Phylum Annelides (segmented worms) obrú čk av
... - secrete mucus to keep skin moist so oxygen will dissolve & diffuse into body Excretory system - long tubules called nephridia filter wastes from blood & excrete it through pores ...
... - secrete mucus to keep skin moist so oxygen will dissolve & diffuse into body Excretory system - long tubules called nephridia filter wastes from blood & excrete it through pores ...
Examination of Physiology Class_____ Name_____________
... Diffusion carried out by carrier protein is termed carrier mediated diffusion. Substances: glucose, amino acid. (2) Secondary active transport : Co-transport (symport): It means the movements of actively transported substances into cell along with sodium through the membrane in the same direction. E ...
... Diffusion carried out by carrier protein is termed carrier mediated diffusion. Substances: glucose, amino acid. (2) Secondary active transport : Co-transport (symport): It means the movements of actively transported substances into cell along with sodium through the membrane in the same direction. E ...
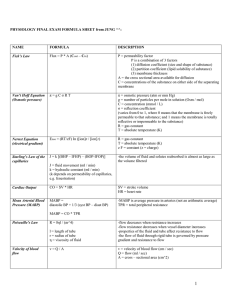
Cumulative Formula Sheet
... -hemoglobin that has released oxygen binds more readily to carbon dioxide than hemoglobin that has oxygen bound to it -in tissue capillaries, carbon dioxide combines with water inside RBCs to form carbonic acid which dissociates to form bicarbonate ions and hydrogen ions ...
... -hemoglobin that has released oxygen binds more readily to carbon dioxide than hemoglobin that has oxygen bound to it -in tissue capillaries, carbon dioxide combines with water inside RBCs to form carbonic acid which dissociates to form bicarbonate ions and hydrogen ions ...
Questions for entire chapter.
... What three factors stimulate renin secretion? In what ways does the composition of the glomerular filtrate differ from plasma? Approximately what percentage of plasma becomes ultrafiltrate during a single pass through the kidneys? Once a substance is filtered into Bowman’s space, what are the severa ...
... What three factors stimulate renin secretion? In what ways does the composition of the glomerular filtrate differ from plasma? Approximately what percentage of plasma becomes ultrafiltrate during a single pass through the kidneys? Once a substance is filtered into Bowman’s space, what are the severa ...
Document
... Sensors in the heart and blood vessels of the kidney signal cells in the glomerulus which secretes renin. Renin activates the plasma protein Angiotensin II which triggers the adrenal cortex to secrete Aldosterone. Aldosterone acts on distal tubule so that they reabsorb Na+ and promote the reabsorpti ...
... Sensors in the heart and blood vessels of the kidney signal cells in the glomerulus which secretes renin. Renin activates the plasma protein Angiotensin II which triggers the adrenal cortex to secrete Aldosterone. Aldosterone acts on distal tubule so that they reabsorb Na+ and promote the reabsorpti ...
AQA PHED 1 Applied Physiology Respiration cardiac Function
... Venous return mechanism Redistribution of blood/vascular shunting Arterio – venous oxygen difference (A-VO2 diff). Cardiac function Cardiac cycle Cardiac output, stroke volume and heart rate and the relationship between them. Heart rate range in response to exercise; hormonal and nervous effects on ...
... Venous return mechanism Redistribution of blood/vascular shunting Arterio – venous oxygen difference (A-VO2 diff). Cardiac function Cardiac cycle Cardiac output, stroke volume and heart rate and the relationship between them. Heart rate range in response to exercise; hormonal and nervous effects on ...
Organizational Overview of Thorax, Abdomen, Pelvis Introduction to
... Cardiovascular system includes pump (heart) and associated vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries) Blood carried within cardiovascular system usually grouped with “connective tissue”. Blood derived from cells in bone marrow, therefore (ultimately) from mesoderm ...
... Cardiovascular system includes pump (heart) and associated vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries) Blood carried within cardiovascular system usually grouped with “connective tissue”. Blood derived from cells in bone marrow, therefore (ultimately) from mesoderm ...
physiol mcq - WordPress.com
... unpressurised cabin of an aircraft at 20,000 feet. Atmospheric pressure falls by approximately 100mmHg for each 5000 feet ascent from sea level: a) cyanosis could present because the alveolar PO2 is decreased b) ventilation is increased because the PCO2 is decreased c) his oxygen utilisation coeffic ...
