Question Bank Periodic Table and Periodic Properties
... nucleus of an atom. The outermost shell is far removed from the nucleus. Thus, the electrons are held very weakly in the outermost shell. These electrons can be easily donated by the atom to acquire a stable octet structure and hence it becomes more metallic in character. (i) What do you understand ...
... nucleus of an atom. The outermost shell is far removed from the nucleus. Thus, the electrons are held very weakly in the outermost shell. These electrons can be easily donated by the atom to acquire a stable octet structure and hence it becomes more metallic in character. (i) What do you understand ...
Particles and Periodic Table
... The amount of energy needed to change state from solid to liquid and from liquid to gas depends on the strength of the forces between the particles of the substance. The nature of the particles involved depends on the type of bonding and the structure of the substance. The stronger the forces betwee ...
... The amount of energy needed to change state from solid to liquid and from liquid to gas depends on the strength of the forces between the particles of the substance. The nature of the particles involved depends on the type of bonding and the structure of the substance. The stronger the forces betwee ...
Unit 3 Notes: Periodic Table Notes
... o Main block elements: These are the s‐ and p‐ sections of the periodic table (groups 1,2, 13‐18) o Transition elements: These are the elements in the d‐ and f‐blocks of the periodic table. The term “transition element”, while technically referring to the d‐ and f‐blocks, usually refers onl ...
... o Main block elements: These are the s‐ and p‐ sections of the periodic table (groups 1,2, 13‐18) o Transition elements: These are the elements in the d‐ and f‐blocks of the periodic table. The term “transition element”, while technically referring to the d‐ and f‐blocks, usually refers onl ...
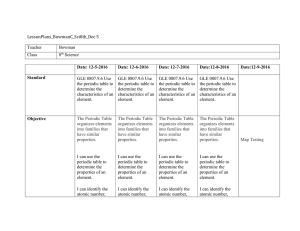
LessonPlans_BowmanC_Sci8th_Dec 5 Teacher Bowman Class 8th
... Group 5. Carbon Group 6. Nitrogen Group 7. Oxygen Group 8. Halogens 9. Noble Gases 10. Hydrogen ...
... Group 5. Carbon Group 6. Nitrogen Group 7. Oxygen Group 8. Halogens 9. Noble Gases 10. Hydrogen ...
Question (1): Explain `Dobereiner`s Triads and its drawback. Answer
... Answer: The amount of energy required to remove a loosely bound electron from the outermost shell of an isolated gaseous atom of an element is called its ionization potential. Question (18): The ionization potential of sodium is much lower than that of chlorine. Explain. Answer: The ionization poten ...
... Answer: The amount of energy required to remove a loosely bound electron from the outermost shell of an isolated gaseous atom of an element is called its ionization potential. Question (18): The ionization potential of sodium is much lower than that of chlorine. Explain. Answer: The ionization poten ...
TOPIC 12. THE ELEMENTS
... thousands of years gold, silver, copper, sulfur and carbon had been known because they do occur in the free form, although they were not necessarily recognised as elements - indeed the concept of an element as we know it today was not firmly established until the 18th century through the visionary w ...
... thousands of years gold, silver, copper, sulfur and carbon had been known because they do occur in the free form, although they were not necessarily recognised as elements - indeed the concept of an element as we know it today was not firmly established until the 18th century through the visionary w ...
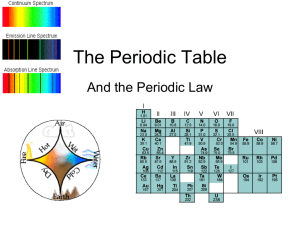
Periodic Table
... Periods and Blocks of the Periodic Table The f-block elements are wedged between Groups 3 and 4 in the sixth and seventh periods. Their position reflects the fact that they involve the filling of the 4f sublevel. The first row of the f block, the lanthanides, are shiny metals similar in reactivity ...
... Periods and Blocks of the Periodic Table The f-block elements are wedged between Groups 3 and 4 in the sixth and seventh periods. Their position reflects the fact that they involve the filling of the 4f sublevel. The first row of the f block, the lanthanides, are shiny metals similar in reactivity ...
