Phase Five Maths Examples - Upton Heath C of E Primary School
... Shape A has been moved 3 squares right and 2 down. This movement is called TRANSLATION ...
... Shape A has been moved 3 squares right and 2 down. This movement is called TRANSLATION ...
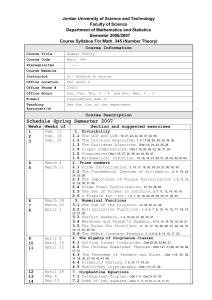
Weeks of - Jordan University of Science and Technology
... Chinese Remainder Theorem as well as the Fermat’s and Euler theorems and their applications. Learn the intuitive approach of the improper 10% integrals and techniques to evaluate such integrals. To prove a special case of Fermat's Last Theorem. ...
... Chinese Remainder Theorem as well as the Fermat’s and Euler theorems and their applications. Learn the intuitive approach of the improper 10% integrals and techniques to evaluate such integrals. To prove a special case of Fermat's Last Theorem. ...
Integers - C on T ech Math : : An application
... Subtraction of Integers To subtract an integer, add its opposite. Example: a = 7 - 10 Subtract +10 by adding (+) its opposite, -10 a = 7 + -10 a = -3 When you add a number’s opposite, the subtraction problem becomes an addition problem. ...
... Subtraction of Integers To subtract an integer, add its opposite. Example: a = 7 - 10 Subtract +10 by adding (+) its opposite, -10 a = 7 + -10 a = -3 When you add a number’s opposite, the subtraction problem becomes an addition problem. ...
Year 4
... initiative to support parents by providing them with information about how to do the calculations required in each class. Each year group is provided with information about what this looks like with visual reminders if you are not ...
... initiative to support parents by providing them with information about how to do the calculations required in each class. Each year group is provided with information about what this looks like with visual reminders if you are not ...
Math 1 – Basic Operations Part 1 NUMBER DEFINITIONS
... Exponents are shorthand for repeated multiplication of the same thing by itself. For instance, the shorthand for multiplying three copies of the number 5 is shown on the right-hand side of the "equals" sign in (5)(5)(5) = 53. The "exponent", being 3 in this example, stands for however many times the ...
... Exponents are shorthand for repeated multiplication of the same thing by itself. For instance, the shorthand for multiplying three copies of the number 5 is shown on the right-hand side of the "equals" sign in (5)(5)(5) = 53. The "exponent", being 3 in this example, stands for however many times the ...
Arithmetic

Arithmetic or arithmetics (from the Greek ἀριθμός arithmos, ""number"") is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics. It consists of the study of numbers, especially the properties of the traditional operations between them—addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Arithmetic is an elementary part of number theory, and number theory is considered to be one of the top-level divisions of modern mathematics, along with algebra, geometry, and analysis. The terms arithmetic and higher arithmetic were used until the beginning of the 20th century as synonyms for number theory and are sometimes still used to refer to a wider part of number theory.