A Star is Born!
... • Giant molecular clouds: consist of mostly H2 plus a small amount of other, more complex molecules ...
... • Giant molecular clouds: consist of mostly H2 plus a small amount of other, more complex molecules ...
Unit 12 Guide: Concepts of Earth Science Stars, Galaxies, and the
... Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast the apparent and actual motion of stars. How can scientists know if a star or galaxy is moving toward ...
... Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast the apparent and actual motion of stars. How can scientists know if a star or galaxy is moving toward ...
Chapter 28.3 Topic questions
... 11. Red Super Giant stars have surface temperatures that are cooler than our earth, so why do they have greater luminosity than the sun? 12. The H-R diagram also includes which stars that are near the end of their life, what are these stars called? 13. A star begins it life in a cloud of gas and dus ...
... 11. Red Super Giant stars have surface temperatures that are cooler than our earth, so why do they have greater luminosity than the sun? 12. The H-R diagram also includes which stars that are near the end of their life, what are these stars called? 13. A star begins it life in a cloud of gas and dus ...
The Relative Ages of M5 and Pal 4/Eridanus from their
... Chaotic structure, lots of young blue stars Moderate rotation in Irregulars, but very chaotic motions as well. Irregulars: ...
... Chaotic structure, lots of young blue stars Moderate rotation in Irregulars, but very chaotic motions as well. Irregulars: ...
Final for Astro 322, Prof. Heinke, April 23rd, 2010 Formula sheet
... a) If the peak of the emission is at 50 µm, what is the typical temperature of the emitting material? b) What is the emitting material likely to be? c) What are two possibilities for the original source of the energy we see? (Describe each in a couple of sentences.) They are not necessarily exclusiv ...
... a) If the peak of the emission is at 50 µm, what is the typical temperature of the emitting material? b) What is the emitting material likely to be? c) What are two possibilities for the original source of the energy we see? (Describe each in a couple of sentences.) They are not necessarily exclusiv ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Stars that glow blue-white are the hottest (15,000 degrees Celsius) Rigel ...
... Stars that glow blue-white are the hottest (15,000 degrees Celsius) Rigel ...
Lives and Deaths of Stars (middle school)
... A puzzle: the Sun and other stars radiate away huge amounts of energy. They should lose all their heat in less than a million years! However, the Sun lives 4.6 billion years ...
... A puzzle: the Sun and other stars radiate away huge amounts of energy. They should lose all their heat in less than a million years! However, the Sun lives 4.6 billion years ...
Astronomers use astronomical units(AU) to measure distances
... • Density: some stars have such low density that they could float on water; others are so dense that 1g would crush the CN Tower ...
... • Density: some stars have such low density that they could float on water; others are so dense that 1g would crush the CN Tower ...
Different types of YSOs
... Early solar system consisted of a planetary nebula-dust and gas surrounding protostar and early sun Chondrites & components clearly formed in nebula. Differentiated bodies too? ...
... Early solar system consisted of a planetary nebula-dust and gas surrounding protostar and early sun Chondrites & components clearly formed in nebula. Differentiated bodies too? ...
the_universe-part-1
... • held together by the gravitational attraction of all its member stars on one another • formed around 200 million years after the “Big Bang” • most large ones seem to have super-massive black holes at their centers • sometimes contain very bright centers called quasars • 3 major types: – Spiral – E ...
... • held together by the gravitational attraction of all its member stars on one another • formed around 200 million years after the “Big Bang” • most large ones seem to have super-massive black holes at their centers • sometimes contain very bright centers called quasars • 3 major types: – Spiral – E ...
Galaxies and the Universe - Mr. Jones's Science Class
... • held together by the gravitational attraction of all its member stars on one another • formed around 200 million years after the “Big Bang” • most large ones seem to have super-massive black holes at their centers • sometimes contain very bright centers called quasars • 3 major types: – Spiral – E ...
... • held together by the gravitational attraction of all its member stars on one another • formed around 200 million years after the “Big Bang” • most large ones seem to have super-massive black holes at their centers • sometimes contain very bright centers called quasars • 3 major types: – Spiral – E ...
Astronomy 360 Physics/Geology 360
... Pleiades has several meanings in different cultures and traditions. The cluster is dominated by hot blue and extremely luminous stars that have formed within the last 100 million years. Dust that forms a faint reflection nebulosity around the brightest stars was thought at first to be left over from ...
... Pleiades has several meanings in different cultures and traditions. The cluster is dominated by hot blue and extremely luminous stars that have formed within the last 100 million years. Dust that forms a faint reflection nebulosity around the brightest stars was thought at first to be left over from ...
the life cycle of stars
... ball of gas and dust. • Gravity pulls the materials into a sphere. • As the sphere gets denser, the temperature rises to 10,000,000* C. • Nuclear fusion occurs as hydrogen combines into helium. ...
... ball of gas and dust. • Gravity pulls the materials into a sphere. • As the sphere gets denser, the temperature rises to 10,000,000* C. • Nuclear fusion occurs as hydrogen combines into helium. ...
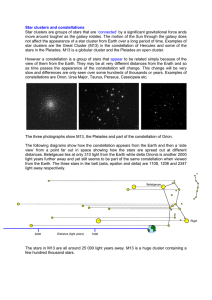
Star clusters and constellations
... The three photographs show M13, the Pleiades and part of the constellation of Orion. The following diagrams show how the constellation appears from the Earth and then a ‘side view’ from a point far out in space showing how the stars are spread out at different distances. Betelgeuse lies at only 310 ...
