Star Life Cycle Web Quiz
... What happens initially (right after it runs out of fuel) to the core temperature AND the gas pressure of a star when it runs out of hydrogen fuel for its fusion reactions? Circle the best answer choice for each. The core temperature ( increases / decreases ) and the gas pressure ( increases / decrea ...
... What happens initially (right after it runs out of fuel) to the core temperature AND the gas pressure of a star when it runs out of hydrogen fuel for its fusion reactions? Circle the best answer choice for each. The core temperature ( increases / decreases ) and the gas pressure ( increases / decrea ...
Star Life Cycle and classroom textbooks for research!
... What phase in the life cycle of a star is our sun in right now? What is the next phase of our sun’s life cycle? How long will it be before our sun becomes this type of star? How long (in years) is the typical lifetime of a star? Where are the blue stars in the HR diagram? Where are the red stars in ...
... What phase in the life cycle of a star is our sun in right now? What is the next phase of our sun’s life cycle? How long will it be before our sun becomes this type of star? How long (in years) is the typical lifetime of a star? Where are the blue stars in the HR diagram? Where are the red stars in ...
Stars are classified by how hot they are (temperature)
... Spectrograph – an instrument used by astronomers to spread starlight out into its colors (similar to a prism) Stars are made of various gases that produce different spectrum of light ...
... Spectrograph – an instrument used by astronomers to spread starlight out into its colors (similar to a prism) Stars are made of various gases that produce different spectrum of light ...
Untitled
... a faint, fuzzy blob of light in the constellation (star group) Dorado. When seen through a telescope, however, the Tarantula Nebula looks like a swirling mass of red and green gases. Its shape resembles a tarantula, a large hairy spider. A light-year is the distance light travels in one year. Light ...
... a faint, fuzzy blob of light in the constellation (star group) Dorado. When seen through a telescope, however, the Tarantula Nebula looks like a swirling mass of red and green gases. Its shape resembles a tarantula, a large hairy spider. A light-year is the distance light travels in one year. Light ...
PowerPoint - Chandra X
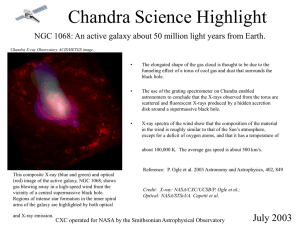
... The use of the grating spectrometer on Chandra enabled astronomers to conclude that the X-rays observed from the torus are scattered and fluorescent X-rays produced by a hidden accretion disk around a supermassive black hole. ...
... The use of the grating spectrometer on Chandra enabled astronomers to conclude that the X-rays observed from the torus are scattered and fluorescent X-rays produced by a hidden accretion disk around a supermassive black hole. ...
COSMOLOGY 1 An Introduction to the Universe
... striking "planetary nebula", much like the nebulae seen around the remnants of other stars. The carbon core will eventually cool and become a white dwarf, the dense dim remnant of a once bright star. ...
... striking "planetary nebula", much like the nebulae seen around the remnants of other stars. The carbon core will eventually cool and become a white dwarf, the dense dim remnant of a once bright star. ...
To the Stars - LBlackwell
... At night, all the stars that you can see are part of our home galaxy; the Milky Way galaxy. A galaxy is a collection of hundreds of billions of stars held together by gravity. The Hubble Space telescope is able to take pictures of galaxies other than our own. All of these galaxies are moving away fr ...
... At night, all the stars that you can see are part of our home galaxy; the Milky Way galaxy. A galaxy is a collection of hundreds of billions of stars held together by gravity. The Hubble Space telescope is able to take pictures of galaxies other than our own. All of these galaxies are moving away fr ...
Exploring the Universe
... collapses because the forces are no longer balanced 2. Core collapses because of its own gravity & then rebounds with a shock wave that violently blows the star’s outer layers away from the core ...
... collapses because the forces are no longer balanced 2. Core collapses because of its own gravity & then rebounds with a shock wave that violently blows the star’s outer layers away from the core ...
ppt
... If same luminosity, this means that they are about 300,000 times further away (i.e. 300,000 AU, or about 5 light years). ...
... If same luminosity, this means that they are about 300,000 times further away (i.e. 300,000 AU, or about 5 light years). ...
22 Stellar Remnant/HR Diagram
... Assigned a letter in alphabetical order from complex looking to simple looking (A-Q) Later they figured out that these lines were absorption lines corresponding to different elements Re-ordered according to which elements were strong (usually H): OBAFGKM was born! ...
... Assigned a letter in alphabetical order from complex looking to simple looking (A-Q) Later they figured out that these lines were absorption lines corresponding to different elements Re-ordered according to which elements were strong (usually H): OBAFGKM was born! ...
Day-6
... All halo stars have some heavy elements, so at least one prior generation of stars must have existed. Halo objects were formed before interstellar gas was all concentrated into the disk. Later star formation was all in the disk. ...
... All halo stars have some heavy elements, so at least one prior generation of stars must have existed. Halo objects were formed before interstellar gas was all concentrated into the disk. Later star formation was all in the disk. ...
History of the Universe and Solar System
... gravitational force. Dark energy is calculated to be ¾ of the massenergy of the universe!) The present velocities give the appearance that the galaxies have been traveling longer than they actually have. Thus the estimates of 14-18 BY, with 14 BY being the current choice of most physicists/astronome ...
