Red Brain, Blue Brain: Evaluative Processes Differ
... cues crucial for subjective feeling states and in signaling potential changes in interoceptive state to possible decision-related outcomes [10,11,19,20]. Further, intolerance of uncertainty is related to posterior insula functioning [11]. The ACC is involved in conflict and error monitoring and in a ...
... cues crucial for subjective feeling states and in signaling potential changes in interoceptive state to possible decision-related outcomes [10,11,19,20]. Further, intolerance of uncertainty is related to posterior insula functioning [11]. The ACC is involved in conflict and error monitoring and in a ...
Unit 2 - Monroe Community College
... Specialization of the Hemispheres in an Intact Brain ● perceptual asymmetries: left/right imbalances in the speed of visual or auditory processing - in normal people the input sent to one hemisphere is quickly shared with the other - but subtle differences can be detected by measuring how long it ta ...
... Specialization of the Hemispheres in an Intact Brain ● perceptual asymmetries: left/right imbalances in the speed of visual or auditory processing - in normal people the input sent to one hemisphere is quickly shared with the other - but subtle differences can be detected by measuring how long it ta ...
CNS
... 2- 4 mm thick • Below cortex is basal ganglia • Right and left hemisphere • Highly convoluted ...
... 2- 4 mm thick • Below cortex is basal ganglia • Right and left hemisphere • Highly convoluted ...
Chapter 9 --- Motivation and Emotion
... On his chart emotions next to each other are more alike those across are more different. His model also deals with intensity. Some challenge the universality of his model. May be too European. In some languages there are not words for various emotions. We have over 2000 words for emotions. Researche ...
... On his chart emotions next to each other are more alike those across are more different. His model also deals with intensity. Some challenge the universality of his model. May be too European. In some languages there are not words for various emotions. We have over 2000 words for emotions. Researche ...
presentation5
... Article focused on predicted area (motor), but the expertise effect activated other areas, some related to emotional experience Ventromedial frontal lobe Responds to pleasurable/rewarding stimuli & social judgement Parahippocampal gyrus Responds to meaningful rather than meaningless actions ...
... Article focused on predicted area (motor), but the expertise effect activated other areas, some related to emotional experience Ventromedial frontal lobe Responds to pleasurable/rewarding stimuli & social judgement Parahippocampal gyrus Responds to meaningful rather than meaningless actions ...
Age-related differences in brain activity underlying identification of
... It has been suggested (Phan et al., 2002) that the anterior cingulate and medial prefrontal cortex, together with their extensive connections to subcortical limbic structures, may represent an interaction zone between affect and cognition. ...
... It has been suggested (Phan et al., 2002) that the anterior cingulate and medial prefrontal cortex, together with their extensive connections to subcortical limbic structures, may represent an interaction zone between affect and cognition. ...
The Brain and Cranial Nerves The Brain
... Sulcus is the Primary Somesthetic Area • Sensory information from the entire body comes into this gyrus • The fraction of this gyrus that functions for any particular area of the body is an indication of how important that region is to sensory input ...
... Sulcus is the Primary Somesthetic Area • Sensory information from the entire body comes into this gyrus • The fraction of this gyrus that functions for any particular area of the body is an indication of how important that region is to sensory input ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 10-24
... a. Lateral ventricles b. Third ventricle c. Cerebral aqueduct d. Fourth ventricle e. Central canal Ventricles The fluid-filled (CSF, cerebrospinal fluid) spaces within the brain resulting from neural tube closure Delivers nutrients and removes wastes How do we tell one part from another? What do ...
... a. Lateral ventricles b. Third ventricle c. Cerebral aqueduct d. Fourth ventricle e. Central canal Ventricles The fluid-filled (CSF, cerebrospinal fluid) spaces within the brain resulting from neural tube closure Delivers nutrients and removes wastes How do we tell one part from another? What do ...
Behavioral Neuroscience
... The Sensory Cortex (parietal cortex) receives information from skin surface and sense organs. ...
... The Sensory Cortex (parietal cortex) receives information from skin surface and sense organs. ...
Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behavior
... – positron emission tomography magnetic resonance imaging Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) ...
... – positron emission tomography magnetic resonance imaging Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) ...
Nature 402
... other cerebral structures and itself. • The PFC is dedicated to the emotional behavior, memory, planning, execution of actions and temporal organization of behavior. ...
... other cerebral structures and itself. • The PFC is dedicated to the emotional behavior, memory, planning, execution of actions and temporal organization of behavior. ...
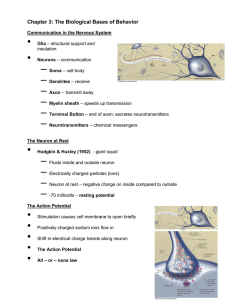
Unit 3 Biology of Behavior The Neuron Dendrites: Tree
... smell (olfaction) and taste (gustatory sense). The LEFT temporal lobe contains Wernicke's Area which control language comprehension and expression. Occipital Lobes: Contains the Primary Visual Cortex. Association Areas: Areas of the cortex not involved in sensory or motor functions. They are involve ...