Activity 2 Elements and Their Properties
... bodies different in form.” The first modern definition of element, which is not much different, is from Robert Boyle: “Bodies, which not being made of any other bodies, or of one another, are the ingredients of which all those . . . mixed bodies are . . . compounded.” Scientists now state that an el ...
... bodies different in form.” The first modern definition of element, which is not much different, is from Robert Boyle: “Bodies, which not being made of any other bodies, or of one another, are the ingredients of which all those . . . mixed bodies are . . . compounded.” Scientists now state that an el ...
The Periodic Table
... AR increase down a group as the electrons are added to higher energy levels and inner core electrons shields the valence electrons from the increased nuclear charge. AR decrease across a period as increased nuclear charge coupled with unchanging shielding by inner core electrons pulls the valence ...
... AR increase down a group as the electrons are added to higher energy levels and inner core electrons shields the valence electrons from the increased nuclear charge. AR decrease across a period as increased nuclear charge coupled with unchanging shielding by inner core electrons pulls the valence ...
Chapter 8 - Inorganic carbon chemistry
... a lump of limestone very strongly to convert it to calcium oxide. Water can then be carefully added dropwise to the calcium oxide. An exothermic reaction takes place as the water and calcium oxide react together in this slaking process to form calcium hydroxide. calcium oxide + water calcium hydro ...
... a lump of limestone very strongly to convert it to calcium oxide. Water can then be carefully added dropwise to the calcium oxide. An exothermic reaction takes place as the water and calcium oxide react together in this slaking process to form calcium hydroxide. calcium oxide + water calcium hydro ...
Chapter 3 Atoms and Elements
... Group 1A (1), the alkali metals, includes lithium, sodium, and potassium. Group 7A (17), the halogens, ...
... Group 1A (1), the alkali metals, includes lithium, sodium, and potassium. Group 7A (17), the halogens, ...
Ch. 5.1 History of the periodic table ppt.
... • In order for similar elements to line up, Mendeleev left gaps in his chart. • Mendeleev stated these were undiscovered elements. He made predictions about these undiscovered elements based on the other elements in the same row. – By 1886, these elements (scandium, gallium, and germanium) were disc ...
... • In order for similar elements to line up, Mendeleev left gaps in his chart. • Mendeleev stated these were undiscovered elements. He made predictions about these undiscovered elements based on the other elements in the same row. – By 1886, these elements (scandium, gallium, and germanium) were disc ...
chapter-5-periodic-classification-of-elements
... It was correct and useful as scandium, gallium and germanium, discovered later, have properties similar to Eka–boron, Eka–aluminium and Eka–silicon, respectively. 16. Write any one of the strength of Mendeléev’s Periodic Table. Answer: One of the strengths of Mendeléev’s Periodic Table was that, whe ...
... It was correct and useful as scandium, gallium and germanium, discovered later, have properties similar to Eka–boron, Eka–aluminium and Eka–silicon, respectively. 16. Write any one of the strength of Mendeléev’s Periodic Table. Answer: One of the strengths of Mendeléev’s Periodic Table was that, whe ...
periodic classification - cpprashanths Chemistry
... 3.Anomalous position of some pairs of elements:- Although the elements in the periodic table are arranged in increasing order of their atomic mass, in some cases elements with higher atomic mass is kept before the atom with lower atomic mass.Eg:- Co ( At.Mass 58.93 is placed before Ni(At Mass58.71) ...
... 3.Anomalous position of some pairs of elements:- Although the elements in the periodic table are arranged in increasing order of their atomic mass, in some cases elements with higher atomic mass is kept before the atom with lower atomic mass.Eg:- Co ( At.Mass 58.93 is placed before Ni(At Mass58.71) ...
The Periodic Table
... Who was ready, who was able to make a periodic table, Who was that chemist? Mendeleev! ...
... Who was ready, who was able to make a periodic table, Who was that chemist? Mendeleev! ...
periods - Madeira City Schools
... electrons that are more “unhappy” than the elements at the top of the periodic table. ¥ Elements at the bottom of the periodic table are larger (greater atomic radius, remember the trend!) because they have more energy levels. Those electrons in the outer energy levels are attracted to the nucleus. ...
