oceanic - Southern Local Schools
... Intertidal Zone contd. • Intertidal organisms must be able to live both underwater and on exposed land. Some organisms attach themselves to rocks and reefs to avoid being washed out to sea during low tide. Some animals can burrow in the sand or between rocks. Plants such as seaweed have strong hold ...
... Intertidal Zone contd. • Intertidal organisms must be able to live both underwater and on exposed land. Some organisms attach themselves to rocks and reefs to avoid being washed out to sea during low tide. Some animals can burrow in the sand or between rocks. Plants such as seaweed have strong hold ...
Earth`s Oceans
... Intertidal Zone contd. • Intertidal organisms must be able to live both underwater and on exposed land. Some organisms attach themselves to rocks and reefs to avoid being washed out to sea during low tide. Some animals can burrow in the sand or between rocks. Plants such as seaweed have strong hold ...
... Intertidal Zone contd. • Intertidal organisms must be able to live both underwater and on exposed land. Some organisms attach themselves to rocks and reefs to avoid being washed out to sea during low tide. Some animals can burrow in the sand or between rocks. Plants such as seaweed have strong hold ...
Coastal Ocean Observing Systems SEACOOS Facilitating Marine
... times with a uniform distribution of particles centered on and to the south of the MR delta. For times beyond the last analysis interval currents are held steady to produce the forecast. These are updated with each new analysis interval. (Note that trajectories omit other effects such as winds for w ...
... times with a uniform distribution of particles centered on and to the south of the MR delta. For times beyond the last analysis interval currents are held steady to produce the forecast. These are updated with each new analysis interval. (Note that trajectories omit other effects such as winds for w ...
The Ocean Floor
... The Ocean Floor What is going on at the Marianas trench? The oceanic plate or in this case the fastmoving pacific plate, plunges downward toward the mantle, while the continental plate or the Philippine Plate, rides up over the top. The forces driving the two plates together are really intense, so ...
... The Ocean Floor What is going on at the Marianas trench? The oceanic plate or in this case the fastmoving pacific plate, plunges downward toward the mantle, while the continental plate or the Philippine Plate, rides up over the top. The forces driving the two plates together are really intense, so ...
1 One of the most important aspects of understanding ocean life is
... Although we focus here on measurement of abiotic factors that affect ocean life, it is worth mentioning measurements of plankton. Plankton are often microscopic in size, poor swimmers or floaters, and make up the bottom of the ocean food chain. Variations in the abundance, location, and type of plan ...
... Although we focus here on measurement of abiotic factors that affect ocean life, it is worth mentioning measurements of plankton. Plankton are often microscopic in size, poor swimmers or floaters, and make up the bottom of the ocean food chain. Variations in the abundance, location, and type of plan ...
F2007_311_summary_V
... Today – ocean circulation is such that warm water flows near surface to N. Atlantic then gets chilled and becomes dense (it is also very saline) and sinks to ocean bottom. This is “North Atlantic deep water” and is the origin of much of the deep water in the world’s oceans (Atlantic conveyor). From ...
... Today – ocean circulation is such that warm water flows near surface to N. Atlantic then gets chilled and becomes dense (it is also very saline) and sinks to ocean bottom. This is “North Atlantic deep water” and is the origin of much of the deep water in the world’s oceans (Atlantic conveyor). From ...
Mid-Term exam Study Guide KEY link
... 84) What are placer deposits and where would you find them? Deposits found in areas where rivers enter oceans 85) How do plants make energy? What are the raw materials and the products? Plants make energy by using carbon dioxide, nutrients in the water and sunlight 86) What are the two major ways t ...
... 84) What are placer deposits and where would you find them? Deposits found in areas where rivers enter oceans 85) How do plants make energy? What are the raw materials and the products? Plants make energy by using carbon dioxide, nutrients in the water and sunlight 86) What are the two major ways t ...
Prince Rupert Community Observatory Information Package
... Prince Rupert harbour has seen progressive growth of marine traffic over the years and the number and size of vessels is projected to increase with expansions to the terminals at Fairfield and Ridley Island, and with the possible addition of a terminal at Lelu Island. It is important to have a basel ...
... Prince Rupert harbour has seen progressive growth of marine traffic over the years and the number and size of vessels is projected to increase with expansions to the terminals at Fairfield and Ridley Island, and with the possible addition of a terminal at Lelu Island. It is important to have a basel ...
The Network of European Marine Research Stations
... marine institutes. In 2000 in Venice, marine biodiversity was chosen as the first priority issue. The reasons are obvious. Fisheries are in crisis. Marine species in general are disappearing at a rate never observed since life began on earth. The extinction crisis ranks with global climate change as ...
