renal physiology tutorial discussion
... more permeable or less permeable than other capillaries. Give reason. ...
... more permeable or less permeable than other capillaries. Give reason. ...
Kidney 1
... There are two basic types of nephrons: cortical or superficial ones with short Loops of Henle, and juxtamedullary ones with loops that descend into the inner medulla. In humans, only about 15% of the nephrons are juxtamedullary ones. ...
... There are two basic types of nephrons: cortical or superficial ones with short Loops of Henle, and juxtamedullary ones with loops that descend into the inner medulla. In humans, only about 15% of the nephrons are juxtamedullary ones. ...
16 Renal Physo Overview Flashcards
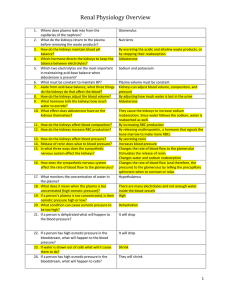
... 25. If the plasma if too dilute, is the osmotic pressure high or low? 26. What does it mean when plasma is too dilute? 27. What condition can cause low osmotic pressure? 28. If a person is over-hydrated what will it cause the blood pressure to do? 29. When plasma osmotic pressure is too low, what wi ...
... 25. If the plasma if too dilute, is the osmotic pressure high or low? 26. What does it mean when plasma is too dilute? 27. What condition can cause low osmotic pressure? 28. If a person is over-hydrated what will it cause the blood pressure to do? 29. When plasma osmotic pressure is too low, what wi ...
Exam 3 study guide Lecture 1 Animal Structure and Function Most
... Predicted that oxygen concentration only needs to be 71% of normal levels How about a spherical sea creature 1 cm wide? The oxygen concentration in the water would need to be 71 times normal levels to support a low metabolic rate Relationship between surface area and volume changes as a function of ...
... Predicted that oxygen concentration only needs to be 71% of normal levels How about a spherical sea creature 1 cm wide? The oxygen concentration in the water would need to be 71 times normal levels to support a low metabolic rate Relationship between surface area and volume changes as a function of ...
13a Renal Physo Overview Flashcards
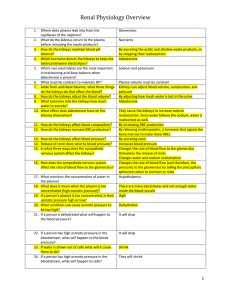
... 25. If the plasma if too dilute, is the osmotic pressure high or low? 26. What does it mean when plasma is too dilute? 27. What condition can cause low osmotic pressure? 28. If a person is over-hydrated what will it cause the blood pressure to do? 29. When plasma osmotic pressure is too low, what wi ...
... 25. If the plasma if too dilute, is the osmotic pressure high or low? 26. What does it mean when plasma is too dilute? 27. What condition can cause low osmotic pressure? 28. If a person is over-hydrated what will it cause the blood pressure to do? 29. When plasma osmotic pressure is too low, what wi ...
Animal Kingdom: Evolution and Diversity
... Projections into the intestinal lumen increase the surface area available for absorption Nutrient Absorption Passage of molecules into internal environment Occurs mainly in small intestine Various methods of absorption Osmosis, transport proteins, diffusion Absorption Mechanisms Mono ...
... Projections into the intestinal lumen increase the surface area available for absorption Nutrient Absorption Passage of molecules into internal environment Occurs mainly in small intestine Various methods of absorption Osmosis, transport proteins, diffusion Absorption Mechanisms Mono ...
Unit 8 * Organism Regulation, Physiology and Development
... external systems with lots of surface area exposed to aquatic environment ...
... external systems with lots of surface area exposed to aquatic environment ...
Renal3
... • Clearance = volume of plasma from which a substance is completely removed (cleared) by the kidneys per unit time. • Clearance of Inulin is 120 ml/min • Cinulin or Ccreatinine = Glomerular Filtration Rate • If C x is greater than GFR ( which is Cinulin) then that substance undergoes NET TUBULAR SE ...
