THE OFFICIAL MAGAZINE OF THE OCEANOGRAPHY SOCIETY
... this impressive book by five of the world’s experts in marine science. Indeed, authors Karson, Kelley, Fornari, Perfit, and Shank combine their vast collective knowledge of the processes that are responsible for the origin and evolution of the ocean floor and crust to produce a book that this review ...
... this impressive book by five of the world’s experts in marine science. Indeed, authors Karson, Kelley, Fornari, Perfit, and Shank combine their vast collective knowledge of the processes that are responsible for the origin and evolution of the ocean floor and crust to produce a book that this review ...
Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO
... meet its consequences. A scheme to improve the coverage in the Indian Ocean has been agreed upon, and the establishement ot the Regional Tsunami Watch Providers will be one of the major decisions for the next meeting of the ICG in April 2009 in Thailand. Numerous activities for capacity building and ...
... meet its consequences. A scheme to improve the coverage in the Indian Ocean has been agreed upon, and the establishement ot the Regional Tsunami Watch Providers will be one of the major decisions for the next meeting of the ICG in April 2009 in Thailand. Numerous activities for capacity building and ...
Press Release Monday, December 21, 2009 Man
... sound absorption in the ocean”, says Zeebe. “What is happening over time is that the low frequencies become louder at distance. It’s similar to the effect when you slowly turn up the bass on your stereo.” However, underwater sound propagation is much more complex; it depends on spatial distribution ...
... sound absorption in the ocean”, says Zeebe. “What is happening over time is that the low frequencies become louder at distance. It’s similar to the effect when you slowly turn up the bass on your stereo.” However, underwater sound propagation is much more complex; it depends on spatial distribution ...
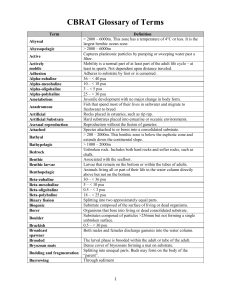
CBRAT Glossary of Terms
... aquatic ecosystem (e.g., sand dunes, estuarine shrub/scrub wetland, estuarine forest wetland). Sediment environments along the coast that are affected by the tides and water activity (shore waves). Ex. sandy beaches. Unconsolidated sediment composed of > 75% by weight of particles in the size range ...
... aquatic ecosystem (e.g., sand dunes, estuarine shrub/scrub wetland, estuarine forest wetland). Sediment environments along the coast that are affected by the tides and water activity (shore waves). Ex. sandy beaches. Unconsolidated sediment composed of > 75% by weight of particles in the size range ...
Coastal and Marine Spatial Planning
... one use, or sector, at a time. This is not an ideal approach if we want the best mix of uses in an area, with minimal conflicts, maximum efficiencies and conservation of resources for future generations. For example, a plan for offshore energy exploration may not effectively consider other uses that ...
... one use, or sector, at a time. This is not an ideal approach if we want the best mix of uses in an area, with minimal conflicts, maximum efficiencies and conservation of resources for future generations. For example, a plan for offshore energy exploration may not effectively consider other uses that ...
Coastal and Marine Spatial Planning
... one use, or sector, at a time. This is not an ideal approach if we want the best mix of uses in an area, with minimal conflicts, maximum efficiencies and conservation of resources for future generations. For example, a plan for offshore energy exploration may not effectively consider other uses that ...
... one use, or sector, at a time. This is not an ideal approach if we want the best mix of uses in an area, with minimal conflicts, maximum efficiencies and conservation of resources for future generations. For example, a plan for offshore energy exploration may not effectively consider other uses that ...
SCCOOS - National Federation of Regional Associations for
... • CalCOFI surveys collected zooplankton biomass, fish and invertebrate larvae and conducted underway measurements of temperature, salinity, irradiance and fluorescence. • Extending the historically offshore stations of CalCOFI closer to the coast brought relevance to the National Pollutant Discharge ...
... • CalCOFI surveys collected zooplankton biomass, fish and invertebrate larvae and conducted underway measurements of temperature, salinity, irradiance and fluorescence. • Extending the historically offshore stations of CalCOFI closer to the coast brought relevance to the National Pollutant Discharge ...
24-25
... Fortunately, Hopkins Marine Station personnel have been meticulously recording seawater temperatures every day for nearly 80 years. The data showed that, during the 60-year interval between the two animal surveys, annual mean water temperatures increased on average by about 0.7 °C. More significantl ...
