BIO 202 Human Anatomy and Physiology II
... Saladin, Kenneth. Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function, 7th Edition. Boston: McGraw-Hill, 2015. Martin, Terry R. Laboratory Manual for Human Anatomy & Physiology: (Fetal Pig Version) 2nd Edition. Boston: McGraw-Hill, 2012. ...
... Saladin, Kenneth. Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function, 7th Edition. Boston: McGraw-Hill, 2015. Martin, Terry R. Laboratory Manual for Human Anatomy & Physiology: (Fetal Pig Version) 2nd Edition. Boston: McGraw-Hill, 2012. ...
segmented.ppt fall 2012
... Tube-within-a-tube digestive tract; opening at each end; metabolic wastes excreted through body wall ...
... Tube-within-a-tube digestive tract; opening at each end; metabolic wastes excreted through body wall ...
Respiratory Physiology
... Filtration is driven by Starling forces across the glomerular capillaries, and changes in these forces and in renal plasma flow alter the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) The glomerulus is more efficient than other capillary beds because: Its filtration membrane is significantly more permeable Glome ...
... Filtration is driven by Starling forces across the glomerular capillaries, and changes in these forces and in renal plasma flow alter the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) The glomerulus is more efficient than other capillary beds because: Its filtration membrane is significantly more permeable Glome ...
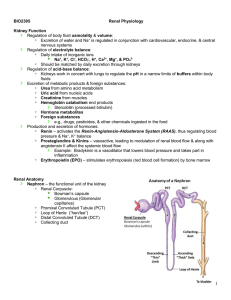
Renal Physiology
... The Transport Maximum - There is a limit to the amount of solute that the renal tubule can reabsorb because there are limited numbers of transport proteins in the plasma membranes. - If all the transporters are occupied as solute molecules pass through, some solute will remain in the tubular fluid ...
... The Transport Maximum - There is a limit to the amount of solute that the renal tubule can reabsorb because there are limited numbers of transport proteins in the plasma membranes. - If all the transporters are occupied as solute molecules pass through, some solute will remain in the tubular fluid ...
1-Acute Control of Local Blood Flow
... 2-Long-term control : means slow, controlled changes in flow over a period of days, weeks, or even months. Mechanism of Long-Term Regulation : 1-By decrease vascularity : if the metabolism is decreased. 2-Formation of new vessels(angiogenesis): deficiency of tissue oxygen or other nutrients, leads t ...
... 2-Long-term control : means slow, controlled changes in flow over a period of days, weeks, or even months. Mechanism of Long-Term Regulation : 1-By decrease vascularity : if the metabolism is decreased. 2-Formation of new vessels(angiogenesis): deficiency of tissue oxygen or other nutrients, leads t ...
Outline 3
... Internal body fluids; external fluids (i.e. Porifera) b) Movement of fluids through/within body cavity may occur instead of or in addition to movement within a “true” circulatory system. Circulatory systems (true) ...
... Internal body fluids; external fluids (i.e. Porifera) b) Movement of fluids through/within body cavity may occur instead of or in addition to movement within a “true” circulatory system. Circulatory systems (true) ...
Biology Lesson 1 Keeping Healthy Learning Objectives: In this
... Biology (6th ed.); EP Solomon, LR Berg & DW Martin; Thomas Learning Inc.; ...
... Biology (6th ed.); EP Solomon, LR Berg & DW Martin; Thomas Learning Inc.; ...
A quick summary: The skeletal system is made up of
... carry nutrients and drugs to the body. Both of these are absolutely vital. Our bodies need fuel to operate. We need the energy that we get from that fuel (carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, etc.) for the muscles to work, for the brain and nervous system to operate, and for all of the ...
... carry nutrients and drugs to the body. Both of these are absolutely vital. Our bodies need fuel to operate. We need the energy that we get from that fuel (carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, etc.) for the muscles to work, for the brain and nervous system to operate, and for all of the ...
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان
... excreted or held onto. The kidneys help maintain the blood PH mainly by excreting hydrogen ions and reabsorbing bicarbonate ions as needed. Removal of metabolic waste products and foreign substances from the plasma. One of the most important things the kidneys excrete is nitrogenous waste. As the li ...
... excreted or held onto. The kidneys help maintain the blood PH mainly by excreting hydrogen ions and reabsorbing bicarbonate ions as needed. Removal of metabolic waste products and foreign substances from the plasma. One of the most important things the kidneys excrete is nitrogenous waste. As the li ...
The Circulatory System
... • Arteries – carry oxygenated blood to the body • Veins – carry unoxygenated blood to the lungs • Capillaries – where O2 and CO2 change; connect arteries to veins. ...
... • Arteries – carry oxygenated blood to the body • Veins – carry unoxygenated blood to the lungs • Capillaries – where O2 and CO2 change; connect arteries to veins. ...
Physiological Correlates of the BOLD
... Water protons (spin 1/2) sense these field shifts which can be measured with the appropriate type of MRI. ...
... Water protons (spin 1/2) sense these field shifts which can be measured with the appropriate type of MRI. ...
1 THE PHYSIOLOGY OF COMPRESSED GAS DIVING Simon
... which ventilation is intentionally slowed or punctuated with short periods of apnoea is called "skip breathing". Net effects of respiratory alterations. Sustained work output by tissues is largely limited by their O2 supply. In normal exercise, tissue O2 supply is limited by cardiac output rather th ...