... • Clearance = volume of plasma from which a substance is completely removed (cleared) by the kidneys per unit time. • Clearance of Inulin is 120 ml/min • Cinulin or Ccreatinine = Glomerular Filtration Rate • If C x is greater than GFR ( which is Cinulin) then that substance undergoes NET TUBULAR SE ...
zoology - IIT Portal.com
... Hybridoma technology is useful for large scale production of 1) Vaccines 2) Hormones 3) Monoclonal antibiotics 4) All types of enzymes ...
... Hybridoma technology is useful for large scale production of 1) Vaccines 2) Hormones 3) Monoclonal antibiotics 4) All types of enzymes ...
Urinary Physiology Urine Formation Urine Formation Glomerular
... – Transport maximum (Tm) reflects the number of carriers in the renal tubules available – When the carriers are saturated, excess of that substance is excreted – Example: too much glucose in the blood entering glomerulus will cause glucosuria ...
... – Transport maximum (Tm) reflects the number of carriers in the renal tubules available – When the carriers are saturated, excess of that substance is excreted – Example: too much glucose in the blood entering glomerulus will cause glucosuria ...
PHYLUM MOLLUSCA
... mollusks include • Mantle • ctendia - special gill which are also used for filter feeding • radula - rasping tongue-like structure used for scraping ...
... mollusks include • Mantle • ctendia - special gill which are also used for filter feeding • radula - rasping tongue-like structure used for scraping ...
Exam 3 study guide Lecture 1 Animal Structure and Function Most
... "Speed" of oxygen diffusion in liquid 1 µm in 10-4 seconds 1000 µm (1 mm) in 100 seconds Thus diffusion can supply oxygen only over very short distances Examples where oxygen diffuses only short distances Vertebrate lung Very small organisms How small does an organism have to be to rely on diffusion ...
... "Speed" of oxygen diffusion in liquid 1 µm in 10-4 seconds 1000 µm (1 mm) in 100 seconds Thus diffusion can supply oxygen only over very short distances Examples where oxygen diffuses only short distances Vertebrate lung Very small organisms How small does an organism have to be to rely on diffusion ...
Exam #3
... Surround the lungs b. Prevent Lungs from collapsing c. Pass oxygen to the blood d. Pass oxygen from the blood ...
... Surround the lungs b. Prevent Lungs from collapsing c. Pass oxygen to the blood d. Pass oxygen from the blood ...
Phylum/
... It is sometimes lined with flagellated cells to help stir the nutrients and distribute them No true circulatory system Oxygen diffuses directly from the water to the cells of the flatworm Carbon dioxide diffuses out of the cells ...
... It is sometimes lined with flagellated cells to help stir the nutrients and distribute them No true circulatory system Oxygen diffuses directly from the water to the cells of the flatworm Carbon dioxide diffuses out of the cells ...
Primary Exam Workshop
... b) is initially carried in vessels which do not contain smooth muscle valves c) is propelled primarily by skeletal muscle contraction d) is made up of interstitial macromolecules endocytosed by endothelial cells e) carries 80L of the total circulatory protein back to the circulation each day ...
... b) is initially carried in vessels which do not contain smooth muscle valves c) is propelled primarily by skeletal muscle contraction d) is made up of interstitial macromolecules endocytosed by endothelial cells e) carries 80L of the total circulatory protein back to the circulation each day ...
Cardiovascular Dynamics, part 1 File
... • Blood flow – Volume of blood flowing through a vessel, an organ, or the entire circulation in a given period • Measured as ml/min • Equivalent to cardiac output (CO) for entire vascular system • Relatively constant when at rest • Varies widely through individual organs, based on needs ...
... • Blood flow – Volume of blood flowing through a vessel, an organ, or the entire circulation in a given period • Measured as ml/min • Equivalent to cardiac output (CO) for entire vascular system • Relatively constant when at rest • Varies widely through individual organs, based on needs ...
Chapter 19
... 13. Identify the basic properties of red blood cells as well as the normal quantity and rate of production. RBC Anatomy 14. Note the structure and content of red blood cells, the presence of membrane antigens, and the usual concentrations of hemoglobin. RBC Physiology 15. Describe the structural fea ...
