STARS In your textbook, read about the properties of the Sun and
... 6. Stars on the main sequence produce energy by fusing hydrogen into----' 7. As a contracts, its rotation forces it into a disk shape with a hot condensed object at the center, which will become a new stsr. 8. During a the entire portion of the star is blown off in a massive explosion! What are Gala ...
... 6. Stars on the main sequence produce energy by fusing hydrogen into----' 7. As a contracts, its rotation forces it into a disk shape with a hot condensed object at the center, which will become a new stsr. 8. During a the entire portion of the star is blown off in a massive explosion! What are Gala ...
FSA school wide Science Olympiad 12/8/2007
... B. They are all objects for which the first detailed study was carried out by the Mauna Kea Observatory in Hawaii C. Objects which lie within 5 degrees on either side of the ecliptic, and are hence occulted by the moon at some time or the other. D. All of them lie in the Milky Way band of the sky (t ...
... B. They are all objects for which the first detailed study was carried out by the Mauna Kea Observatory in Hawaii C. Objects which lie within 5 degrees on either side of the ecliptic, and are hence occulted by the moon at some time or the other. D. All of them lie in the Milky Way band of the sky (t ...
Planetary Configurations
... certain kinds of stuff that can be crammed into a given space (particles with “personal space”). • When densities approach this limit, matter becomes “degenerate”. • Gas pressure depends on density only, and not temperature. ...
... certain kinds of stuff that can be crammed into a given space (particles with “personal space”). • When densities approach this limit, matter becomes “degenerate”. • Gas pressure depends on density only, and not temperature. ...
LT 5: I can describe how astronomers determine the composition
... All stars have dark-line spectra Because different elements absorb different wavelengths of light, scientists can determine the elements that make up a star by studying its spectrum ...
... All stars have dark-line spectra Because different elements absorb different wavelengths of light, scientists can determine the elements that make up a star by studying its spectrum ...
Scientists confirm most distant galaxy ever
... every year. The z8_GND_5296 galaxy converts hydrogen in the amount of 300 times the mass of our sun into new stars each year. By contrast, the Milky Way only produces stars at one or two solar masses per year. Scientists established through previous research that in the first billion years of the un ...
... every year. The z8_GND_5296 galaxy converts hydrogen in the amount of 300 times the mass of our sun into new stars each year. By contrast, the Milky Way only produces stars at one or two solar masses per year. Scientists established through previous research that in the first billion years of the un ...
Slide 1
... Scientists can tell the elements present in a star by looking at its light through a spectroscope. Each element will have its own unique spectral lines of color, just as people each have a unique ...
... Scientists can tell the elements present in a star by looking at its light through a spectroscope. Each element will have its own unique spectral lines of color, just as people each have a unique ...
astronomy - Mr. Barnard
... According to this flowchart, the Sun will become (1) hotter and dimmer in stage 2, then cooler and brighter in stage 3 (2) cooler and dimmer in stage 2, then hotter and brighter in stage 3 (3) hotter and brighter in stage 2, then cooler and dimmer in stage 3 (4) cooler and brighter in stage 2, then ...
... According to this flowchart, the Sun will become (1) hotter and dimmer in stage 2, then cooler and brighter in stage 3 (2) cooler and dimmer in stage 2, then hotter and brighter in stage 3 (3) hotter and brighter in stage 2, then cooler and dimmer in stage 3 (4) cooler and brighter in stage 2, then ...
Globular Cluster Formation in CDM Cosmologies
... primordial gas contains hydrogen and helium. Start with a small, cold, dark matter halo – about a million times mass of the Sun. Gas within it cools down to 200 K, (molecular hydrogen is the coolant) A 100 solar mass core forms inside a filamentary “molecular cloud” ...
... primordial gas contains hydrogen and helium. Start with a small, cold, dark matter halo – about a million times mass of the Sun. Gas within it cools down to 200 K, (molecular hydrogen is the coolant) A 100 solar mass core forms inside a filamentary “molecular cloud” ...
What is the net result of the proton-proton chain? a. 2 protons make
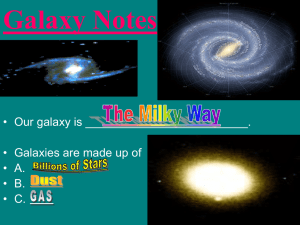
... c. Carbon dioxide d. Methane e. Ammonia Some regions of the Milky Way appear dark because: a. There are no stars there b. Stars in that direction are obscured by interstellar gas c. Stars in that direction are obscured by interstellar dust d. The magnetic field has directed the polarized light away ...
... c. Carbon dioxide d. Methane e. Ammonia Some regions of the Milky Way appear dark because: a. There are no stars there b. Stars in that direction are obscured by interstellar gas c. Stars in that direction are obscured by interstellar dust d. The magnetic field has directed the polarized light away ...
PHYSICS 015
... unimaginable. There would be room!) Overall, at this stage the average density is less than that of water. (It is higher in the centres of individual stars, of course, but not dramatically so.) ...
... unimaginable. There would be room!) Overall, at this stage the average density is less than that of water. (It is higher in the centres of individual stars, of course, but not dramatically so.) ...
