Ocean and Coastal Processes Ocean Basins Ocean Basins Tides
... Sediment Sorting • Waves sort sediment particles by ...
... Sediment Sorting • Waves sort sediment particles by ...
Oceanographer publishes atlas of seafloor volcanoes
... "These systems have really changed how we think about the oceans, and life on Earth and on other planets," Kelley said. "When I was first going to sea, we were still using 35 mm cameras, and one of my first jobs at sea Provided by University of Washington was processing film on a rolling ship," Kell ...
... "These systems have really changed how we think about the oceans, and life on Earth and on other planets," Kelley said. "When I was first going to sea, we were still using 35 mm cameras, and one of my first jobs at sea Provided by University of Washington was processing film on a rolling ship," Kell ...
Measuring `rogue waves` in extreme sea conditions
... the Northwestern coast of Ireland. Prof. Dias, an applied mathematician working in Ireland, aims to produce finely-attuned sensors for a similar buoy specially designed to measure such 'rogue waves' in extreme sea conditions. During his previous ERC project he studied the fundamental mechanisms unde ...
... the Northwestern coast of Ireland. Prof. Dias, an applied mathematician working in Ireland, aims to produce finely-attuned sensors for a similar buoy specially designed to measure such 'rogue waves' in extreme sea conditions. During his previous ERC project he studied the fundamental mechanisms unde ...
Full Text
... beachexcept that the distance between crestsis very large (hundredsof miles). Hencetidesare often called long waves. Tides occur because of the gravitational forces of the sun and the moon acting uponthe earth. The height of the tides vary with the distance and relative positions of the sun and the ...
... beachexcept that the distance between crestsis very large (hundredsof miles). Hencetidesare often called long waves. Tides occur because of the gravitational forces of the sun and the moon acting uponthe earth. The height of the tides vary with the distance and relative positions of the sun and the ...
the Role of Citizen Science in Marine Habitat Conservation
... promoting the participation of non-divers and in particular students from primary school to university level, a protocol for intertidal monitoring has been established, the Emerged Coastal Environment Monitoring (E-CEM). On rocky shores observed items would include marine organisms living at the fri ...
... promoting the participation of non-divers and in particular students from primary school to university level, a protocol for intertidal monitoring has been established, the Emerged Coastal Environment Monitoring (E-CEM). On rocky shores observed items would include marine organisms living at the fri ...
Our Australia - One Place, Many Stories: Oceans
... kilometres along a pathway less than 300 metres deep and 100 kilometres wide. Like the East Australian Current, the strength and speed of the Leeuwin Current varies during the year – but in the opposite way. It’s strongest in winter, and weakest in summer, when it barely reaches the Great Australian ...
... kilometres along a pathway less than 300 metres deep and 100 kilometres wide. Like the East Australian Current, the strength and speed of the Leeuwin Current varies during the year – but in the opposite way. It’s strongest in winter, and weakest in summer, when it barely reaches the Great Australian ...
Oceans and Continental Profiles Activity
... Profiles are cross-sectional views of underwater or land surface features. (seen from the side) They are made by plotting ocean depth & land elevation in meters versus horizontal distance in kilometers. The vertical scale exaggerates the steepness of mountains so that you can see them on these drawi ...
... Profiles are cross-sectional views of underwater or land surface features. (seen from the side) They are made by plotting ocean depth & land elevation in meters versus horizontal distance in kilometers. The vertical scale exaggerates the steepness of mountains so that you can see them on these drawi ...
24. Ocean Basins p. 350-372
... the flattest places on Earth because the ruggedness of the sea floor has been buried by sediments deposited on the ocean bottom, mostly by turbidity currents. Sediment also forms by settling out of ocean water far from land. This type of sediment is called _____________________. There are two types ...
... the flattest places on Earth because the ruggedness of the sea floor has been buried by sediments deposited on the ocean bottom, mostly by turbidity currents. Sediment also forms by settling out of ocean water far from land. This type of sediment is called _____________________. There are two types ...
