level-e-maths-upper-primary-secondary
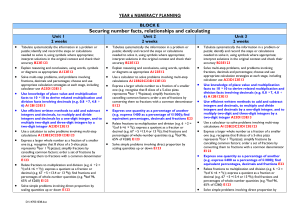
... Find simple fractions and percentages of whole number quantities (e.g. 3 quarters, 5 eighths, 25%, 60%, 10%) ...
... Find simple fractions and percentages of whole number quantities (e.g. 3 quarters, 5 eighths, 25%, 60%, 10%) ...
y6 block e plan - School
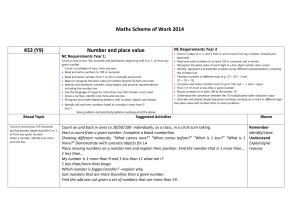
... decimal places, to multiply HTU U and TU TU, and to divide TU U find equivalent fractions understand percentage as the number of parts in every 100, and express tenths and hundredths as percentages use sequences to scale numbers up or down find simple fractions of percentages of quantities ...
... decimal places, to multiply HTU U and TU TU, and to divide TU U find equivalent fractions understand percentage as the number of parts in every 100, and express tenths and hundredths as percentages use sequences to scale numbers up or down find simple fractions of percentages of quantities ...
60-265-01
... Draw its block diagram showing only all the inputs and outputs. Show how an AND gate and an INVERTER can be used to convert the 4-bit binary counter to a divide-by-10 counter. (10 Marks) Q.4 a) An 8-bit register R contains the binary value 10011100. Determine the sequence of binary values in R in ea ...
... Draw its block diagram showing only all the inputs and outputs. Show how an AND gate and an INVERTER can be used to convert the 4-bit binary counter to a divide-by-10 counter. (10 Marks) Q.4 a) An 8-bit register R contains the binary value 10011100. Determine the sequence of binary values in R in ea ...
Integer Arithmetic
... • Multiply multiplicand by least significant multiplier digit + 0 or 1 ! no actual multiplication, add multiplicand or not • Add to total: we know how to do that • Shift multiplicand left, multiplier right by one digit CIS371 (Roth/Martin): Integer Arithmetic ...
... • Multiply multiplicand by least significant multiplier digit + 0 or 1 ! no actual multiplication, add multiplicand or not • Add to total: we know how to do that • Shift multiplicand left, multiplier right by one digit CIS371 (Roth/Martin): Integer Arithmetic ...
Chapter 3
... Finally, put on a coat of wax • What problem-solving methods can help you solve complex word problems? ...
... Finally, put on a coat of wax • What problem-solving methods can help you solve complex word problems? ...
grade 8 midterm
... Part I – 15 multiple choice questions – 2 pts. each. No partial credit Part II – 6 questions – 5 pts. each. Partial credit will be given Part III – 4 questions – 6 pts. each. Partial credit will be given Part IV – 2 questions – 8 pts. each. Partial credit will be given The exam will count as TWO tes ...
... Part I – 15 multiple choice questions – 2 pts. each. No partial credit Part II – 6 questions – 5 pts. each. Partial credit will be given Part III – 4 questions – 6 pts. each. Partial credit will be given Part IV – 2 questions – 8 pts. each. Partial credit will be given The exam will count as TWO tes ...
Let`s Do Algebra Tiles
... removing of all zero pairs. For each of the given examples, use algebra tiles to model the addition. ...
... removing of all zero pairs. For each of the given examples, use algebra tiles to model the addition. ...
maths-SOW-year-9 - Barbara Priestman Academy
... Count in multiples of twos, fives and tens Read and write numbers to 100 in numerals Read and write numbers from 1 to 20 in numerals and words Begin to recognise the place value of numbers beyond 20 (tens and ones) Identify and represent numbers using objects and pictorial representations in ...
... Count in multiples of twos, fives and tens Read and write numbers to 100 in numerals Read and write numbers from 1 to 20 in numerals and words Begin to recognise the place value of numbers beyond 20 (tens and ones) Identify and represent numbers using objects and pictorial representations in ...
Unit 1:Integers and divisibility
... Whole numbers greater than zero are called positive integers. These numbers are to the right of zero on the number line. Whole numbers less than zero are called negative integers. These numbers are to the left of zero on the number line. The integer zero is neutral. It is neither positive nor ...
... Whole numbers greater than zero are called positive integers. These numbers are to the right of zero on the number line. Whole numbers less than zero are called negative integers. These numbers are to the left of zero on the number line. The integer zero is neutral. It is neither positive nor ...
section 1.8 words into symbols
... 2.) SUBTRACTION – minus, difference, decreased by, less than 3.) MULTIPLICATION – product of, times, of 4.) DIVISION – divided by, quotient of 5.) EQUALS – is, is equal to, are, was, will be - use this to help you write an equation to represent the given sentence in terms of a variable. A.) WORD PRO ...
... 2.) SUBTRACTION – minus, difference, decreased by, less than 3.) MULTIPLICATION – product of, times, of 4.) DIVISION – divided by, quotient of 5.) EQUALS – is, is equal to, are, was, will be - use this to help you write an equation to represent the given sentence in terms of a variable. A.) WORD PRO ...
Honors Algebra 1 Summer Assignment Below is a list of vocabulary
... KhanAcademy.org. No problem should be left blank. Some attempt/answer is expected for each ...
... KhanAcademy.org. No problem should be left blank. Some attempt/answer is expected for each ...
Arithmetic

Arithmetic or arithmetics (from the Greek ἀριθμός arithmos, ""number"") is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics. It consists of the study of numbers, especially the properties of the traditional operations between them—addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Arithmetic is an elementary part of number theory, and number theory is considered to be one of the top-level divisions of modern mathematics, along with algebra, geometry, and analysis. The terms arithmetic and higher arithmetic were used until the beginning of the 20th century as synonyms for number theory and are sometimes still used to refer to a wider part of number theory.