... gravitational force. Dark energy is calculated to be ¾ of the massenergy of the universe!) The present velocities give the appearance that the galaxies have been traveling longer than they actually have. Thus the estimates of 14-18 BY, with 14 BY being the current choice of most physicists/astronome ...
Galaxies
... • There are 200 billion stars in the Milky Way. • Stars, gas, and dust are considered visible matter. • We can also estimate the mass in black holes. • The visible mass does not explain the orbits of stars in the galaxy. • The apparent mass is much larger (10 times). ...
... • There are 200 billion stars in the Milky Way. • Stars, gas, and dust are considered visible matter. • We can also estimate the mass in black holes. • The visible mass does not explain the orbits of stars in the galaxy. • The apparent mass is much larger (10 times). ...
Lecture 10: Stars
... Spacetime & Gravity (Black Holes) & First Mid-Term Exam in class today (9:50am) -- 50 minutes & Observatory #3 was last night & Homework #4 due on in class on Tues & Fiske Planetarium next Thur (20 Feb) on “Black Holes: Other Side of Inifinity” ...
... Spacetime & Gravity (Black Holes) & First Mid-Term Exam in class today (9:50am) -- 50 minutes & Observatory #3 was last night & Homework #4 due on in class on Tues & Fiske Planetarium next Thur (20 Feb) on “Black Holes: Other Side of Inifinity” ...
Constellation, Star, and Deep Sky Object
... Pulsar – supernova remnant ≈ 20 miles across with mass of 2-3 times our sun and composed completely of neutrons (neutron star) Black Hole – supernova remnant where ≥ 3-4 solar masses are compressed into infinitely small space, gravity around it is so intense that not even light can escape the gravit ...
... Pulsar – supernova remnant ≈ 20 miles across with mass of 2-3 times our sun and composed completely of neutrons (neutron star) Black Hole – supernova remnant where ≥ 3-4 solar masses are compressed into infinitely small space, gravity around it is so intense that not even light can escape the gravit ...
File - Physical Science
... There are billions of solar systems in our galaxy and billions of galaxies in the known universe! ...
... There are billions of solar systems in our galaxy and billions of galaxies in the known universe! ...
Watching Galaxies Form Near the Beginning of Time
... • Galaxy spectra show a cutoff at 912 A due to absorption by neutral hydrogen • This allows a straightforward multicolor selection (blue in two bands, missing shortward of that) • Thousands of galaxies at z>2.7 have now been found in this way ...
... • Galaxy spectra show a cutoff at 912 A due to absorption by neutral hydrogen • This allows a straightforward multicolor selection (blue in two bands, missing shortward of that) • Thousands of galaxies at z>2.7 have now been found in this way ...
Chapter 25 - Notes Super Size
... • Large group of stars, gas, and dust held together by _________________. -_________________ Galaxies- they have spiral arms that wind outward from the center. They can be normal or barred. -Elliptical Galaxies- common type of galaxy that are oval or_________________shaped. -Irregular Galaxies- ____ ...
... • Large group of stars, gas, and dust held together by _________________. -_________________ Galaxies- they have spiral arms that wind outward from the center. They can be normal or barred. -Elliptical Galaxies- common type of galaxy that are oval or_________________shaped. -Irregular Galaxies- ____ ...
Homework, November 16, 2006 AST110-6
... how many stars have Earth-like planets, nor do we know the likelihood that such planets might harbor advanced civilizations like our own. However, some stars can probably be ruled out as candidates for advanced civilizations. For example, given that it took a few billion years for humans to evolve o ...
... how many stars have Earth-like planets, nor do we know the likelihood that such planets might harbor advanced civilizations like our own. However, some stars can probably be ruled out as candidates for advanced civilizations. For example, given that it took a few billion years for humans to evolve o ...
Stars & Galaxies
... held together by gravity. Probably 50 billion galaxies with 50 billion stars in each Our galaxy is the spiraled Milky Way Galaxies can be elliptical, irregular, and spiral ...
... held together by gravity. Probably 50 billion galaxies with 50 billion stars in each Our galaxy is the spiraled Milky Way Galaxies can be elliptical, irregular, and spiral ...
Chapter 3: Elements and the Periodic Table
... produce elements heavier than oxygen • Eventually, shrinks and its elements blow away o Forms a nebula – cloudlike region of gases. ...
... produce elements heavier than oxygen • Eventually, shrinks and its elements blow away o Forms a nebula – cloudlike region of gases. ...
H II region

An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. The first known H II region was the Orion Nebula, which was discovered in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc.H II regions are named for the large amount of ionised atomic hydrogen they contain, referred to as H II, pronounced H-two by astronomers (an H I region being neutral atomic hydrogen, and H2 being molecular hydrogen). Such regions have extremely diverse shapes, because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing bizarre shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regions may give birth to thousands of stars over a period of several million years. In the end, supernova explosions and strong stellar winds from the most massive stars in the resulting star cluster will disperse the gases of the H II region, leaving behind a cluster of birthed stars such as the Pleiades.H II regions can be seen to considerable distances in the universe, and the study of extragalactic H II regions is important in determining the distance and chemical composition of other galaxies. Spiral and irregular galaxies contain many H II regions, while elliptical galaxies are almost devoid of them. In the spiral galaxies, including the Milky Way, H II regions are concentrated in the spiral arms, while in the irregular galaxies they are distributed chaotically. Some galaxies contain huge H II regions, which may contain tens of thousands of stars. Examples include the 30 Doradus region in the Large Magellanic Cloud and NGC 604 in the Triangulum Galaxy.