The Frontal Cortex and Working with Memory
... but spared procedural learning and memory that could be applied when subsequently tested on either maze A or B. In contrast, the FC-lesioned group had good memory for the salient maze A-learning experience, but were unable to use that memory in a flexible, strategic way that would enable savings on ...
... but spared procedural learning and memory that could be applied when subsequently tested on either maze A or B. In contrast, the FC-lesioned group had good memory for the salient maze A-learning experience, but were unable to use that memory in a flexible, strategic way that would enable savings on ...
Understanding Adolescent Brain Development and Its Implications
... immature frontal lobes, too, but do not exhibit the degree of risky behavior exhibited by many teenagers. According to the authors, “[a]dolescence is a developmental period characterized by suboptimal decisions and actions that are associated with an increased incidence of unintentional injuries, vi ...
... immature frontal lobes, too, but do not exhibit the degree of risky behavior exhibited by many teenagers. According to the authors, “[a]dolescence is a developmental period characterized by suboptimal decisions and actions that are associated with an increased incidence of unintentional injuries, vi ...
Impulsivity-related brain volume deficits in schizophrenia
... related to grey matter volume deficits in prefrontal areas. We employed a voxel-based morphometry approach as well as neuropsychological assessment of executive functions and trait impulsivity in 51 participants (age range 23–55). The schizophrenia group comprised 24 patients (12 patients with paran ...
... related to grey matter volume deficits in prefrontal areas. We employed a voxel-based morphometry approach as well as neuropsychological assessment of executive functions and trait impulsivity in 51 participants (age range 23–55). The schizophrenia group comprised 24 patients (12 patients with paran ...
PDF
... the transmission properties of synapses (Marder and Calabrese 1996). They also have profound impacts on behavioral responsiveness—wakefulness and sleep being a prime example. However, neuromodulators are thought to work on a rather coarse scale, both temporally and spatially. Thus, while they might ...
... the transmission properties of synapses (Marder and Calabrese 1996). They also have profound impacts on behavioral responsiveness—wakefulness and sleep being a prime example. However, neuromodulators are thought to work on a rather coarse scale, both temporally and spatially. Thus, while they might ...
Neural computations associated with goal
... However, health information had a greater influence on the OFC value signals (and choices) when a region of left DLPFC was activated. A functional connectivity analysis suggested that DLPFC might modulate ...
... However, health information had a greater influence on the OFC value signals (and choices) when a region of left DLPFC was activated. A functional connectivity analysis suggested that DLPFC might modulate ...
Sympathetic Division (cont)
... Higher-Order Functions (cont) How memories are consolidated is poorly understood. How they are retrieved is even less well understood. What is known: a synapse that is frequently active does increase its output of neurotransmitter to produce a greater effect on the postsynaptic neuron(s). Circuits ...
... Higher-Order Functions (cont) How memories are consolidated is poorly understood. How they are retrieved is even less well understood. What is known: a synapse that is frequently active does increase its output of neurotransmitter to produce a greater effect on the postsynaptic neuron(s). Circuits ...
Cortical and basal ganglia contributions to habit learning and
... the substantia nigra pars compacta, which projects predominantly back to the rest of the basal ganglia, and the ventral tegmental area, which projects to all of frontal cortex and limbic areas (e.g. amygdala, hippocampus and nucleus accumbens). In Parkinson’s disease, these dopamine-producing cells ...
... the substantia nigra pars compacta, which projects predominantly back to the rest of the basal ganglia, and the ventral tegmental area, which projects to all of frontal cortex and limbic areas (e.g. amygdala, hippocampus and nucleus accumbens). In Parkinson’s disease, these dopamine-producing cells ...
An architectural model of conscious and unconscious brain
... version of Baddeley’s WM has a new conscious component, called the Episodic Buffer (Baddeley, 2000). However, it does not have a central role in recruiting linguistic, visuospatial and executive functions; the current concept of the Episodic Buffer is only the front end of long-term episodic memory. ...
... version of Baddeley’s WM has a new conscious component, called the Episodic Buffer (Baddeley, 2000). However, it does not have a central role in recruiting linguistic, visuospatial and executive functions; the current concept of the Episodic Buffer is only the front end of long-term episodic memory. ...