... The three photographs show M13, the Pleiades and part of the constellation of Orion. The following diagrams show how the constellation appears from the Earth and then a ‘side view’ from a point far out in space showing how the stars are spread out at different distances. Betelgeuse lies at only 310 ...
Lecture 18
... A. They’re stuck to the interstellar medium. B. The gravity of disk stars pulls them toward the disk. C. Halo stars knock them back into the disk. ...
... A. They’re stuck to the interstellar medium. B. The gravity of disk stars pulls them toward the disk. C. Halo stars knock them back into the disk. ...
Chapter 24 Test:Stars/Galaxies
... The positions of the constellations appear to change throughout the year because _____. (a) the sun revolves around the galaxy, (b) Earth revolves around the sun, (c) the constellations revolve around Earth, (d) Earth revolves around the stars. ...
... The positions of the constellations appear to change throughout the year because _____. (a) the sun revolves around the galaxy, (b) Earth revolves around the sun, (c) the constellations revolve around Earth, (d) Earth revolves around the stars. ...
Star
... -Some dwarf stars are as small as the Earth. -Our sun is a medium size star (1,390,000 km). -Some stars are 1,000 times larger than our sun. -Density affects mass…no relationship between size and mass. Example: a star can be smaller than our sun, but have a greater mass…meaning it is more dense! ...
... -Some dwarf stars are as small as the Earth. -Our sun is a medium size star (1,390,000 km). -Some stars are 1,000 times larger than our sun. -Density affects mass…no relationship between size and mass. Example: a star can be smaller than our sun, but have a greater mass…meaning it is more dense! ...
E1 Introduction to the Universe NEW
... Distance between galaxies • 100 kpc for galaxies in clusters • A few Mpc for galaxies in different clusters ...
... Distance between galaxies • 100 kpc for galaxies in clusters • A few Mpc for galaxies in different clusters ...
PH142 - Mohawk Valley Community College
... MA045 Basic Math Skills, or MA050 Introductory Mathematics This course covers these topics: the sun and other stars, multiple star systems, the Milky Way and other galaxies, nebulae, intergalactic material, cosmology and the evolution of stars, pulsars, and black holes. Laboratory sessions may be sc ...
... MA045 Basic Math Skills, or MA050 Introductory Mathematics This course covers these topics: the sun and other stars, multiple star systems, the Milky Way and other galaxies, nebulae, intergalactic material, cosmology and the evolution of stars, pulsars, and black holes. Laboratory sessions may be sc ...
Word
... Milky Way any more. We lie around 10 kpc from the centre of this galaxy. We have not been able to detect any spiral galaxies elsewhere in the sky. Instead, all we detect are spherical systems which are probably elliptical galaxies. This suggests that we are no longer in our own universe. Artifical S ...
... Milky Way any more. We lie around 10 kpc from the centre of this galaxy. We have not been able to detect any spiral galaxies elsewhere in the sky. Instead, all we detect are spherical systems which are probably elliptical galaxies. This suggests that we are no longer in our own universe. Artifical S ...
Messing Up a Galaxy
... stars themselves are very rare indeed. This is because the spaces between the stars in a galaxy are typically very large compared with the stars' sizes. In our region of space, the distance from the Sun to its nearest stellar neighbour is about 29 million times the Sun's diameter! Our Milky Way Gala ...
... stars themselves are very rare indeed. This is because the spaces between the stars in a galaxy are typically very large compared with the stars' sizes. In our region of space, the distance from the Sun to its nearest stellar neighbour is about 29 million times the Sun's diameter! Our Milky Way Gala ...
Life Cycle of Stars: Chapter 21
... • Expands and collapses to facilitate helium burning – Becomes helium burning star ...
... • Expands and collapses to facilitate helium burning – Becomes helium burning star ...
What is a star`s life cycle?
... ____________________ 1. A star changes its heat into energy. ____________________ 2. In 1987, a protostar was observed in the Large Magellanic Cloud. ____________________ 3. During nuclear reactions in large stars, helium is changed into carbon. ____________________ 4. A star stays in the main seque ...
... ____________________ 1. A star changes its heat into energy. ____________________ 2. In 1987, a protostar was observed in the Large Magellanic Cloud. ____________________ 3. During nuclear reactions in large stars, helium is changed into carbon. ____________________ 4. A star stays in the main seque ...
Yes, we are all star dust. Even Gary!
... • Supernovae (exploding massive stars) = all other naturally occurring elements heavier than Iron (ie the metals and rare earths) ...
... • Supernovae (exploding massive stars) = all other naturally occurring elements heavier than Iron (ie the metals and rare earths) ...
H II region

An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. The first known H II region was the Orion Nebula, which was discovered in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc.H II regions are named for the large amount of ionised atomic hydrogen they contain, referred to as H II, pronounced H-two by astronomers (an H I region being neutral atomic hydrogen, and H2 being molecular hydrogen). Such regions have extremely diverse shapes, because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing bizarre shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regions may give birth to thousands of stars over a period of several million years. In the end, supernova explosions and strong stellar winds from the most massive stars in the resulting star cluster will disperse the gases of the H II region, leaving behind a cluster of birthed stars such as the Pleiades.H II regions can be seen to considerable distances in the universe, and the study of extragalactic H II regions is important in determining the distance and chemical composition of other galaxies. Spiral and irregular galaxies contain many H II regions, while elliptical galaxies are almost devoid of them. In the spiral galaxies, including the Milky Way, H II regions are concentrated in the spiral arms, while in the irregular galaxies they are distributed chaotically. Some galaxies contain huge H II regions, which may contain tens of thousands of stars. Examples include the 30 Doradus region in the Large Magellanic Cloud and NGC 604 in the Triangulum Galaxy.