Word format
... the flattest places on Earth because the ruggedness of the sea floor has been buried by sediments deposited on the ocean bottom, mostly by turbidity currents. Sediment also forms by settling out of ocean water far from land. This type of sediment is called _____________________. There are two types ...
... the flattest places on Earth because the ruggedness of the sea floor has been buried by sediments deposited on the ocean bottom, mostly by turbidity currents. Sediment also forms by settling out of ocean water far from land. This type of sediment is called _____________________. There are two types ...
web-june-ijms
... Biomass distribution, horizontal zonation, relative dominance and vertical distribution of polychaetes were studied. Highest biomass was recorded in the mid tidal region in both study areas. The monthly values varied from 4.43 to 128.28 g.m-2 at st 1 and 2.57 to 67.31 g.m-2 at st 2. Multiple regress ...
... Biomass distribution, horizontal zonation, relative dominance and vertical distribution of polychaetes were studied. Highest biomass was recorded in the mid tidal region in both study areas. The monthly values varied from 4.43 to 128.28 g.m-2 at st 1 and 2.57 to 67.31 g.m-2 at st 2. Multiple regress ...
Chapter 8 Powerpoint
... Half of coastal wetlands lost to agriculture and urban development Over one-fifth of mangrove forests lost to agriculture, aquaculture, and development Beaches eroding due to development and rising sea levels ...
... Half of coastal wetlands lost to agriculture and urban development Over one-fifth of mangrove forests lost to agriculture, aquaculture, and development Beaches eroding due to development and rising sea levels ...
Ocean`s Role in Climate Change
... Oceans remove up to 1/3 of the CO2 produced by burning fossil fuels Oceans, atmosphere, land and snow & ice form the climate system. ...
... Oceans remove up to 1/3 of the CO2 produced by burning fossil fuels Oceans, atmosphere, land and snow & ice form the climate system. ...
Exam 1
... because: a. the break up of Panthalassa has destroyed all ancient seafloor b. all the older seafloor is layered under the present continental crust c. new seafloor eventually subducts and melts in deep-sea trenches; this process rarely takes longer than 200 million years., d. older seafloor is destr ...
... because: a. the break up of Panthalassa has destroyed all ancient seafloor b. all the older seafloor is layered under the present continental crust c. new seafloor eventually subducts and melts in deep-sea trenches; this process rarely takes longer than 200 million years., d. older seafloor is destr ...
ocean noise
... pollution on a political level in its campaign, Silent Oceans, and international bodies are increasingly taking this human-induced environmental threat seriously. In certain marine areas, the ocean noise level has doubled every decade over the last sixty years. The increase in ship traffic generates ...
... pollution on a political level in its campaign, Silent Oceans, and international bodies are increasingly taking this human-induced environmental threat seriously. In certain marine areas, the ocean noise level has doubled every decade over the last sixty years. The increase in ship traffic generates ...
The Ocean Floor
... Less than 0.1 percent of the world's seamounts have been explored to learn what species live on them, but many of the species that have been found so far are new to science. It has been estimated that more than 30,000 seamounts reaching more than 1,000 meters tall are found in the Pacific Ocean. App ...
... Less than 0.1 percent of the world's seamounts have been explored to learn what species live on them, but many of the species that have been found so far are new to science. It has been estimated that more than 30,000 seamounts reaching more than 1,000 meters tall are found in the Pacific Ocean. App ...
Recognizing Continents and Oceans
... was a great salt lake surrounded by land. They assumed Asia could be reached from the west only by land. ...
... was a great salt lake surrounded by land. They assumed Asia could be reached from the west only by land. ...
Oceans 11 Bathymetry and the Use of Technology Name Date Our
... Bathymetry and the Use of Technology Our knowledge of the diverse topography of the ocean floor is relatively recent. Up to the 1920’s depths to the ocean floor were determined by lowering a weighted rope until it touched bottom and then measuring the length of the rope. Ocean floor composition was ...