... Fortunately, Hopkins Marine Station personnel have been meticulously recording seawater temperatures every day for nearly 80 years. The data showed that, during the 60-year interval between the two animal surveys, annual mean water temperatures increased on average by about 0.7 °C. More significantl ...
History of Deep Sea Biology - Monterey Bay Aquarium Research
... Reading for Sept. 29, Oct.1 Sept. 29 Physical Environment: • Gage and Tyler 1991. Chapter 2. Oct. 1 Faunal composition, depth zonation: • Carney, R.S. Zonation of deep biota on continental margins. 2005. Oceanogr. and Mar. Biol: An Annual Review 43: 211-278. • Gage and Tyler 1991. Skim through imag ...
... Reading for Sept. 29, Oct.1 Sept. 29 Physical Environment: • Gage and Tyler 1991. Chapter 2. Oct. 1 Faunal composition, depth zonation: • Carney, R.S. Zonation of deep biota on continental margins. 2005. Oceanogr. and Mar. Biol: An Annual Review 43: 211-278. • Gage and Tyler 1991. Skim through imag ...
Pat Halpin: CoML Mapping and Visualization II
... Map-centric website allowing users to zoom to any place on Earth and switch map themes between physical oceanographic variables, large marine ecosystems, marine ecoregions, species diversity, CoML surveys and findings (grouped by past, present, and future), marine protected areas, threats, ecosystem ...
... Map-centric website allowing users to zoom to any place on Earth and switch map themes between physical oceanographic variables, large marine ecosystems, marine ecoregions, species diversity, CoML surveys and findings (grouped by past, present, and future), marine protected areas, threats, ecosystem ...
Chapter 1. - Seagrass
... available light for growth (nutrient and sediment loading). Various combinations of these parameters will permit, encourage or eliminate seagrass from a specific location. Seagrasses occupy a variety of coastal habitats. Seagrass meadows typically occur in most shallow, sheltered soft-bottomed marin ...
... available light for growth (nutrient and sediment loading). Various combinations of these parameters will permit, encourage or eliminate seagrass from a specific location. Seagrasses occupy a variety of coastal habitats. Seagrass meadows typically occur in most shallow, sheltered soft-bottomed marin ...
Structure And Function Of Marine Shoreline Ecosystems
... Within a decade, the giant oil field, Bombay High, was discovered and put into production. The western continental margin is typically a passive margin and like other divergent margins has a favorable habitat for hydrocarbon generation and accumulation. Of the 1.78 million km2 of sedimentary basins ...
... Within a decade, the giant oil field, Bombay High, was discovered and put into production. The western continental margin is typically a passive margin and like other divergent margins has a favorable habitat for hydrocarbon generation and accumulation. Of the 1.78 million km2 of sedimentary basins ...
From the 4th Global Conference on Oceans, Coasts, and Islands
... experienced, which is threatening human security. Most of the increased heat of the earth during recent decades has gone into the ocean. The increased energy of the ocean atmosphere system is driving an increase in more extreme weather events. Storm intensity is about five times larger than expected ...
... experienced, which is threatening human security. Most of the increased heat of the earth during recent decades has gone into the ocean. The increased energy of the ocean atmosphere system is driving an increase in more extreme weather events. Storm intensity is about five times larger than expected ...
A New Carbon-Based Algal Biomass Proxy for Photoacclimation
... Photoacclimation changes the intracellular chlorophyll-a concentration (Chl), and is not currently taken into account by standard ocean color algorithms. Chl production is a process enhanced under high nutrient and low light conditions (e.g. winter and spring in the Mediterranean Sea). Historically, ...
... Photoacclimation changes the intracellular chlorophyll-a concentration (Chl), and is not currently taken into account by standard ocean color algorithms. Chl production is a process enhanced under high nutrient and low light conditions (e.g. winter and spring in the Mediterranean Sea). Historically, ...
Biomes of the World
... Broken into four layers: Photic zone: enough light for PS Aphotic zone: very little light Thermoclines: mid level region with fast temperature change (deeper colder) 4. Benthic zone: bottom of the biome (sand, organic sediments, detritus) ...
... Broken into four layers: Photic zone: enough light for PS Aphotic zone: very little light Thermoclines: mid level region with fast temperature change (deeper colder) 4. Benthic zone: bottom of the biome (sand, organic sediments, detritus) ...
