Chemistry – 5071
... on the understanding and application of scientific concepts and principles. This approach has been adopted in recognition of the need of students to develop skills that will be of long term value in an increasing technological world rather than focusing on large quantities of actual material which m ...
... on the understanding and application of scientific concepts and principles. This approach has been adopted in recognition of the need of students to develop skills that will be of long term value in an increasing technological world rather than focusing on large quantities of actual material which m ...
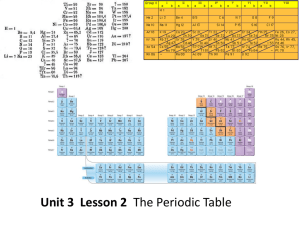
The Periodic Table
... By the year 1700, only a handful of elements had been identified and isolated. Several of these, such as copper and lead, had been known since ancient times. As scientific methods improved, the rate of discovery dramatically increased ( Figure 1.1). With the ever-increasing number of elements, chemi ...
... By the year 1700, only a handful of elements had been identified and isolated. Several of these, such as copper and lead, had been known since ancient times. As scientific methods improved, the rate of discovery dramatically increased ( Figure 1.1). With the ever-increasing number of elements, chemi ...
The Organization of the Elements
... The periodic table we use today is similar to the one developed by Mendeleev, but is not exactly the same. There are some important distinctions: His table did not include any of the noble gases, which were discovered later. These were added by Sir William Ramsay as Group 0, without any disturbance ...
... The periodic table we use today is similar to the one developed by Mendeleev, but is not exactly the same. There are some important distinctions: His table did not include any of the noble gases, which were discovered later. These were added by Sir William Ramsay as Group 0, without any disturbance ...
Section 2 Electron Configuration and the Periodic
... • In many compounds, the negative charge of the valence electrons is concentrated closer to one atom than to another. • Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons from another atom in the compound. • Electronegativities tend to increase acros ...
... • In many compounds, the negative charge of the valence electrons is concentrated closer to one atom than to another. • Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons from another atom in the compound. • Electronegativities tend to increase acros ...
The Periodic Table
... chemical properties. However, even with the use of placeholders, there were some elements that did not quite fit the pattern. For example, Mendeleev listed tellurium before iodine even though its atomic mass is higher, because he knew that the properties of iodine were much more similar to those of ...
... chemical properties. However, even with the use of placeholders, there were some elements that did not quite fit the pattern. For example, Mendeleev listed tellurium before iodine even though its atomic mass is higher, because he knew that the properties of iodine were much more similar to those of ...
Periodic Table ppt
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
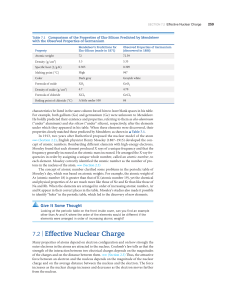
7.2 | Effective Nuclear Charge
... In molecules, the attractive interaction between any two adjacent atoms is what we recognize as a chemical bond. We discuss bonding in Chapters 8 and 9. For now, we need to realize that two bonded atoms are closer together than they would be in a nonbonding collision where the atoms ricochet apart. ...
... In molecules, the attractive interaction between any two adjacent atoms is what we recognize as a chemical bond. We discuss bonding in Chapters 8 and 9. For now, we need to realize that two bonded atoms are closer together than they would be in a nonbonding collision where the atoms ricochet apart. ...
60. Write the electron configuration for Zn
... Ionization energy – Amount of energy required to remove one electron 53. Why does atomic radius decrease as you go across a period? Atomic radius decreases because as you move left to right on the periodic table, the elements are all in the same quantum level but have increasing numbers of protons i ...
... Ionization energy – Amount of energy required to remove one electron 53. Why does atomic radius decrease as you go across a period? Atomic radius decreases because as you move left to right on the periodic table, the elements are all in the same quantum level but have increasing numbers of protons i ...
Spring Semester
... Ionization energy – Amount of energy required to remove one electron 64. Why does atomic radius decrease as you go across a period? Atomic radius decreases because as you move left to right on the periodic table, the elements are all in the same quantum level but have increasing numbers of protons i ...
... Ionization energy – Amount of energy required to remove one electron 64. Why does atomic radius decrease as you go across a period? Atomic radius decreases because as you move left to right on the periodic table, the elements are all in the same quantum level but have increasing numbers of protons i ...
Families and Periods of the Periodic Table - CK
... being the energy level involved. Each larger member of the family has its single s electron in the next larger principal energy level. As the atomic sizes in this family increase, the valence electrons are located further from the nucleus and are therefore easier to lose. Lithium reacts readily with ...
... being the energy level involved. Each larger member of the family has its single s electron in the next larger principal energy level. As the atomic sizes in this family increase, the valence electrons are located further from the nucleus and are therefore easier to lose. Lithium reacts readily with ...
C H A P T E R
... A horizontal row on the periodic table is called a period. Elements in the same period have the same number of occupied energy levels. For example, all elements in Period 2 have atoms whose electrons occupy two principal energy levels, including the 2s and 2p orbitals. Elements in Period 5 have oute ...
... A horizontal row on the periodic table is called a period. Elements in the same period have the same number of occupied energy levels. For example, all elements in Period 2 have atoms whose electrons occupy two principal energy levels, including the 2s and 2p orbitals. Elements in Period 5 have oute ...
The Periodic Table
... With the ever-increasing number of elements, chemists recognized that there may be some kind of systematic way to organize the elements. The question was: how? A logical way to begin to group elements together was by their chemical properties. In other words, putting elements in separate groups base ...
... With the ever-increasing number of elements, chemists recognized that there may be some kind of systematic way to organize the elements. The question was: how? A logical way to begin to group elements together was by their chemical properties. In other words, putting elements in separate groups base ...
