwater
... * Many of the plants that live in freshwater have strong roots to keep them in one place. ...
... * Many of the plants that live in freshwater have strong roots to keep them in one place. ...
Document
... _____ 3. a mountain built from magma _____ 4. transfer of energy through space _____ 5. water movements in the ocean that are driven by the wind _____ 6. layer of Earth between the crust and the core _____ 7. a molecule made up of three oxygen atoms _____ 8. smaller streams or rivers that flow into ...
... _____ 3. a mountain built from magma _____ 4. transfer of energy through space _____ 5. water movements in the ocean that are driven by the wind _____ 6. layer of Earth between the crust and the core _____ 7. a molecule made up of three oxygen atoms _____ 8. smaller streams or rivers that flow into ...
How can we minimise negative impacts on ocean health?
... What are the changing stresses on the marine environment? Warming The ocean surface is currently warming by about 0.1ºC per decade. Such temperature changes affect ocean currents and mixing; they also alter the distribution (and abundance) of fish that prefer cooler or warmer conditions, such as cod ...
... What are the changing stresses on the marine environment? Warming The ocean surface is currently warming by about 0.1ºC per decade. Such temperature changes affect ocean currents and mixing; they also alter the distribution (and abundance) of fish that prefer cooler or warmer conditions, such as cod ...
Marine habitats
.jpg?width=300)
The marine environment supplies many kinds of habitats that support marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater that is in the sea (the term marine comes from the Latin mare, meaning sea or ocean). A habitat is an ecological or environmental area inhabited by one or more living species.Marine habitats can be divided into coastal and open ocean habitats. Coastal habitats are found in the area that extends from as far as the tide comes in on the shoreline out to the edge of the continental shelf. Most marine life is found in coastal habitats, even though the shelf area occupies only seven percent of the total ocean area. Open ocean habitats are found in the deep ocean beyond the edge of the continental shelf.Alternatively, marine habitats can be divided into pelagic and demersal habitats. Pelagic habitats are found near the surface or in the open water column, away from the bottom of the ocean. Demersal habitats are near or on the bottom of the ocean. An organism living in a pelagic habitat is said to be a pelagic organism, as in pelagic fish. Similarly, an organism living in a demersal habitat is said to be a demersal organism, as in demersal fish. Pelagic habitats are intrinsically shifting and ephemeral, depending on what ocean currents are doing.Marine habitats can be modified by their inhabitants. Some marine organisms, like corals, kelp, mangroves and seagrasses, are ecosystem engineers which reshape the marine environment to the point where they create further habitat for other organisms.