Cryptanalysis of Stream Cipher
... No security reduction but easy to analyze Not resistant to nonce reuse No incremental tags Flexible implementation sizes: 128/256 Performance: speed/size ...
... No security reduction but easy to analyze Not resistant to nonce reuse No incremental tags Flexible implementation sizes: 128/256 Performance: speed/size ...
Lect 1 - Intro
... to attain the applicable objectives of preserving integrity, availability, and confidentiality of information system resources (includes hardware, software, firmware, information/data, and ...
... to attain the applicable objectives of preserving integrity, availability, and confidentiality of information system resources (includes hardware, software, firmware, information/data, and ...
Symmetric-Key Cryptography - Sensorweb Research Laboratory
... Practical Substitutionpermutation Networks In practice we need to be able to decrypt ...
... Practical Substitutionpermutation Networks In practice we need to be able to decrypt ...
Secure Deduplication with Efficient and Reliable
... keys. To this end, we propose Dekey, a new construction in which users do not need to manage any keys on their own but instead securely distribute the convergent key shares across multiple servers. Security analysis demonstrates that Dekey is secure in terms of the definitions specified in the propo ...
... keys. To this end, we propose Dekey, a new construction in which users do not need to manage any keys on their own but instead securely distribute the convergent key shares across multiple servers. Security analysis demonstrates that Dekey is secure in terms of the definitions specified in the propo ...
Security - UTRGV Faculty Web
... A computer needs a public IP address to attach to a public network. Private IP addresses are not visible from the outside world. It makes sense to use only private IP to secure your computer. When outside communication is needed the private IP is mapped to public IP address using a port number. ...
... A computer needs a public IP address to attach to a public network. Private IP addresses are not visible from the outside world. It makes sense to use only private IP to secure your computer. When outside communication is needed the private IP is mapped to public IP address using a port number. ...
Public-Key Cryptosystems Based on Hard Problems
... United Kingdom, the United States, Germany and France. The greatest milestone in the history of cryptography was the breaking of the Enigma Code during the World War II. Alan Turing developed a machine which was able to dechiper the Germans' messages using mathematical techniques. A movie, The Imita ...
... United Kingdom, the United States, Germany and France. The greatest milestone in the history of cryptography was the breaking of the Enigma Code during the World War II. Alan Turing developed a machine which was able to dechiper the Germans' messages using mathematical techniques. A movie, The Imita ...
Chapter 5 - Department of Computer Science and Information Systems
... The Internet is the medium over which ecommerce data is transferred Messages on the Internet travel a random path from a source node to a destination node The content of messages is not protected and anyone on the message path can record its ...
... The Internet is the medium over which ecommerce data is transferred Messages on the Internet travel a random path from a source node to a destination node The content of messages is not protected and anyone on the message path can record its ...
CIT 016 Review for Final
... Operating systems are intended to be dynamic As users’ needs change, new hardware is introduced, and more sophisticated attacks are unleashed, operating systems must be updated on a regular basis However, vendors release a new version of an operating system every two to four years Vendors use certai ...
... Operating systems are intended to be dynamic As users’ needs change, new hardware is introduced, and more sophisticated attacks are unleashed, operating systems must be updated on a regular basis However, vendors release a new version of an operating system every two to four years Vendors use certai ...
Security
... • The data encryption standard (DES): – block cipher adopted by the US Government in Jan. 1977. – encryption based on 56-bit key. ...
... • The data encryption standard (DES): – block cipher adopted by the US Government in Jan. 1977. – encryption based on 56-bit key. ...
(Public-Key) Cryptography
... • The title of the accompanying book “Understanding Cryptography” by Springer and the author’s names must remain on each slide. ...
... • The title of the accompanying book “Understanding Cryptography” by Springer and the author’s names must remain on each slide. ...
Tallinn University of Technology Quantum computer impact on
... No known efficient algorithm for number factorization on classical computer. Available algorithms take exponential time in respect to input size. Factorization of hundreds digits long numbers is practically impossible. ...
... No known efficient algorithm for number factorization on classical computer. Available algorithms take exponential time in respect to input size. Factorization of hundreds digits long numbers is practically impossible. ...
D`Amo - softfarm
... • D’Amo enables strict separation of authority between the Security Manager and the Database Administrator. ...
... • D’Amo enables strict separation of authority between the Security Manager and the Database Administrator. ...
CN 2015 5 - SNGCE DIGITAL LIBRARY
... A security association is simply the bundle of algorithms and parameters (such as keys) that is being used to encrypt and authenticate a particular flow in one direction. IPsec supports two encryption modes: Transport and ...
... A security association is simply the bundle of algorithms and parameters (such as keys) that is being used to encrypt and authenticate a particular flow in one direction. IPsec supports two encryption modes: Transport and ...
6.1. Elliptic Curve Cryptography
... unfortunately their security depends on unproven mathematical assumptions, such as the difficulty of factoring large integers (RSA - the most popular public key cryptosystem gets its security from the difficulty of factoring large numbers. This means that if and when mathematicians or computer scien ...
... unfortunately their security depends on unproven mathematical assumptions, such as the difficulty of factoring large integers (RSA - the most popular public key cryptosystem gets its security from the difficulty of factoring large numbers. This means that if and when mathematicians or computer scien ...