... marine institutes. In 2000 in Venice, marine biodiversity was chosen as the first priority issue. The reasons are obvious. Fisheries are in crisis. Marine species in general are disappearing at a rate never observed since life began on earth. The extinction crisis ranks with global climate change as ...
MIT Sea Grant College Program
... NEW METHODS AND SOFTWARE DEVELOPED AT MIT CAN PREDICT OPTIMAL PATHS FOR AUTOMATED UNDERWATER VEHICLES The work of MIT Sea Grant funded Doherty Associate Professor in Ocean Utilization, Pierre Lermusiaux, was recently featured on the MIT News site in an article by David L. Chandler: ...
... NEW METHODS AND SOFTWARE DEVELOPED AT MIT CAN PREDICT OPTIMAL PATHS FOR AUTOMATED UNDERWATER VEHICLES The work of MIT Sea Grant funded Doherty Associate Professor in Ocean Utilization, Pierre Lermusiaux, was recently featured on the MIT News site in an article by David L. Chandler: ...
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Part 1 Multiple Choice
... 1. The existence of coal beds in Antarctica indicates that the continent once had ____. a. been part of Africa c. a cold, dry climate b. a temperate, rainy climate d. been farther from the equator ...
... 1. The existence of coal beds in Antarctica indicates that the continent once had ____. a. been part of Africa c. a cold, dry climate b. a temperate, rainy climate d. been farther from the equator ...
A literature review was used to obtain stable isotope values
... increased and provided a more conservative estimate of the mean regional value. If isotope data for a particular species and region were available from multiple studies, the study that had the largest sample size was used. A prey species’ isotopic values are assumed to be representative of both that ...
... increased and provided a more conservative estimate of the mean regional value. If isotope data for a particular species and region were available from multiple studies, the study that had the largest sample size was used. A prey species’ isotopic values are assumed to be representative of both that ...
IM_chapter9 Seafloor
... because they harbor such an incredible abundance and diversity of life. These spectacular and beautiful ecosystems are home to more than one-fourth of all marine plant and animal species. Reefs are built of tiny coral polyps that construct calcium carbonate (CaCO3) shells around their bodies. The co ...
... because they harbor such an incredible abundance and diversity of life. These spectacular and beautiful ecosystems are home to more than one-fourth of all marine plant and animal species. Reefs are built of tiny coral polyps that construct calcium carbonate (CaCO3) shells around their bodies. The co ...
Primary Production
... 9 Th The ocean is much larger than land (70% vs 30%) i hl th l d (70% 30%) 9 Marine plants double every 2‐3 days, terrestrial plants average years 9 Thus, even though there is less “plant” material in the ocean, as a whole the ocean is about as productive as land. Sometimes called the “invisible ...
... 9 Th The ocean is much larger than land (70% vs 30%) i hl th l d (70% 30%) 9 Marine plants double every 2‐3 days, terrestrial plants average years 9 Thus, even though there is less “plant” material in the ocean, as a whole the ocean is about as productive as land. Sometimes called the “invisible ...
OCEANOGRAPHY
... The geofluids are naturally studied in axes of reference fixed with the rotating Earth. In such a system of reference, the main correction for the motion of the reference frame is the existence of the “fictive” Coriolis force that tends to deflect any projectile or ocean current perpendicularly to i ...
... The geofluids are naturally studied in axes of reference fixed with the rotating Earth. In such a system of reference, the main correction for the motion of the reference frame is the existence of the “fictive” Coriolis force that tends to deflect any projectile or ocean current perpendicularly to i ...
November 2013 Newsletter
... This is Ari Panjanadum, one of the teachers of the Mauritius Marine Guide Programme. Ari is living in Pointe d'Esny since 1990. He is a professional primary school teacher working in a French school. His qualifications are British Sub Aquatic Club (BS-AC) Advanced Diver, Advanced Scuba Diving Instru ...
... This is Ari Panjanadum, one of the teachers of the Mauritius Marine Guide Programme. Ari is living in Pointe d'Esny since 1990. He is a professional primary school teacher working in a French school. His qualifications are British Sub Aquatic Club (BS-AC) Advanced Diver, Advanced Scuba Diving Instru ...
coral reefs - bankstowntafehsc
... Coral reefs occur where: - shallow areas in tropical latitudes, or where warm ocean currents flow in temperate areas - a zone extending from Latitudes 30°N to 30°S of the equator; - water depths from 2 to 30m because they need light to allow the algae (zooxanthellae) to photosynthesise in the coral ...
... Coral reefs occur where: - shallow areas in tropical latitudes, or where warm ocean currents flow in temperate areas - a zone extending from Latitudes 30°N to 30°S of the equator; - water depths from 2 to 30m because they need light to allow the algae (zooxanthellae) to photosynthesise in the coral ...