... unpressurised cabin of an aircraft at 20,000 feet. Atmospheric pressure falls by approximately 100mmHg for each 5000 feet ascent from sea level: a) cyanosis could present because the alveolar PO2 is decreased b) ventilation is increased because the PCO2 is decreased c) his oxygen utilisation coeffic ...
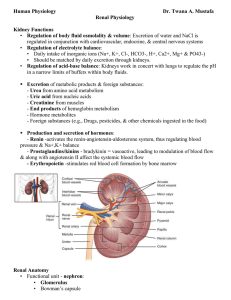
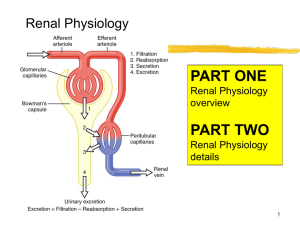
Renal Physiology
... • Solutes smaller than 180 nanometers in radius are freely filtered • Solutes greater than 360 nanometers do not • Solutes between 180 and 360 nm are filtered to various degrees • Serum albumin is anionic and has a 355 nm radius, only ~7 g is filtered per day (out of ~70 kg/day passing through glome ...
... • Solutes smaller than 180 nanometers in radius are freely filtered • Solutes greater than 360 nanometers do not • Solutes between 180 and 360 nm are filtered to various degrees • Serum albumin is anionic and has a 355 nm radius, only ~7 g is filtered per day (out of ~70 kg/day passing through glome ...
Glomerular Filtration
... Mechanisms of Urine Formation • The kidneys filter the body’s entire plasma volume 60 times each day. • The filtrate: – Contains all plasma components except protein – Loses water, nutrients, and essential ions to become urine • The urine contains metabolic wastes and unneeded substances ...
... Mechanisms of Urine Formation • The kidneys filter the body’s entire plasma volume 60 times each day. • The filtrate: – Contains all plasma components except protein – Loses water, nutrients, and essential ions to become urine • The urine contains metabolic wastes and unneeded substances ...
BDS Ist YEAR EXAMINATION 2008-09
... High quantity of Clc) Low amount of water Q.9 Plasma osmotic pressure is maintained to a d) High quantity of K+ large extent by: a) Globutea Q.4 Glucose and amino acids are absorbed from b) Fibrinogen proximalcixcoluted tubule mostly by: c) Albumin a) Primary actioe transport d) Immuno globulins b) ...
... High quantity of Clc) Low amount of water Q.9 Plasma osmotic pressure is maintained to a d) High quantity of K+ large extent by: a) Globutea Q.4 Glucose and amino acids are absorbed from b) Fibrinogen proximalcixcoluted tubule mostly by: c) Albumin a) Primary actioe transport d) Immuno globulins b) ...
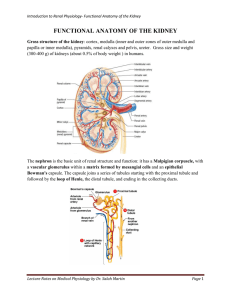
functional anatomy of the kidney
... are excreted. These solutes may be excreted in as little as 0.5 L/day or in as much as 12 L/day depending on water availability. The amount of solute excreted depends on diet (more when high protein-K rich diets that generate much urea, or highly salted foods, are eaten). The kidneys regulate volume ...
... are excreted. These solutes may be excreted in as little as 0.5 L/day or in as much as 12 L/day depending on water availability. The amount of solute excreted depends on diet (more when high protein-K rich diets that generate much urea, or highly salted foods, are eaten). The kidneys regulate volume ...
Lecture: Renal Physiology
... antidiuretic hormone (ADH) – causes increased permeability of collecting duct to water, resulting in more reabsorption (B.P. ??? ...
... antidiuretic hormone (ADH) – causes increased permeability of collecting duct to water, resulting in more reabsorption (B.P. ??? ...
Renal Physiology 1
... substances from it, and in a few cases, by adding substances to it. • Works with cardiovascular system (and others!) in integrated manner ...
... substances from it, and in a few cases, by adding substances to it. • Works with cardiovascular system (and others!) in integrated manner ...
13 Renal Clearance overview
... When a person is dehydrated and has low blood pressure, the hypothalamus will sense that the osmotic pressure of the plasma is too high (above homeostatic levels; plasma is too concentrated: too many electrolytes and not enough water is in the plasma), it tells the pituitary gland to release ADH ( ...