Impaired associative learning in schizophrenia: behavioral and
... In the human brain, the interplay between evolutionarily mature prefrontal and hippocampal regions underlies associative learning. Whereas the precise contributions of each of these regions is the subject of debate (McClelland et al. 1995), conscious associative encoding may involve persistent prefr ...
... In the human brain, the interplay between evolutionarily mature prefrontal and hippocampal regions underlies associative learning. Whereas the precise contributions of each of these regions is the subject of debate (McClelland et al. 1995), conscious associative encoding may involve persistent prefr ...
Habit formation
... as do habits 29. This is true even for fixed action patterns such as grooming in rodents 43. Such similarity across types of repetitive behaviors raises the possibility that the DLS may in part be promoting the skill aspects of habits, or in other words, supporting them as sequences with structure ...
... as do habits 29. This is true even for fixed action patterns such as grooming in rodents 43. Such similarity across types of repetitive behaviors raises the possibility that the DLS may in part be promoting the skill aspects of habits, or in other words, supporting them as sequences with structure ...
Neurophysiological Mechanisms Underlying Auditory Image
... The N100 represents a conglomerate of brain processes associated with processing an auditory stimulus (Näätänen & Picton, 1987), and it may overlap with other ERP components such as the mismatch negativity (MMN) (Näätänen, 1992). In tasks employing continuous stimulus situations in which individual ...
... The N100 represents a conglomerate of brain processes associated with processing an auditory stimulus (Näätänen & Picton, 1987), and it may overlap with other ERP components such as the mismatch negativity (MMN) (Näätänen, 1992). In tasks employing continuous stimulus situations in which individual ...
The Neural Basis of the Object Concept in Ambiguous and
... orientation and/or color can vary. Aside from nonuniformity there are cases of ambiguous stimuli: two distinct objects that overlap with each other and are alike in one or more feature dimensions, can generate the same retinal activation pattern as a single object with non-uniform properties. Furthe ...
... orientation and/or color can vary. Aside from nonuniformity there are cases of ambiguous stimuli: two distinct objects that overlap with each other and are alike in one or more feature dimensions, can generate the same retinal activation pattern as a single object with non-uniform properties. Furthe ...
The role of neuronal synchronization in selective attention
... stimulus-induced gamma-band synchronization could predict later memory of that stimulus [43–49]. This capability to predict successful encoding is not restricted to synchronization in the gamma-frequency band: it is frequently accompanied by modulation of oscillatory activity in the theta-frequency ...
... stimulus-induced gamma-band synchronization could predict later memory of that stimulus [43–49]. This capability to predict successful encoding is not restricted to synchronization in the gamma-frequency band: it is frequently accompanied by modulation of oscillatory activity in the theta-frequency ...
doc - physiologicalcomputing.org
... experiences because highly moving artworks ‘strike a chord’ with the viewer and this resonance activates the medial rPFC area. The second system related to the ToM is the mirror neuron system (MNS), which coactivates actions, intention and emotions of both the self and others (Mahy et al., 2014; Mo ...
... experiences because highly moving artworks ‘strike a chord’ with the viewer and this resonance activates the medial rPFC area. The second system related to the ToM is the mirror neuron system (MNS), which coactivates actions, intention and emotions of both the self and others (Mahy et al., 2014; Mo ...
phys chapter 56 [10-19
... o Almost all communication between this area and cerebral cortex through premotor area and primary and association somatosensory areas (not primary cerebral motor cortex) o Destruction of this area with their deep nuclei (dentate nuclei) can lead to extreme incoordination of complex purposeful movem ...
... o Almost all communication between this area and cerebral cortex through premotor area and primary and association somatosensory areas (not primary cerebral motor cortex) o Destruction of this area with their deep nuclei (dentate nuclei) can lead to extreme incoordination of complex purposeful movem ...
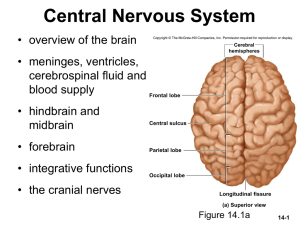
CNS Slide Show
... two thalami are joined medially by a narrow intermediate mass composed of at least 23 nuclei – we will consider five major functional groups the “gateway to the cerebral cortex” – nearly all input to the cerebrum passes by way of synapses in the thalamic nuclei, filters information on its way to cer ...