... 13. Identify the basic properties of red blood cells as well as the normal quantity and rate of production. RBC Anatomy 14. Note the structure and content of red blood cells, the presence of membrane antigens, and the usual concentrations of hemoglobin. RBC Physiology 15. Describe the structural fea ...
7- Introduction and functional anatomy of vascular physiology
... 1- The blood and lymph carry absorbed products of digestion to the liver. Then the blood transport of these substances which are essential for cellular metabolism. 2- The blood carries oxygen from the lungs to all the body cells. 3- Excrete metabolic waste products such as urea, excess water and ion ...
... 1- The blood and lymph carry absorbed products of digestion to the liver. Then the blood transport of these substances which are essential for cellular metabolism. 2- The blood carries oxygen from the lungs to all the body cells. 3- Excrete metabolic waste products such as urea, excess water and ion ...
Segmented Worms: Phylum Annelida EX: Earthworms
... d. If they do not stay moist, they will die D. Circulatory System a. closed circulatory system: runs through vessels b. blood travels from anterior to posterior end by ventral blood vessel c. blood travels from posterior to anterior end by a dorsal blood vessel. d. Aortic Arches( 5 hearts) 1. in the ...
... d. If they do not stay moist, they will die D. Circulatory System a. closed circulatory system: runs through vessels b. blood travels from anterior to posterior end by ventral blood vessel c. blood travels from posterior to anterior end by a dorsal blood vessel. d. Aortic Arches( 5 hearts) 1. in the ...
Download PDF
... aspects of the NDE have been reported by people who were fully conscious, and (2) hypoxic conditions give rise to mental states such as mental laziness, irritability, slowness of reasoning, and difficulty of remembering. These are contrary to the cognitive experiences regu ...
... aspects of the NDE have been reported by people who were fully conscious, and (2) hypoxic conditions give rise to mental states such as mental laziness, irritability, slowness of reasoning, and difficulty of remembering. These are contrary to the cognitive experiences regu ...
Physiology of urinary system
... The rate of glomerular filtration is a function of the - net filtration pressure, - the permeability of the filtration membrane, - the surface area available for filtration. The measured GFR reflects these factors, and the total number of functioning nephrons. Average GFR is 125 ml/min for a healthy ...
... The rate of glomerular filtration is a function of the - net filtration pressure, - the permeability of the filtration membrane, - the surface area available for filtration. The measured GFR reflects these factors, and the total number of functioning nephrons. Average GFR is 125 ml/min for a healthy ...
SChapter26
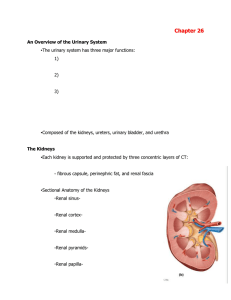
... loops of Henle extend deep into the medulla of the kidney. ▫The renal corpuscle contains the glomerular capsule and the glomerular capillaries -The outer wall of the capsule is lined by a simple squamous parietal epithelium, which is continuous with the visceral epithelium that covers the glomerular ...
... loops of Henle extend deep into the medulla of the kidney. ▫The renal corpuscle contains the glomerular capsule and the glomerular capillaries -The outer wall of the capsule is lined by a simple squamous parietal epithelium, which is continuous with the visceral epithelium that covers the glomerular ...
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions
... 2. a. The osmolarity of tubular fluid in Bowman's capsule is identical to its osmolarity the beginning of the descending thin limb of the loop of Henle. [Although a huge amount of solute is reabsorbed in the proximal tubule, its osmotic equivalent amount of water is also reabsorbed, changing the sol ...
... 2. a. The osmolarity of tubular fluid in Bowman's capsule is identical to its osmolarity the beginning of the descending thin limb of the loop of Henle. [Although a huge amount of solute is reabsorbed in the proximal tubule, its osmotic equivalent amount of water is also reabsorbed, changing the sol ...