Sample Chapter
... and Nikolas Gardner. Includes bibliographical references and index. Issued in print and electronic formats. ...
... and Nikolas Gardner. Includes bibliographical references and index. Issued in print and electronic formats. ...
AP26 TEST BANK 2015
... e. the big increase in Germany’s armed forces 15. Total war during World War I included A. universal conscription, and naval blockades. B. increased taxes, censorship of the press. C. use of propaganda on both sides and women in the work force. D. all of the above. 16. The book "All Quiet on the Wes ...
... e. the big increase in Germany’s armed forces 15. Total war during World War I included A. universal conscription, and naval blockades. B. increased taxes, censorship of the press. C. use of propaganda on both sides and women in the work force. D. all of the above. 16. The book "All Quiet on the Wes ...
File
... • Committee on Public Information formed by President Wilson to help persuade the public to support the war effort. • Espionage Act of 1917 and the Sedition Act of 1918 limited freedoms in the United States. • Selective Service Act was enacted in 1917 to prepare the U.S. military for war. – Required ...
... • Committee on Public Information formed by President Wilson to help persuade the public to support the war effort. • Espionage Act of 1917 and the Sedition Act of 1918 limited freedoms in the United States. • Selective Service Act was enacted in 1917 to prepare the U.S. military for war. – Required ...
File - US History Options
... create cars ten times faster than before. This also made it so that ...
... create cars ten times faster than before. This also made it so that ...
World War II Begins
... • Purpose: A meeting to avoid war • Attended by: Germany, France and Great Britain, & Italy • Great Britain and France believed that by giving in to what Germany wants, this would be the last territorial demand Germany would ask for…Germany had ...
... • Purpose: A meeting to avoid war • Attended by: Germany, France and Great Britain, & Italy • Great Britain and France believed that by giving in to what Germany wants, this would be the last territorial demand Germany would ask for…Germany had ...
The Great War 1914-1918 - Prairie Spirit School Division
... • During the War's early years Britain (supported loyally by troops from her Empire and Commonwealth, such as; Canada, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa) and her Allies, France and Russia, fought against Germany and Austro-Hungary. At the War's end many more countries were involved, including; t ...
... • During the War's early years Britain (supported loyally by troops from her Empire and Commonwealth, such as; Canada, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa) and her Allies, France and Russia, fought against Germany and Austro-Hungary. At the War's end many more countries were involved, including; t ...
Slide one: (Background to why alliances were getting formed)
... -The alliances were countries that _________ together against other countries. -This system led to the ____________________________________________________ -during world war one, there were two alliance’s that fought against each other. -They were called the “________________” which was Russia F ...
... -The alliances were countries that _________ together against other countries. -This system led to the ____________________________________________________ -during world war one, there were two alliance’s that fought against each other. -They were called the “________________” which was Russia F ...
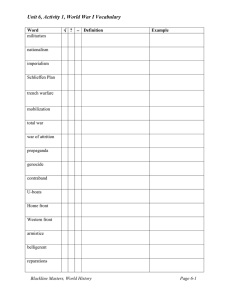
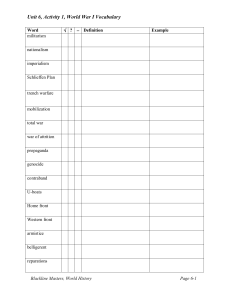
Social Studies High School World History Unit 6 Blackline Master
... Austria informs Great Britain, Germany, France, Russia, Italy, and Turkey of their ultimatum to Serbia (content of the ultimatum had been secretly given to the German government two weeks earlier). Austrian foreign minister notes: “Any conditional acceptance [of the ultimatum], or one accompanied by ...
... Austria informs Great Britain, Germany, France, Russia, Italy, and Turkey of their ultimatum to Serbia (content of the ultimatum had been secretly given to the German government two weeks earlier). Austrian foreign minister notes: “Any conditional acceptance [of the ultimatum], or one accompanied by ...
Unit 6, Activity 1, World War I Vocabulary
... Austria informs Great Britain, Germany, France, Russia, Italy, and Turkey of their ultimatum to Serbia (content of the ultimatum had been secretly given to the German government two weeks earlier). Austrian foreign minister notes: “Any conditional acceptance [of the ultimatum], or one accompanied by ...
... Austria informs Great Britain, Germany, France, Russia, Italy, and Turkey of their ultimatum to Serbia (content of the ultimatum had been secretly given to the German government two weeks earlier). Austrian foreign minister notes: “Any conditional acceptance [of the ultimatum], or one accompanied by ...
WW1 Study Guide Closely linked with industrialization, this long
... What reason did Senators give for opposing U.S. membership in the League of Nations? These people opposed World War I because they saw it as an imperialist struggle. In 1914, this alliance consisted of Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire. This long-term cause of the war encouraged compe ...
... What reason did Senators give for opposing U.S. membership in the League of Nations? These people opposed World War I because they saw it as an imperialist struggle. In 1914, this alliance consisted of Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire. This long-term cause of the war encouraged compe ...
BELL RINGERS DAY 1 1. The period in American history that
... B decrease the United States Navy’s sailing time between the Atlantic and the Pacific. C fulfill obligations under a treaty with the French. D protect the environment and native cultures of the Central American countries. ________________________________________________________________________ ...
... B decrease the United States Navy’s sailing time between the Atlantic and the Pacific. C fulfill obligations under a treaty with the French. D protect the environment and native cultures of the Central American countries. ________________________________________________________________________ ...