DCN-7-Network_Security
... –Asymmetric/Public Key Cryptography: •Uses 2 different (mathematically related) keys for, –Encryption and Decryption where, »Encryption is done using Receiver’s Public Key and, »Decryption is done using Receiver’s Private Key. ...
... –Asymmetric/Public Key Cryptography: •Uses 2 different (mathematically related) keys for, –Encryption and Decryption where, »Encryption is done using Receiver’s Public Key and, »Decryption is done using Receiver’s Private Key. ...
MT311-14
... Information security Information security, however, refers to the secrecy and integrity of data. For example, when you send an email, how do you ensure that only the targeted recipients can read the message? When you receive an email, how do you ensure that the message has not been tampered with an ...
... Information security Information security, however, refers to the secrecy and integrity of data. For example, when you send an email, how do you ensure that only the targeted recipients can read the message? When you receive an email, how do you ensure that the message has not been tampered with an ...
QuestionFile3Cryptography
... 18. Name three mathematical problems that are underlying components of RSA. Make sure your answer includes the fundamental problem which renders RSA secure, and identify it as such. ...
... 18. Name three mathematical problems that are underlying components of RSA. Make sure your answer includes the fundamental problem which renders RSA secure, and identify it as such. ...
Introduction to quantum cryptography
... • and telescopes with 8-inch mirrors to send and receive photons over the air. • Using the quantum transmitted key messages were encrypted at the rate 1 million bits per second. The speed was impressive but the distance between two NIST buildings was only 730 ...
... • and telescopes with 8-inch mirrors to send and receive photons over the air. • Using the quantum transmitted key messages were encrypted at the rate 1 million bits per second. The speed was impressive but the distance between two NIST buildings was only 730 ...
Guide to Firewalls and Network Security with Intrusion Detection and
... Firewall-Based Encryption Public and private keys Need to generate public keys Need to securely manage private keys Need to use a key server either on network ...
... Firewall-Based Encryption Public and private keys Need to generate public keys Need to securely manage private keys Need to use a key server either on network ...
Hidden Markov Model Cryptanalysis
... Markov Models (HMMs). The idea behind randomized countermeasures is: Randomize side channel information, thus make it harder to analyze. ...
... Markov Models (HMMs). The idea behind randomized countermeasures is: Randomize side channel information, thus make it harder to analyze. ...
Security
... Requires the communication of the key between sender and receiver! Basis of nuclear war-head command and control security ...
... Requires the communication of the key between sender and receiver! Basis of nuclear war-head command and control security ...
Section2.3
... Practice HW from Barr Textbook (not to hand in) p. 92 # 1, 2 # 3-5 (Use Internet Site) ...
... Practice HW from Barr Textbook (not to hand in) p. 92 # 1, 2 # 3-5 (Use Internet Site) ...
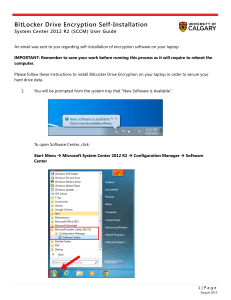
BitLocker Drive Encryption Self
... System Center 2012 R2 (SCCM) User Guide An email was sent to you regarding self-installation of encryption software on your laptop. IMPORTANT: Remember to save your work before running this process as it will require to reboot the computer. Please follow these instructions to install BitLocker Drive ...
... System Center 2012 R2 (SCCM) User Guide An email was sent to you regarding self-installation of encryption software on your laptop. IMPORTANT: Remember to save your work before running this process as it will require to reboot the computer. Please follow these instructions to install BitLocker Drive ...
Cryptography

Cryptography or cryptology; from Greek κρυπτός kryptós, ""hidden, secret""; and γράφειν graphein, ""writing"", or -λογία -logia, ""study"", respectively is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of third parties (called adversaries). More generally, it is about constructing and analyzing protocols that block adversaries; various aspects in information security such as data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation are central to modern cryptography. Modern cryptography exists at the intersection of the disciplines of mathematics, computer science, and electrical engineering. Applications of cryptography include ATM cards, computer passwords, and electronic commerce.Cryptography prior to the modern age was effectively synonymous with encryption, the conversion of information from a readable state to apparent nonsense. The originator of an encrypted message shared the decoding technique needed to recover the original information only with intended recipients, thereby precluding unwanted persons from doing the same. Since World War I and the advent of the computer, the methods used to carry out cryptology have become increasingly complex and its application more widespread.Modern cryptography is heavily based on mathematical theory and computer science practice; cryptographic algorithms are designed around computational hardness assumptions, making such algorithms hard to break in practice by any adversary. It is theoretically possible to break such a system, but it is infeasible to do so by any known practical means. These schemes are therefore termed computationally secure; theoretical advances, e.g., improvements in integer factorization algorithms, and faster computing technology require these solutions to be continually adapted. There exist information-theoretically secure schemes that provably cannot be broken even with unlimited computing power—an example is the one-time pad—but these schemes are more difficult to implement than the best theoretically breakable but computationally secure mechanisms.The growth of cryptographic technology has raised a number of legal issues in the information age. Cryptography's potential for use as a tool for espionage and sedition has led many governments to classify it as a weapon and to limit or even prohibit its use and export. In some jurisdictions where the use of cryptography is legal, laws permit investigators to compel the disclosure of encryption keys for documents relevant to an investigation. Cryptography also plays a major role in digital rights management and piracy of digital media.