Elements and the Periodic Table
... Organizing the Elements Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids Elements From Stardust ...
... Organizing the Elements Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids Elements From Stardust ...
periodic table
... How are the elements arranged on the periodic table? • Each vertical column of elements on the periodic table is called a group, or family. There are 18 groups. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. • Valence electrons are the electrons foun ...
... How are the elements arranged on the periodic table? • Each vertical column of elements on the periodic table is called a group, or family. There are 18 groups. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. • Valence electrons are the electrons foun ...
The Periodic Table
... a.The second ionization energy of sodium is about three times greater than the second ionization energy of magnesium. b.The difference between atomic radii of Na and K is relatively large compared to the difference between atomic radii of Rb and Cs. c.A sample of nickel chloride is attracted into a ma ...
... a.The second ionization energy of sodium is about three times greater than the second ionization energy of magnesium. b.The difference between atomic radii of Na and K is relatively large compared to the difference between atomic radii of Rb and Cs. c.A sample of nickel chloride is attracted into a ma ...
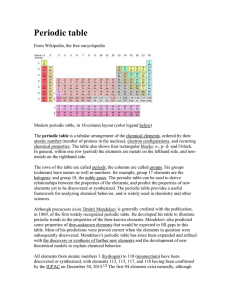
Periodic Table (Wiki)
... periodic trends in the properties of the then-known elements. Mendeleev also predicted some properties of then-unknown elements that would be expected to fill gaps in this table. Most of his predictions were proved correct when the elements in question were subsequently discovered. Mendeleev's perio ...
... periodic trends in the properties of the then-known elements. Mendeleev also predicted some properties of then-unknown elements that would be expected to fill gaps in this table. Most of his predictions were proved correct when the elements in question were subsequently discovered. Mendeleev's perio ...
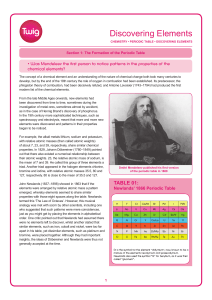
Discovering Elements
... • What patterns in the elements did Mendeleev use in his periodic table? Dmitri Mendeleev (1834–1927) published the first version of his periodic table in 1869. Like Newlands, he arranged the elements in order of their relative atomic masses, so that they fell into horizontal rows of similar elements ...
... • What patterns in the elements did Mendeleev use in his periodic table? Dmitri Mendeleev (1834–1927) published the first version of his periodic table in 1869. Like Newlands, he arranged the elements in order of their relative atomic masses, so that they fell into horizontal rows of similar elements ...
xi_chem_ch3_classification of elements
... 49. Elements from lanthanum (Z=57), Hafnium (Z=72) to mercury (Z=80) are called 5d transition series of elements or third transition series. 50. Fourteen elements from Cerium (Z=58) to Lutetium (Z=71) are called elements of inner transition series or lanthanoid series. 51. Fourteen elements from Tho ...
... 49. Elements from lanthanum (Z=57), Hafnium (Z=72) to mercury (Z=80) are called 5d transition series of elements or third transition series. 50. Fourteen elements from Cerium (Z=58) to Lutetium (Z=71) are called elements of inner transition series or lanthanoid series. 51. Fourteen elements from Tho ...
periodic table
... – An element is identified by its chemical symbol. – The number above the symbol is the atomic number – The number below the symbol is the rounded, weighted atomic mass of the element. – A row is called a period – A column is called a group or family ...
... – An element is identified by its chemical symbol. – The number above the symbol is the atomic number – The number below the symbol is the rounded, weighted atomic mass of the element. – A row is called a period – A column is called a group or family ...
School of Elements 1. - mt
... 3. The nuclear charge also increases but increase in number of shells dominates over increase in nuclear charge. So, atomic size increases down the group. Valency varies gradually across a period. 1. In the modern periodic table, the elements are arranged in increasing order of atomic number (Z). 2. ...
... 3. The nuclear charge also increases but increase in number of shells dominates over increase in nuclear charge. So, atomic size increases down the group. Valency varies gradually across a period. 1. In the modern periodic table, the elements are arranged in increasing order of atomic number (Z). 2. ...
Learning Outcomes
... (j) calculate stoichiometric reacting masses and volumes of gases (one mole of gas occupies 24 dm3 at room temperature and pressure); calculations involving the idea of limiting reactants may be set (Knowledge of the gas laws and the calculations of gaseous volumes at different temperatures and pres ...
... (j) calculate stoichiometric reacting masses and volumes of gases (one mole of gas occupies 24 dm3 at room temperature and pressure); calculations involving the idea of limiting reactants may be set (Knowledge of the gas laws and the calculations of gaseous volumes at different temperatures and pres ...
The Periodic Table and The Periodic Law
... Usually, solids at room temperature. Solid at room temperature (all but Hg) malleable- can be rolled or hammered into sheets ductile- can be made into wire high tensile strength- can resist breakage when pulled Lustrous – shiny most have silvery or grayish white luster ...
... Usually, solids at room temperature. Solid at room temperature (all but Hg) malleable- can be rolled or hammered into sheets ductile- can be made into wire high tensile strength- can resist breakage when pulled Lustrous – shiny most have silvery or grayish white luster ...
Table of Contents Chapter 5 Objectives Chapter 5 Mendeleev and
... has a positive or negative charge. • Sodium (Na), for example, easily loses an electron to form Na+. • Any process that results in the formation of an ion is referred to as ionization. • The energy required to remove one electron from a neutral atom of an element is the ionization ...
... has a positive or negative charge. • Sodium (Na), for example, easily loses an electron to form Na+. • Any process that results in the formation of an ion is referred to as ionization. • The energy required to remove one electron from a neutral atom of an element is the ionization ...