The Aftermath of World War I
... Global Impact of World War I • Political and economic instability during the postwar years, combined with the resentment felt by the German people towards the Treaty of Versailles, eventually led Europe back into war within just a few years. ...
... Global Impact of World War I • Political and economic instability during the postwar years, combined with the resentment felt by the German people towards the Treaty of Versailles, eventually led Europe back into war within just a few years. ...
World War I
... The US never joined the League and decided to sign a separate treaty with Germany in ...
... The US never joined the League and decided to sign a separate treaty with Germany in ...
Document
... Identify the long-term causes 1. Analyze world resources and the immediate and determine their circumstances that led to impact. WW1 2. Discuss the U.S. Summarize U.S. public entrance into WW1 opinion of the war. 3. Determine the main Explain why the United states Causes of U.S. entrance entered the ...
... Identify the long-term causes 1. Analyze world resources and the immediate and determine their circumstances that led to impact. WW1 2. Discuss the U.S. Summarize U.S. public entrance into WW1 opinion of the war. 3. Determine the main Explain why the United states Causes of U.S. entrance entered the ...
The War to End Wars
... 1917 European Allies were running out of men, money, and everything else. Selective Service Act (1st since the Civil War). ...
... 1917 European Allies were running out of men, money, and everything else. Selective Service Act (1st since the Civil War). ...
From Neutrality to War
... its ally if war came. The confident Austria-Hungary declared War on Serbia on July 28, 1914. Because of the alliance system that was in place many other countries became involved. If the alliances were not made then it would have been a local issue. ...
... its ally if war came. The confident Austria-Hungary declared War on Serbia on July 28, 1914. Because of the alliance system that was in place many other countries became involved. If the alliances were not made then it would have been a local issue. ...
World War I – Allied Victory 1 US Entry 1. US Entry 2
... Strong economy and large, well equipped, well-trained army. Strategic position in middle of Europe. War fought on Allied territory. Germany could be defensive on Western Front while Allies had to make costly attacks. Disadvantages Di d t iin a llong war after ft ffailure il off Schlieffen S hli ff P ...
... Strong economy and large, well equipped, well-trained army. Strategic position in middle of Europe. War fought on Allied territory. Germany could be defensive on Western Front while Allies had to make costly attacks. Disadvantages Di d t iin a llong war after ft ffailure il off Schlieffen S hli ff P ...
Tom Renick
... Roles will be assigned to role play everyday such as: a German soldier, a captured French soldier, a poisoned Russian soldier, an Austrian nurse, etc. ...
... Roles will be assigned to role play everyday such as: a German soldier, a captured French soldier, a poisoned Russian soldier, an Austrian nurse, etc. ...
The First Day of the Somme
... The Battle of Somme was in many ways typical trench warfare. Up until June 1926 this sector in Northeastern France was inactive. German divisions had been present since 1914 and had constructed three defensive lines of trenches running back from “no man’s land,” an area of 500 to 1000 yards wide on ...
... The Battle of Somme was in many ways typical trench warfare. Up until June 1926 this sector in Northeastern France was inactive. German divisions had been present since 1914 and had constructed three defensive lines of trenches running back from “no man’s land,” an area of 500 to 1000 yards wide on ...
Chapter 23
... The alliances aimed to keep peace by maintaining a balance of power. A hotbed of nationalist and ethnic rivalries existed in the early 1900s in the Balkan Peninsula in southeastern Europe. Gavrilo Princip; Princip and other terrorists plotted the murder to advance the cause of the unification of ...
... The alliances aimed to keep peace by maintaining a balance of power. A hotbed of nationalist and ethnic rivalries existed in the early 1900s in the Balkan Peninsula in southeastern Europe. Gavrilo Princip; Princip and other terrorists plotted the murder to advance the cause of the unification of ...
The Entry of Canada
... French believed that Canada’s contribution would be the protection of Canada English Canadians disagreed and felt loyalty to the crown and argued that the British Navy protected Canada ...
... French believed that Canada’s contribution would be the protection of Canada English Canadians disagreed and felt loyalty to the crown and argued that the British Navy protected Canada ...
chapter summary
... Germany’s declaration of unlimited ___________________________ warfare, supplemented by the ________________________ note proposing an alliance with Mexico, finally caused the United States to declare war. Wilson aroused the country to patriotic heights by making the war an idealistic crusade for __ ...
... Germany’s declaration of unlimited ___________________________ warfare, supplemented by the ________________________ note proposing an alliance with Mexico, finally caused the United States to declare war. Wilson aroused the country to patriotic heights by making the war an idealistic crusade for __ ...
The Battle of the Somme: The Missing Pages of
... Friday 1 July 2016 marked 100 years since the start of the First Battle of the Somme. This battle ended on 18 November 1916. It was one of the bloodiest campaigns of World War I, with British forces suffering more than 57,000 casualties in the first day of fighting. By the end of the campaign there ...
... Friday 1 July 2016 marked 100 years since the start of the First Battle of the Somme. This battle ended on 18 November 1916. It was one of the bloodiest campaigns of World War I, with British forces suffering more than 57,000 casualties in the first day of fighting. By the end of the campaign there ...
WWI documents - Paulding County Schools
... 1. Which three countries had the largest size empires in terms of land area? 2. What two European countries did not have any colonial empire holdings in 1913? ...
... 1. Which three countries had the largest size empires in terms of land area? 2. What two European countries did not have any colonial empire holdings in 1913? ...