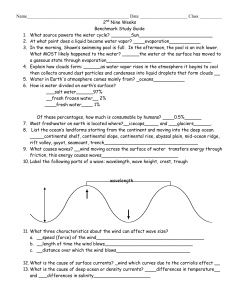
2nd Nine Weeks
... 17. Explain neap and spring tides. Neap:__occurs during 1st or 3rd quarter when sun/moon gravity pulls in different directions causing lower high tides and higher low tides so there is a small tidal range_____ Spring- _occurs during new/full moon when sun/moon gravity pulls together causing extra hi ...
... 17. Explain neap and spring tides. Neap:__occurs during 1st or 3rd quarter when sun/moon gravity pulls in different directions causing lower high tides and higher low tides so there is a small tidal range_____ Spring- _occurs during new/full moon when sun/moon gravity pulls together causing extra hi ...
Ch 15 Earth`s Oceans
... 16. Today average global sea level is slowly ________________ at a rate of 1 to 2 mm per year. Answer the following questions. (8 points) 17. Why is Earth known as the blue planet? 18. What is the average depth of the oceans? 19. How much of the northern hemisphere is covered by oceans? 20. How much ...
... 16. Today average global sea level is slowly ________________ at a rate of 1 to 2 mm per year. Answer the following questions. (8 points) 17. Why is Earth known as the blue planet? 18. What is the average depth of the oceans? 19. How much of the northern hemisphere is covered by oceans? 20. How much ...
Hazards Chapter3b
... of waves similar to those resulting from objects thrown into the water These seismographically-induced waves may be unnoticeable in the open sea, but upon reaching shallow waters they begin to grow to massive proportions – may reach 30 m (100’) of more They have awesome kinetic energy from the mass ...
... of waves similar to those resulting from objects thrown into the water These seismographically-induced waves may be unnoticeable in the open sea, but upon reaching shallow waters they begin to grow to massive proportions – may reach 30 m (100’) of more They have awesome kinetic energy from the mass ...
Canada - CoML Secretariat
... Conlan K, Aitken A, Hendrycks E, McClelland C, Melling H (2008) Distribution patterns of Canadian Beaufort Shelf macrobenthos. Journal of Marine System xx:xx Cusson M, Archambault P, Aitken A (2007) Biodiversity of benthic assemblages on the Arctic continental shelf: historical data from Canada. Mar ...
... Conlan K, Aitken A, Hendrycks E, McClelland C, Melling H (2008) Distribution patterns of Canadian Beaufort Shelf macrobenthos. Journal of Marine System xx:xx Cusson M, Archambault P, Aitken A (2007) Biodiversity of benthic assemblages on the Arctic continental shelf: historical data from Canada. Mar ...
marine technology
... the port and facilities have expanded for increased shipping and business. This expansion has seen a renewed focus on the interplay between the port’s operational, maritime and natural environments. For example, a large tidal range of almost 8 m drives strong and complex currents, having speeds to 2 ...
... the port and facilities have expanded for increased shipping and business. This expansion has seen a renewed focus on the interplay between the port’s operational, maritime and natural environments. For example, a large tidal range of almost 8 m drives strong and complex currents, having speeds to 2 ...
Notes and Investigation
... how current flows might affect ocean organisms and species. Scientists seek to understand and explain how the natural world works. Many of the questions raised in this endeavor have no absolute answers. Although many sea creatures are powerful, efficient swimmers, many others are ungainly or even im ...
... how current flows might affect ocean organisms and species. Scientists seek to understand and explain how the natural world works. Many of the questions raised in this endeavor have no absolute answers. Although many sea creatures are powerful, efficient swimmers, many others are ungainly or even im ...
Marine habitats
.jpg?width=300)
The marine environment supplies many kinds of habitats that support marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater that is in the sea (the term marine comes from the Latin mare, meaning sea or ocean). A habitat is an ecological or environmental area inhabited by one or more living species.Marine habitats can be divided into coastal and open ocean habitats. Coastal habitats are found in the area that extends from as far as the tide comes in on the shoreline out to the edge of the continental shelf. Most marine life is found in coastal habitats, even though the shelf area occupies only seven percent of the total ocean area. Open ocean habitats are found in the deep ocean beyond the edge of the continental shelf.Alternatively, marine habitats can be divided into pelagic and demersal habitats. Pelagic habitats are found near the surface or in the open water column, away from the bottom of the ocean. Demersal habitats are near or on the bottom of the ocean. An organism living in a pelagic habitat is said to be a pelagic organism, as in pelagic fish. Similarly, an organism living in a demersal habitat is said to be a demersal organism, as in demersal fish. Pelagic habitats are intrinsically shifting and ephemeral, depending on what ocean currents are doing.Marine habitats can be modified by their inhabitants. Some marine organisms, like corals, kelp, mangroves and seagrasses, are ecosystem engineers which reshape the marine environment to the point where they create further habitat for other organisms.