... smell (olfaction) and taste (gustatory sense). The LEFT temporal lobe contains Wernicke's Area which control language comprehension and expression. Occipital Lobes: Contains the Primary Visual Cortex. Association Areas: Areas of the cortex not involved in sensory or motor functions. They are involve ...
NS Student Notes 2
... Prefrontal area = association area in frontal lobes that receives info from other association areas and uses this information to reason and plan our actions ...
... Prefrontal area = association area in frontal lobes that receives info from other association areas and uses this information to reason and plan our actions ...
The Nervous System allows communication
... o B. *cerebral palsy – refers to a group of nonprogressive neurological disorders that are the result of damage to the brain before, during , or just after birth or in early childhood. ...
... o B. *cerebral palsy – refers to a group of nonprogressive neurological disorders that are the result of damage to the brain before, during , or just after birth or in early childhood. ...
PSY 750 Attitudes and Emotions
... behaviors and measuring neural activity This approach has been informative but it is limited because researchers are forced to attribute affective states to animals based on their behaviors ...
... behaviors and measuring neural activity This approach has been informative but it is limited because researchers are forced to attribute affective states to animals based on their behaviors ...
Neuroscience 14c – The Limbic System and Drugs of Abuse
... Septum: lies beneath the rostral corpus callosum. Receives input from the amygdala, olfactory tract, hippocampus and brainstem. It projects onto the stria medularis thalami, hippocampus and hypothalamus. It is involved with reward and reinforcement of behaviours. The Papez circuit is a pathway of t ...
... Septum: lies beneath the rostral corpus callosum. Receives input from the amygdala, olfactory tract, hippocampus and brainstem. It projects onto the stria medularis thalami, hippocampus and hypothalamus. It is involved with reward and reinforcement of behaviours. The Papez circuit is a pathway of t ...
Somatic Sensory Systems
... in this part of the cortex are very complex, most require multi-sensory stimuli to be activated. Most of what we know about this part of the cortex comes from people that have had damage to this part of the brain. Damage to the posterior parietal cortex can cause a variety of deficits ranging from a ...
... in this part of the cortex are very complex, most require multi-sensory stimuli to be activated. Most of what we know about this part of the cortex comes from people that have had damage to this part of the brain. Damage to the posterior parietal cortex can cause a variety of deficits ranging from a ...
Unit 5: Study Guide Biological Bases of Behavior (Neuroscience)
... range of techniques scientists have used to learn about brain function, from procedures such as ablation, direct stimulation, EEG, CAT scans, PET scans, MRI, and fMRI. We also emphasize the brain’s role in the body’s nervous system, examining the anatomical and functional relationships of the centra ...
... range of techniques scientists have used to learn about brain function, from procedures such as ablation, direct stimulation, EEG, CAT scans, PET scans, MRI, and fMRI. We also emphasize the brain’s role in the body’s nervous system, examining the anatomical and functional relationships of the centra ...
Cognitive neuroscience
... necessary at a level much lower that today (resolution of neuroimage mechanisms deal with brain areas too large) • Using lesions and image techniques, Uttal considers that we cannot decompose a cognitive system in components that can be localized. ...
... necessary at a level much lower that today (resolution of neuroimage mechanisms deal with brain areas too large) • Using lesions and image techniques, Uttal considers that we cannot decompose a cognitive system in components that can be localized. ...
"The Hidden Mind" - Emotion, Memory and the Brain by
... eral nucleus can influence the central nucleus via the basolateral nucleus. The lateral nucleus can also influence the central nucleus by way of the accessory basal or basomedial nucleus. Clearly, ample opportunities exist for the lateral nucleus to communicate with the central nucleus once a stimul ...
... eral nucleus can influence the central nucleus via the basolateral nucleus. The lateral nucleus can also influence the central nucleus by way of the accessory basal or basomedial nucleus. Clearly, ample opportunities exist for the lateral nucleus to communicate with the central nucleus once a stimul ...
Nervous System - teacherver.com
... Association cortex/Association areas comprises 75% of the cerebral cortex integrates information among the other cortex + a damage to a specific part does not result in specific loss of a function (except for the language areas eg: Broca’s area which is involved in speech production Wernicke’ ...
... Association cortex/Association areas comprises 75% of the cerebral cortex integrates information among the other cortex + a damage to a specific part does not result in specific loss of a function (except for the language areas eg: Broca’s area which is involved in speech production Wernicke’ ...
Abstract Book Brain Circuits for Positive Emotions
... mood and arousal. However, while a growing body of neuroscience research has been able to reveal neural correlates of distinct musical emotions ranging from the basic (e.g. happy and sad) to the aesthetic (e.g. wonder and nostalgia), still elusive are insights into the dynamics of the communication ...
... mood and arousal. However, while a growing body of neuroscience research has been able to reveal neural correlates of distinct musical emotions ranging from the basic (e.g. happy and sad) to the aesthetic (e.g. wonder and nostalgia), still elusive are insights into the dynamics of the communication ...