... two thalami are joined medially by a narrow intermediate mass composed of at least 23 nuclei – we will consider five major functional groups the “gateway to the cerebral cortex” – nearly all input to the cerebrum passes by way of synapses in the thalamic nuclei, filters information on its way to cer ...
What insights can fMRI offer into the structure and function of mid-tier visual areas?
... our understanding of just how distributed information processing is—would be far behind current levels without functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). In spite of the fact that fMRI provides only an indirect measure of neural responses (hemodynamic measures like blood flow and oxygenation are ...
... our understanding of just how distributed information processing is—would be far behind current levels without functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). In spite of the fact that fMRI provides only an indirect measure of neural responses (hemodynamic measures like blood flow and oxygenation are ...
Computational modeling of responses in human visual
... Furthermore, pRF parameters will depend on the specific population of neurons stimulated by the pattern that defines the texture within the moving bar. Features such as the temporal frequency, wavelength composition, and so on may excite different populations and influence the pRF parameters. The RF ...
... Furthermore, pRF parameters will depend on the specific population of neurons stimulated by the pattern that defines the texture within the moving bar. Features such as the temporal frequency, wavelength composition, and so on may excite different populations and influence the pRF parameters. The RF ...
Neural network activation during a stopsignal task discriminates
... Cocaine dependence is defined by a loss of inhibitory control over drug-use behaviors, mirrored by measurable impairments in laboratory tasks of inhibitory control. The current study tested the hypothesis that deficits in multiple subprocesses of behavioral control are associated with reliable neura ...
... Cocaine dependence is defined by a loss of inhibitory control over drug-use behaviors, mirrored by measurable impairments in laboratory tasks of inhibitory control. The current study tested the hypothesis that deficits in multiple subprocesses of behavioral control are associated with reliable neura ...
cortex
... association areas have rich callosal connections in keeping with their role to disperse their information to form widest associations of the primary sensory data. The primary sensory receptive areas represent their modalities in a strict, keyboard topography. The cerebrum must still interpret the sy ...
... association areas have rich callosal connections in keeping with their role to disperse their information to form widest associations of the primary sensory data. The primary sensory receptive areas represent their modalities in a strict, keyboard topography. The cerebrum must still interpret the sy ...
Category-specific Conceptual Processing of
... words (Preissl et al., 1995; Martin et al., 1996; Pulvermüller et al., 1999). Among the action words, those related to movements of the face, arm or leg activated fronto-central cortex in a somatotopic fashion (Hauk et al., 2004; Shtyrov et al., 2004), consistent with the claim that sensorimotor co ...
... words (Preissl et al., 1995; Martin et al., 1996; Pulvermüller et al., 1999). Among the action words, those related to movements of the face, arm or leg activated fronto-central cortex in a somatotopic fashion (Hauk et al., 2004; Shtyrov et al., 2004), consistent with the claim that sensorimotor co ...
Neuronal correlates of decision
... many cortical areas14–23 and is thus appropriately placed to integrate both bottom-up (sensory) and top-down (memory) information. Neurons in S2 show complex somatosensory responses24–27 and are known to be modulated by attention27. Based largely on S2’s pattern of connections with other cortical ar ...
... many cortical areas14–23 and is thus appropriately placed to integrate both bottom-up (sensory) and top-down (memory) information. Neurons in S2 show complex somatosensory responses24–27 and are known to be modulated by attention27. Based largely on S2’s pattern of connections with other cortical ar ...
Eagleman Ch 7. The Motor System
... somatosensory feedback helps guide movements. The intraparietal sulcus contains several areas that represent the location of objects in space in relation to different parts of the body. ...
... somatosensory feedback helps guide movements. The intraparietal sulcus contains several areas that represent the location of objects in space in relation to different parts of the body. ...
Executive functions

Executive functions (also known as cognitive control and supervisory attentional system) is an umbrella term for the management (regulation, control) of cognitive processes, including working memory, reasoning, task flexibility, and problem solving as well as planning and execution.The executive system is a theorized cognitive system in psychology that controls and manages other cognitive processes, such as executive functions. The prefrontal areas of the frontal lobe are necessary but not solely sufficient for carrying out these functions.