Early Filtrate Processing
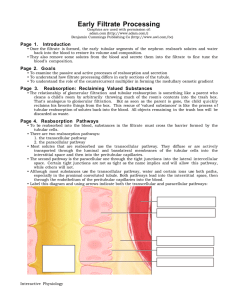
... increasing its concentration, while restricting the diffusion of water. • The interstitium surrounding the tubule becomes more concentrated, while the fluid inside becomes more dilute. • As the fluid moves up the loop there is progressively less solute to pump out, so the highest concentrations of s ...
... increasing its concentration, while restricting the diffusion of water. • The interstitium surrounding the tubule becomes more concentrated, while the fluid inside becomes more dilute. • As the fluid moves up the loop there is progressively less solute to pump out, so the highest concentrations of s ...
Genericity of confined chemical garden patterns with regard to
... of steep pH variations between the metallic salt and the alkaline solution. We have therefore investigated the possible role of the pH of the metallic salt solutions. Table 1 shows that the pH of CoCl2 solutions used in the reference diagram (Fig. 2A) varies by two units within the range of concentr ...
... of steep pH variations between the metallic salt and the alkaline solution. We have therefore investigated the possible role of the pH of the metallic salt solutions. Table 1 shows that the pH of CoCl2 solutions used in the reference diagram (Fig. 2A) varies by two units within the range of concentr ...
Transport Processes: Momentum, Heat, and Mass
... For example, the separation process distillation is used to purify or separate alcohol in the beverage industry and hydrocarbons in the petroleum industry. Drying of grain and other foods is similar to drying of lumber, filtered precipitates, and wool. The separation process absorption occurs in abs ...
... For example, the separation process distillation is used to purify or separate alcohol in the beverage industry and hydrocarbons in the petroleum industry. Drying of grain and other foods is similar to drying of lumber, filtered precipitates, and wool. The separation process absorption occurs in abs ...
Rheology and Viscoelastic Properties of Fluids
... We have to support our rheological results by using another techniques; such as NMR or Dynamic light scattering; in order to get more information about the main physical parameters; such as diffusion coefficients and relaxation times; that provide us with more accurate information about the internal ...
... We have to support our rheological results by using another techniques; such as NMR or Dynamic light scattering; in order to get more information about the main physical parameters; such as diffusion coefficients and relaxation times; that provide us with more accurate information about the internal ...
Chp-1. Pure substances
... phases i.e. steam and ice, and also it is almost freely available as gift of nature. Pure substance refers to the substance with chemical homogenecity and constant chemical composition. Water is a pure substance it meets both the above requirements. Any substance, if it undergoes a chemical reaction ...
... phases i.e. steam and ice, and also it is almost freely available as gift of nature. Pure substance refers to the substance with chemical homogenecity and constant chemical composition. Water is a pure substance it meets both the above requirements. Any substance, if it undergoes a chemical reaction ...
Nature of the anomalies in the supercooled liquid state of the mW
... linearly at 10 K/ns, the slowest rate that results in the vitrification of mW water. Liquid mW water can be equilibrated down to Ti at a cooling rate of 10 K/ns, but any property extracted from the quenching simulations at T < Ti may depend on the cooling rate. In the two-state thermodynamics, as gi ...
... linearly at 10 K/ns, the slowest rate that results in the vitrification of mW water. Liquid mW water can be equilibrated down to Ti at a cooling rate of 10 K/ns, but any property extracted from the quenching simulations at T < Ti may depend on the cooling rate. In the two-state thermodynamics, as gi ...
Effect of ultrasonic bath temperature on recovery rate of
... until sample preparation. Unless otherwise stated, all solvents were of HPLC grade. Ultrapure water was obtained by running demineralized water through a Milli-Q water purification system. All glass material was washed with Liqui-Nox soap and rinsed with ultrapure water, methanol and ethylenediamine ...
... until sample preparation. Unless otherwise stated, all solvents were of HPLC grade. Ultrapure water was obtained by running demineralized water through a Milli-Q water purification system. All glass material was washed with Liqui-Nox soap and rinsed with ultrapure water, methanol and ethylenediamine ...
Chapter 11 Absorption Air Conditioners
... Figure 8.2b Saturation properties of Lithium bromide and water (SI units) The mechanisms by which the absorption processes lead to refrigeration can be illustrated using Figure 8.2a. An absorption refrigeration system could be designed to use water as the refrigerant and to operate between an evapo ...
... Figure 8.2b Saturation properties of Lithium bromide and water (SI units) The mechanisms by which the absorption processes lead to refrigeration can be illustrated using Figure 8.2a. An absorption refrigeration system could be designed to use water as the refrigerant and to operate between an evapo ...
Performance Studies on Sub-cooling of Cryogenic Liquids Used for
... The curve with diamond marks in fig 6 is the case of finite heat transfer and instantaneous mass transfer. The curve with triangle marks is the case of instantaneous heat and mass transfer for comparison. This curve indicates the maximum sub cooling of Liquid Oxygen. The case of finite heat transfer ...
... The curve with diamond marks in fig 6 is the case of finite heat transfer and instantaneous mass transfer. The curve with triangle marks is the case of instantaneous heat and mass transfer for comparison. This curve indicates the maximum sub cooling of Liquid Oxygen. The case of finite heat transfer ...
Countercurrent exchange

Countercurrent exchange is a mechanism occurring in nature and mimicked in industry and engineering, in which there is a crossover of some property, usually heat or some component, between two flowing bodies flowing in opposite directions to each other. The flowing bodies can be liquids, gases, or even solid powders, or any combination of those. For example, in a distillation column, the vapors bubble up through the downward flowing liquid while exchanging both heat and mass.The maximum amount of heat or mass transfer that can be obtained is higher with countercurrent than co-current (parallel) exchange because countercurrent maintains a slowly declining difference or gradient (usually temperature or concentration difference). In cocurrent exchange the initial gradient is higher but falls off quickly, leading to wasted potential. For example, in the diagram at the right, the fluid being heated (exiting top) has a higher exiting temperature than the cooled fluid (exiting bottom) that was used for heating. With cocurrent or parallel exchange the heated and cooled fluids can only approach one another. The result is that countercurrent exchange can achieve a greater amount of heat or mass transfer than parallel under otherwise similar conditions. See: flow arrangement.Countercurrent exchange when set up in a circuit or loop can be used for building up concentrations, heat, or other properties of flowing liquids. Specifically when set up in a loop with a buffering liquid between the incoming and outgoing fluid running in a circuit, and with active transport pumps on the outgoing fluid's tubes, the system is called a Countercurrent multiplier, enabling a multiplied effect of many small pumps to gradually build up a large concentration in the buffer liquid.Other countercurrent exchange circuits where the incoming and outgoing fluids touch each other are used for retaining a high concentration of a dissolved substance or for retaining heat, or for allowing the external buildup of the heat or concentration at one point in the system.Countercurrent exchange circuits or loops are found extensively in nature, specifically in biologic systems. In vertebrates, they are called a Rete mirabile, originally the name of an organ in fish gills for absorbing oxygen from the water. It is mimicked in industrial systems. Countercurrent exchange is a key concept in chemical engineering thermodynamics and manufacturing processes, for example in extracting sucrose from sugar beet roots.Countercurrent multiplication is a similar but different concept where liquid moves in a loop followed by a long length of movement in opposite directions with an intermediate zone. The tube leading to the loop passively building up a gradient of heat (or cooling) or solvent concentration while the returning tube has a constant small pumping action all along it, so that a gradual intensification of the heat or concentration is created towards the loop. Countercurrent multiplication has been found in the kidneys as well as in many other biological organs.