... When a person is dehydrated and has low blood pressure, the hypothalamus will sense that the osmotic pressure of the plasma is too high (above homeostatic levels; plasma is too concentrated: too many electrolytes and not enough water is in the plasma), it tells the pituitary gland to release ADH ( ...
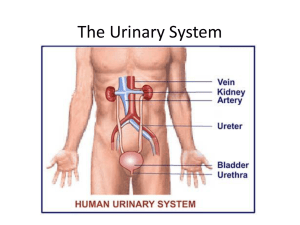
The Urinary System
... completely reabsorbed but the reabsorption of water and ions are regulated by hormones • Which hormone regulates the reabsorption of water by adjusting the permeability of the collecting ducts? ...
... completely reabsorbed but the reabsorption of water and ions are regulated by hormones • Which hormone regulates the reabsorption of water by adjusting the permeability of the collecting ducts? ...
Function of plasma proteins
... proteins play a special role in providing the body with immunity. 5- Fibrinogen other plasma proteins are concerned with blood clotting ...
... proteins play a special role in providing the body with immunity. 5- Fibrinogen other plasma proteins are concerned with blood clotting ...
Renal Physiology
... collecting tubule - urine from many nephron peritubular capillaries - "around" the "tubes" ...
... collecting tubule - urine from many nephron peritubular capillaries - "around" the "tubes" ...
Name
... the stomach is the DUODENUM. The coiled middle section is the ILEUM. A fan-like membrane called the MESENTERY holds the folds of the small intestine together. The SMALL INTESTINE receives bile from the LIVER and pancreatic enzymes (including trypsin) from the PANCREAS. Digestion is completed here an ...
... the stomach is the DUODENUM. The coiled middle section is the ILEUM. A fan-like membrane called the MESENTERY holds the folds of the small intestine together. The SMALL INTESTINE receives bile from the LIVER and pancreatic enzymes (including trypsin) from the PANCREAS. Digestion is completed here an ...
(Renal haemodynamic and GFR).
... Mechanisms of Urine Formation • The kidneys filter the body’s entire plasma volume 40 times each day. • The filtrate: – Contains all plasma components except protein – Loses water, nutrients, and essential ions to become urine • The urine contains metabolic wastes and unneeded substances ...
... Mechanisms of Urine Formation • The kidneys filter the body’s entire plasma volume 40 times each day. • The filtrate: – Contains all plasma components except protein – Loses water, nutrients, and essential ions to become urine • The urine contains metabolic wastes and unneeded substances ...
Body Fluids and Fluid Compartments
... 3. Maintaining electrolyte balance of the blood. 4. Ensuring proper blood pH. In healthy young adult, water probably is half or more of body weight—50 percent in females and about 60 percent in males. These differences reflect the fact that females have relatively less muscle and a larger amount of ...
... 3. Maintaining electrolyte balance of the blood. 4. Ensuring proper blood pH. In healthy young adult, water probably is half or more of body weight—50 percent in females and about 60 percent in males. These differences reflect the fact that females have relatively less muscle and a larger amount of ...
Respiratory Care Anatomy and Physiology, 3rd
... of substances excreted as urine (180 L of water is filtered, and 0.5–3.0 L is excreted). The filtered volume is reabsorbed into the blood unless it is present in amounts greater than normal. 5. Osmotic pressure in the efferent arterioles’ blood is much higher than in afferent arteriole blood because ...
... of substances excreted as urine (180 L of water is filtered, and 0.5–3.0 L is excreted). The filtered volume is reabsorbed into the blood unless it is present in amounts greater than normal. 5. Osmotic pressure in the efferent arterioles’ blood is much higher than in afferent arteriole blood because ...
The formation of urine
... (high pressure filter) then out through the efferent arteriole • Dissolved solutes (ex: ions, glucose, amino acids,urea) pass through the walls of the glomerulus into the Bowman’s capsule moving from highlow pressure • The following are too large to move through the walls of the glomerulus: plasma ...
... (high pressure filter) then out through the efferent arteriole • Dissolved solutes (ex: ions, glucose, amino acids,urea) pass through the walls of the glomerulus into the Bowman’s capsule moving from highlow pressure • The following are too large to move through the walls of the glomerulus: plasma ...