... electrons that are more “unhappy” than the elements at the top of the periodic table. ¥ Elements at the bottom of the periodic table are larger (greater atomic radius, remember the trend!) because they have more energy levels. Those electrons in the outer energy levels are attracted to the nucleus. ...
File
... Describe a chemical test to show that the fat is unsaturated. name of reagent ................................................................................................................ result of test .............................................................................................. ...
... Describe a chemical test to show that the fat is unsaturated. name of reagent ................................................................................................................ result of test .............................................................................................. ...
(Periodic Trends) - stroh
... Discovered by boiling urine There are 2 forms: white and red The white forms combusts in air ...
... Discovered by boiling urine There are 2 forms: white and red The white forms combusts in air ...
Daily Inquiry: 10-31-2011
... • Every element had its own unique atomic number. • When Moseley arranged elements by increasing atomic number, the inconsistencies disappeared. ...
... • Every element had its own unique atomic number. • When Moseley arranged elements by increasing atomic number, the inconsistencies disappeared. ...
3. d-Block elements. Biological role, application in medicine.
... an element and decrease at transition from IA to IIA-group. The closeness of ionic radiuses of Li+, K+, Ba2+ plays an important role in the biochemistry of these metals. S-Block elements are characterized by small ionization energy at big radiuses of atoms and ions. Mainly s-elements form compounds ...
... an element and decrease at transition from IA to IIA-group. The closeness of ionic radiuses of Li+, K+, Ba2+ plays an important role in the biochemistry of these metals. S-Block elements are characterized by small ionization energy at big radiuses of atoms and ions. Mainly s-elements form compounds ...
biogenic s, p, d-block elements, biological role, application in medicine
... an element and decrease at transition from IA to IIA-group. The closeness of ionic radiuses of Li+, K+, Ba2+ plays an important role in the biochemistry of these metals. S-Block elements are characterized by small ionization energy at big radiuses of atoms and ions. Mainly s-elements form compounds ...
... an element and decrease at transition from IA to IIA-group. The closeness of ionic radiuses of Li+, K+, Ba2+ plays an important role in the biochemistry of these metals. S-Block elements are characterized by small ionization energy at big radiuses of atoms and ions. Mainly s-elements form compounds ...
Chemistry Transition Information
... 1) Calcium atoms reacts with chlorine atoms to form the ionic compound calcium chloride. Calcium atoms each lose two electrons to form calcium ions. Chlorine atoms each gain one electron to form chloride ions. This means that calcium atoms react with chlorine atoms in the ratio of one calcium atom f ...
... 1) Calcium atoms reacts with chlorine atoms to form the ionic compound calcium chloride. Calcium atoms each lose two electrons to form calcium ions. Chlorine atoms each gain one electron to form chloride ions. This means that calcium atoms react with chlorine atoms in the ratio of one calcium atom f ...
Chemical Periodicity
... 3 How is the modern periodic table different from the first periodic table? The first periodic table was in columns, not rows, only shows their atomic number. 4 What is the modern periodic law? Characteristics of the elements occur periodically when organized by atomic number. 5 Organization of ...
... 3 How is the modern periodic table different from the first periodic table? The first periodic table was in columns, not rows, only shows their atomic number. 4 What is the modern periodic law? Characteristics of the elements occur periodically when organized by atomic number. 5 Organization of ...
How can atomic theory explain patterns in the periodic table?
... source of chemical information 150 years later? Today, all of the elements that occur naturally have been discovered. Therefore, the discovery of new elements involves making them in laboratories and analyzing complex results to confirm their existence. Who decides when a new element has been made a ...
... source of chemical information 150 years later? Today, all of the elements that occur naturally have been discovered. Therefore, the discovery of new elements involves making them in laboratories and analyzing complex results to confirm their existence. Who decides when a new element has been made a ...
Experimental skills and abilities
... During the experiment the solution filtered steadily. White cubic crystals of sodium chloride were produced on slow crystallisation. ...
... During the experiment the solution filtered steadily. White cubic crystals of sodium chloride were produced on slow crystallisation. ...