Surface Currents - Mrs. Leachman Science
... Surface currents transport this energy all over the world Surface currents move warmer water into cooler regions and return cooler water to the warmer regions (tropics) Currents can have a cooling effect on an area’s climate or a warming effect on an area’s climate As warm water flows from t ...
... Surface currents transport this energy all over the world Surface currents move warmer water into cooler regions and return cooler water to the warmer regions (tropics) Currents can have a cooling effect on an area’s climate or a warming effect on an area’s climate As warm water flows from t ...
FRAMEWORK
... the continental shelf, the continental slope, and The continental rise. These areas are covered with thick layers of sediments (sand, mud, rocks). • The depth of the ocean varies. Ocean trenches are very deep, and the continental shelf is relatively shallow. • Ocean water is a complex mixture of gas ...
... the continental shelf, the continental slope, and The continental rise. These areas are covered with thick layers of sediments (sand, mud, rocks). • The depth of the ocean varies. Ocean trenches are very deep, and the continental shelf is relatively shallow. • Ocean water is a complex mixture of gas ...
Oceans - Jefferson Township Public Schools
... are also the main gases dissolved in ocean water. • While carbon dioxide, CO2, is not a major component of the atmosphere, a large amount of this gas is dissolved in ocean water. • Gases can enter the ocean from streams, volcanoes, organisms, and the atmosphere. ...
... are also the main gases dissolved in ocean water. • While carbon dioxide, CO2, is not a major component of the atmosphere, a large amount of this gas is dissolved in ocean water. • Gases can enter the ocean from streams, volcanoes, organisms, and the atmosphere. ...
Marine Microbial Processes Outline
... Autotroph: carbon and energy for growth comes from non-organic sources. For example, phytoplankton are autotrophs because they use CO2 for their carbon source and use sunlight for their energy source Heterotroph: carbon and energy for growth comes from pre-formed organic material. For example, herbi ...
... Autotroph: carbon and energy for growth comes from non-organic sources. For example, phytoplankton are autotrophs because they use CO2 for their carbon source and use sunlight for their energy source Heterotroph: carbon and energy for growth comes from pre-formed organic material. For example, herbi ...
here - Great British Oceans
... The UK has the fifth largest area of ocean in the world under its jurisdiction when its Overseas Territories (UKOTs) are taken into account. Over 94% of the UK’s unique biodiversity is found in the UKOTs, which support a large number of rare and threatened species and habitats found nowhere else on ...
... The UK has the fifth largest area of ocean in the world under its jurisdiction when its Overseas Territories (UKOTs) are taken into account. Over 94% of the UK’s unique biodiversity is found in the UKOTs, which support a large number of rare and threatened species and habitats found nowhere else on ...
Oslo / Geesthacht
... coastal waters, from small lagoons to the continental shelf," said Dennis Swaney, a researcher in biogeochemistry at Cornell University. "Watersheds which formerly provided nutrients to coastal waters only from within their boundaries now see additional sources from outside their boundaries, due to ...
... coastal waters, from small lagoons to the continental shelf," said Dennis Swaney, a researcher in biogeochemistry at Cornell University. "Watersheds which formerly provided nutrients to coastal waters only from within their boundaries now see additional sources from outside their boundaries, due to ...
Marine habitats
.jpg?width=300)
The marine environment supplies many kinds of habitats that support marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater that is in the sea (the term marine comes from the Latin mare, meaning sea or ocean). A habitat is an ecological or environmental area inhabited by one or more living species.Marine habitats can be divided into coastal and open ocean habitats. Coastal habitats are found in the area that extends from as far as the tide comes in on the shoreline out to the edge of the continental shelf. Most marine life is found in coastal habitats, even though the shelf area occupies only seven percent of the total ocean area. Open ocean habitats are found in the deep ocean beyond the edge of the continental shelf.Alternatively, marine habitats can be divided into pelagic and demersal habitats. Pelagic habitats are found near the surface or in the open water column, away from the bottom of the ocean. Demersal habitats are near or on the bottom of the ocean. An organism living in a pelagic habitat is said to be a pelagic organism, as in pelagic fish. Similarly, an organism living in a demersal habitat is said to be a demersal organism, as in demersal fish. Pelagic habitats are intrinsically shifting and ephemeral, depending on what ocean currents are doing.Marine habitats can be modified by their inhabitants. Some marine organisms, like corals, kelp, mangroves and seagrasses, are ecosystem engineers which reshape the marine environment to the point where they create further habitat for other organisms.