... which ventilation is intentionally slowed or punctuated with short periods of apnoea is called "skip breathing". Net effects of respiratory alterations. Sustained work output by tissues is largely limited by their O2 supply. In normal exercise, tissue O2 supply is limited by cardiac output rather th ...
Circulation Angina Hypertension Arrhythmias
... blood is thickened it moves more slowly than when it is very fluid and the pressure increases to push it around. * Irregularities in the surface of the blood vessels tend to slow down the flow, which increases the pressure. (Guyton 1982) There are two types of hypertension; primary and secondary. Ki ...
... blood is thickened it moves more slowly than when it is very fluid and the pressure increases to push it around. * Irregularities in the surface of the blood vessels tend to slow down the flow, which increases the pressure. (Guyton 1982) There are two types of hypertension; primary and secondary. Ki ...
Placenta - Academics
... 2. Heart rate 3. Mean arterial pressure 4. Systemic vascular resistance ...
... 2. Heart rate 3. Mean arterial pressure 4. Systemic vascular resistance ...
BSC1005 400 – Assignment I
... 3. Explain the structure of the plasma membrane. Include descriptions of the proteins present and the reason some substances pass through while others do not. 4. Give the relationship between the endoplasmic reticulum, the golgi apparatus and lysosomes. Detail the function of each one. 5. Describe t ...
... 3. Explain the structure of the plasma membrane. Include descriptions of the proteins present and the reason some substances pass through while others do not. 4. Give the relationship between the endoplasmic reticulum, the golgi apparatus and lysosomes. Detail the function of each one. 5. Describe t ...
The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels
... Flow, Pressure, and Resistance Blood flow (F) is directly proportional to the difference in blood pressure (P) between two points in the circulation and inversely proportional to the peripheral resistance (R) in the systemic flow. Therefore: F = DP R ...
... Flow, Pressure, and Resistance Blood flow (F) is directly proportional to the difference in blood pressure (P) between two points in the circulation and inversely proportional to the peripheral resistance (R) in the systemic flow. Therefore: F = DP R ...
Animal Form and Function – Intro Integumentary System
... environment in food via digestive system • digestion breaks down food into nutrient molecules + some energy returns to environment as feces – elimination of waste • nutrient molecules travel to body cells via circulatory system + convert to useful form (ATP) in cells - water and CO2 are excreted fro ...
... environment in food via digestive system • digestion breaks down food into nutrient molecules + some energy returns to environment as feces – elimination of waste • nutrient molecules travel to body cells via circulatory system + convert to useful form (ATP) in cells - water and CO2 are excreted fro ...
File
... • O2 and nutrients from the blood to tissues • CO2 and metabolic wastes from tissues to the blood • Lipid-soluble molecules diffuse directly through endothelial membranes • Water-soluble solutes pass through clefts and fenestrations • Larger molecules, such as proteins, are actively transported in p ...
... • O2 and nutrients from the blood to tissues • CO2 and metabolic wastes from tissues to the blood • Lipid-soluble molecules diffuse directly through endothelial membranes • Water-soluble solutes pass through clefts and fenestrations • Larger molecules, such as proteins, are actively transported in p ...
Chordates and Fishes - Fulton County Schools
... modified bone that grow from pockets of skin 2. Overlap like roof shingles, all pointing toward tail to minimize friction 3. Grow during entire life of fish 4. Scales grow quickly when food is abundant and slowly when scarce 5. Skin contains pigmented chromatophores-which create various color patter ...
... modified bone that grow from pockets of skin 2. Overlap like roof shingles, all pointing toward tail to minimize friction 3. Grow during entire life of fish 4. Scales grow quickly when food is abundant and slowly when scarce 5. Skin contains pigmented chromatophores-which create various color patter ...
Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... A. The substance is freely filtered but not reabsorbed B. The substance is freely filtered but part is reabsorbed C. The substance is freely filtered but not excreted because all is reabsorbed. D. The substance is freely filtered but is not reabsorbed but secreted from the peritubular capillaries i ...
... A. The substance is freely filtered but not reabsorbed B. The substance is freely filtered but part is reabsorbed C. The substance is freely filtered but not excreted because all is reabsorbed. D. The substance is freely filtered but is not reabsorbed but secreted from the peritubular capillaries i ...
Chapter 13 Invertebrates with Coeloms
... EYES. ***Insect eyes lack a focussing mechanism and each lightunit ‘sees’ only one dot of light…so, they can’t see very well, but sense movement well. • ANTENNAE - touch (and possibly low-light) sensitive organs • PITS - mechanical and chemical sensitive openings in the cuticle. • OPEN CICULATORY SY ...
... EYES. ***Insect eyes lack a focussing mechanism and each lightunit ‘sees’ only one dot of light…so, they can’t see very well, but sense movement well. • ANTENNAE - touch (and possibly low-light) sensitive organs • PITS - mechanical and chemical sensitive openings in the cuticle. • OPEN CICULATORY SY ...
Physiology د. نصير جواد المختار Lecture X: Acid – Base Balance The
... When the hydrostatic pressure increase, blood flow in the afferent arterioles also increase and this causes an increase in the rate of filtration. However, this usually doesn’t occur except for a fraction of a second, as in the wall of the afferent arterioles there are a certain receptors that are v ...
... When the hydrostatic pressure increase, blood flow in the afferent arterioles also increase and this causes an increase in the rate of filtration. However, this usually doesn’t occur except for a fraction of a second, as in the wall of the afferent arterioles there are a certain receptors that are v ...