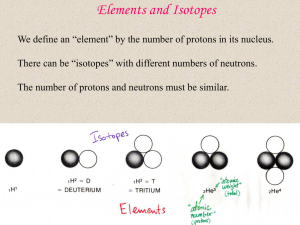
Elements and Isotopes - University of California, Berkeley
... inner 50% because the density is much higher. ...
... inner 50% because the density is much higher. ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... formed iron, no more reactions can occur, and the core violently collapses in on itself Supernova ...
... formed iron, no more reactions can occur, and the core violently collapses in on itself Supernova ...
Death of Low Mass Stars 8 Solar Masses or less
... reach at least 600 million K for C to ignite into heavier elements (mainly O). Low mass stars cannot do this. • Creation of a Planetary Nebula ...
... reach at least 600 million K for C to ignite into heavier elements (mainly O). Low mass stars cannot do this. • Creation of a Planetary Nebula ...
1. a) Astronomers use the parallax method to measure
... b) Instead of the parallax method, we use the standard candle method to measure the distance to stars in other galaxies. In particular, we use the standard candle method to measure the distances to Cepheid variable stars in other galaxies. What is special about Cepheid variable stars that makes them ...
... b) Instead of the parallax method, we use the standard candle method to measure the distance to stars in other galaxies. In particular, we use the standard candle method to measure the distances to Cepheid variable stars in other galaxies. What is special about Cepheid variable stars that makes them ...
galaxy phenomenology
... ‣ ~102-104 stars, irregular ‣ most younger than 1 Gyr, in disk ‣ most stars probably formed in open clusters, which have since dissolved ...
... ‣ ~102-104 stars, irregular ‣ most younger than 1 Gyr, in disk ‣ most stars probably formed in open clusters, which have since dissolved ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... The apparent magnitude of a star tells you how bright the star is as viewed from A nebula is a huge cloud of gas, primarily composed of hydrogen A nebula becomes a star when _______fusion takes place______________ Our sun is what color ? _____________yellow____________________ ...
... The apparent magnitude of a star tells you how bright the star is as viewed from A nebula is a huge cloud of gas, primarily composed of hydrogen A nebula becomes a star when _______fusion takes place______________ Our sun is what color ? _____________yellow____________________ ...
Big Bang Theory Scientific origin of the Universe
... pitch as the train passes by and recedes. The effect arises because the sound waves arrive at the listener's ear closer together as the source approaches, and further apart as it recedes. ...
... pitch as the train passes by and recedes. The effect arises because the sound waves arrive at the listener's ear closer together as the source approaches, and further apart as it recedes. ...
Name: Notes – #45 The Diverse Sizes of Stars 1. A Hertzsprung
... of energy stars emit is proportional to their surface temperature to the ______ power. 4. A star that is twice as hot as another star with the same surface area emits ______ times more energy per second. 5. What is the equation for the luminosity of a star? 6. Super giants tend to have surface tempe ...
... of energy stars emit is proportional to their surface temperature to the ______ power. 4. A star that is twice as hot as another star with the same surface area emits ______ times more energy per second. 5. What is the equation for the luminosity of a star? 6. Super giants tend to have surface tempe ...
less than 1 million years
... 7. In the newly formed star, the heat from _________ causes pressure to increase. This pressure balances the attraction due to ________. The star becomes a main sequence star. It continues to use its __________ fuel. 8. When __________ in the core of the star is depleted, a balance no longer exists ...
... 7. In the newly formed star, the heat from _________ causes pressure to increase. This pressure balances the attraction due to ________. The star becomes a main sequence star. It continues to use its __________ fuel. 8. When __________ in the core of the star is depleted, a balance no longer exists ...
November | Activity of the Month
... Part I: A ‘speed of light’ trip through the Universe 1. It’s a big place out there so to see a lot we need to go fast. The fastest thing in the universe is light – it travels at 299,792 kilometres every second. Light is so fast that it takes only 8 minutes to get from the Sun to us. The same distan ...
... Part I: A ‘speed of light’ trip through the Universe 1. It’s a big place out there so to see a lot we need to go fast. The fastest thing in the universe is light – it travels at 299,792 kilometres every second. Light is so fast that it takes only 8 minutes to get from the Sun to us. The same distan ...
H II region

An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. The first known H II region was the Orion Nebula, which was discovered in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc.H II regions are named for the large amount of ionised atomic hydrogen they contain, referred to as H II, pronounced H-two by astronomers (an H I region being neutral atomic hydrogen, and H2 being molecular hydrogen). Such regions have extremely diverse shapes, because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing bizarre shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regions may give birth to thousands of stars over a period of several million years. In the end, supernova explosions and strong stellar winds from the most massive stars in the resulting star cluster will disperse the gases of the H II region, leaving behind a cluster of birthed stars such as the Pleiades.H II regions can be seen to considerable distances in the universe, and the study of extragalactic H II regions is important in determining the distance and chemical composition of other galaxies. Spiral and irregular galaxies contain many H II regions, while elliptical galaxies are almost devoid of them. In the spiral galaxies, including the Milky Way, H II regions are concentrated in the spiral arms, while in the irregular galaxies they are distributed chaotically. Some galaxies contain huge H II regions, which may contain tens of thousands of stars. Examples include the 30 Doradus region in the Large Magellanic Cloud and NGC 604 in the Triangulum Galaxy.