SODA 6A1 - Teachinglinks.net
... 6. From the digit cards 6, 3, 5, 2 make a 2-digit square number 7. From the digit cards 6, 3, 5, 2 make a 2-digit multiple of 9 8. From the digit cards 6, 3, 5, 2 make a 2-digit factor of 64 9. Write a calculation to show the 6th square number 10. Draw a quadrilateral with 2 lines of symmetry Year 6 ...
... 6. From the digit cards 6, 3, 5, 2 make a 2-digit square number 7. From the digit cards 6, 3, 5, 2 make a 2-digit multiple of 9 8. From the digit cards 6, 3, 5, 2 make a 2-digit factor of 64 9. Write a calculation to show the 6th square number 10. Draw a quadrilateral with 2 lines of symmetry Year 6 ...
4.5 Complex Numbers
... This pattern of {i, −1, −i, 1} will continue for even higher patterns. A shortcut to evaluating higher powers requires you to memorize this pattern, but it is not necessary to evaluate them. ...
... This pattern of {i, −1, −i, 1} will continue for even higher patterns. A shortcut to evaluating higher powers requires you to memorize this pattern, but it is not necessary to evaluate them. ...
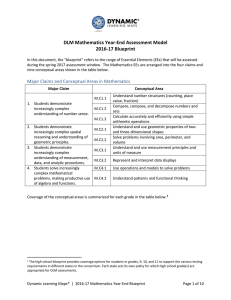
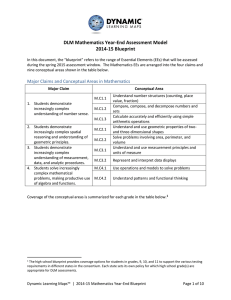
DLM Mathematics Year-End Assessment Model 2014-15 Blueprint
... Count by tens using models such as objects, base ten blocks, or money. Differentiate a fractional part from a whole. ...
... Count by tens using models such as objects, base ten blocks, or money. Differentiate a fractional part from a whole. ...
7.NS.2_11_28_12_formatted
... knowledge of addition and subtraction of integers (i.e. two color counters, arrows on a number line) to extend to division. Ability to use patterns and concrete models to devise a general rule for dividing. ...
... knowledge of addition and subtraction of integers (i.e. two color counters, arrows on a number line) to extend to division. Ability to use patterns and concrete models to devise a general rule for dividing. ...
RAFINARE IN PASI SUCCESIVI
... Without sorting these elements, and with the smallest number of swaps, arrange the elements such that all components smaller than a are placed before all elements larger than a. 2. Let us consider the natural number n and the vector X = (x[1], x[2], ... , x[m]) Remove all repeating values from X. 3. ...
... Without sorting these elements, and with the smallest number of swaps, arrange the elements such that all components smaller than a are placed before all elements larger than a. 2. Let us consider the natural number n and the vector X = (x[1], x[2], ... , x[m]) Remove all repeating values from X. 3. ...
Document
... Combining like Terms Terms: Variable expressions separated by a plus or minus sign. Like terms: Terms with the same variable(s) raised to the same power. Combine Like Terms: Add the the numbers the liked terms are being ...
... Combining like Terms Terms: Variable expressions separated by a plus or minus sign. Like terms: Terms with the same variable(s) raised to the same power. Combine Like Terms: Add the the numbers the liked terms are being ...
UNIT II Algebra 1 - Sections 2.2, 2.3, & 2.5
... Subtracting can be thought of as the “opposite of”. ...
... Subtracting can be thought of as the “opposite of”. ...
Exponents, Factors, and Fractions
... Repeating Decimal • If when we divide, we discover the same digit or group of digits in the quotient repeats without end, that decimal is a repeating decimal • Ex: 3/11 = 3 ÷ 11 = 0.272727… = 0.27 ...
... Repeating Decimal • If when we divide, we discover the same digit or group of digits in the quotient repeats without end, that decimal is a repeating decimal • Ex: 3/11 = 3 ÷ 11 = 0.272727… = 0.27 ...
3.OA.9 Task 1 - 3-5 Formative Instructional and Assessment Tasks
... numbers. We also know that every other column/row is even numbered because the even numbers are found counting by 2’s which skips one whole number each time. Adjacent columns cannot contain odd numbers because one of the columns is an even column (which contains only even numbers) and one is an odd ...
... numbers. We also know that every other column/row is even numbered because the even numbers are found counting by 2’s which skips one whole number each time. Adjacent columns cannot contain odd numbers because one of the columns is an even column (which contains only even numbers) and one is an odd ...
Arithmetic

Arithmetic or arithmetics (from the Greek ἀριθμός arithmos, ""number"") is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics. It consists of the study of numbers, especially the properties of the traditional operations between them—addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Arithmetic is an elementary part of number theory, and number theory is considered to be one of the top-level divisions of modern mathematics, along with algebra, geometry, and analysis. The terms arithmetic and higher arithmetic were used until the beginning of the 20th century as synonyms for number theory and are sometimes still used to refer to a wider part of number theory.