... Bathymetry and the Use of Technology Our knowledge of the diverse topography of the ocean floor is relatively recent. Up to the 1920’s depths to the ocean floor were determined by lowering a weighted rope until it touched bottom and then measuring the length of the rope. Ocean floor composition was ...
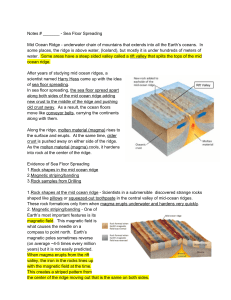
Notes # ______ Sea Floor Spreading Mid Ocean Ridge underwater
... in the central valley of midocean ridges. These rock formations only form when magma erupts underwater and hardens very quickly ...
... in the central valley of midocean ridges. These rock formations only form when magma erupts underwater and hardens very quickly ...
lecture notes
... Phosphorite is a shelf deposit formed where upwelling of nutrient-rich water generates high biological productivity resulting in a high concentration of phosphate-rich organic debris within shelf sediments o The distribution of sediments in the deep ocean varies greatly, but is strongly controlled ...
... Phosphorite is a shelf deposit formed where upwelling of nutrient-rich water generates high biological productivity resulting in a high concentration of phosphate-rich organic debris within shelf sediments o The distribution of sediments in the deep ocean varies greatly, but is strongly controlled ...
3-2
... Water Covers Most of the Earth and Sustains Biodiversity • Aquatic life zones – Key factors determining types and numbers of organisms in different layers • Water temperature • Dissolved oxygen content • Food availability • Availability of light and nutrients for photosynthesis ...
... Water Covers Most of the Earth and Sustains Biodiversity • Aquatic life zones – Key factors determining types and numbers of organisms in different layers • Water temperature • Dissolved oxygen content • Food availability • Availability of light and nutrients for photosynthesis ...
chapter7 - Everglades High School
... the photosynthetic activity of marine plants. Oxygen concentration decreases below the sunlit layer because of the respiration of marine animals and bacteria, and because of the oxygen consumed by the decay of tiny dead organisms slowly sinking through the area. In contrast, because plants use carbo ...
... the photosynthetic activity of marine plants. Oxygen concentration decreases below the sunlit layer because of the respiration of marine animals and bacteria, and because of the oxygen consumed by the decay of tiny dead organisms slowly sinking through the area. In contrast, because plants use carbo ...
Nordic Master`s Programme in Marine Ecosystems and Climate
... To give the student an introduction to how the ocean physics and ocean chemistry influence production and distribution of organisms at trophic levels of marine ecosystems from phytoplankton to fish, and how the physics and chemistry influence the flow of energy through the food web. It will be empha ...
... To give the student an introduction to how the ocean physics and ocean chemistry influence production and distribution of organisms at trophic levels of marine ecosystems from phytoplankton to fish, and how the physics and chemistry influence the flow of energy through the food web. It will be empha ...
Marine habitats
.jpg?width=300)
The marine environment supplies many kinds of habitats that support marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater that is in the sea (the term marine comes from the Latin mare, meaning sea or ocean). A habitat is an ecological or environmental area inhabited by one or more living species.Marine habitats can be divided into coastal and open ocean habitats. Coastal habitats are found in the area that extends from as far as the tide comes in on the shoreline out to the edge of the continental shelf. Most marine life is found in coastal habitats, even though the shelf area occupies only seven percent of the total ocean area. Open ocean habitats are found in the deep ocean beyond the edge of the continental shelf.Alternatively, marine habitats can be divided into pelagic and demersal habitats. Pelagic habitats are found near the surface or in the open water column, away from the bottom of the ocean. Demersal habitats are near or on the bottom of the ocean. An organism living in a pelagic habitat is said to be a pelagic organism, as in pelagic fish. Similarly, an organism living in a demersal habitat is said to be a demersal organism, as in demersal fish. Pelagic habitats are intrinsically shifting and ephemeral, depending on what ocean currents are doing.Marine habitats can be modified by their inhabitants. Some marine organisms, like corals, kelp, mangroves and seagrasses, are ecosystem engineers which reshape the marine environment to the point where they create further habitat for other organisms.