L2 Atomic and Nuclear Physics 1
... • Over 100 other “elementary particles” were discovered since 1930. These particles are all made from quarks and/or leptons. • Today quarks, leptons, and their associated anti-particles are candidates for being the fundamental building blocks, from which all thing are made. • The current theory of m ...
... • Over 100 other “elementary particles” were discovered since 1930. These particles are all made from quarks and/or leptons. • Today quarks, leptons, and their associated anti-particles are candidates for being the fundamental building blocks, from which all thing are made. • The current theory of m ...
UQ3
... 2. Cesium-137 radioactively decays via beta particle decay. Write the nuclear equation for this beta particle decay process and identify the nuclide produced. ...
... 2. Cesium-137 radioactively decays via beta particle decay. Write the nuclear equation for this beta particle decay process and identify the nuclide produced. ...
Electric Field Lines
... transistors in electric circuits. 5e. Know charged particles are sources of electric fields and are subject to the forces of the electric fields from other charges. 5h. Know changing magnetic fields produce electric fields, thereby inducing currents in nearby conductors. 5i. Know plasmas, a fourth s ...
... transistors in electric circuits. 5e. Know charged particles are sources of electric fields and are subject to the forces of the electric fields from other charges. 5h. Know changing magnetic fields produce electric fields, thereby inducing currents in nearby conductors. 5i. Know plasmas, a fourth s ...
Developing an Atomic Model
... negatively charged particles that came from the INSIDE of atoms. THEREFORE, ATOMS COULD BE DIVIDED INTO SMALLER PARTS! ...
... negatively charged particles that came from the INSIDE of atoms. THEREFORE, ATOMS COULD BE DIVIDED INTO SMALLER PARTS! ...
Experimental Aspects of Jet Reconstruction in Collider
... Closest to the interaction vertex Reconstructs charged particle tracks in magnetic field Charged particles generate current Silicon pixel elements → fit tracks to (x,y,z) space points defined by hit sensor location Collect secondary charges from gas ionizations by passing charged particles on wires ...
... Closest to the interaction vertex Reconstructs charged particle tracks in magnetic field Charged particles generate current Silicon pixel elements → fit tracks to (x,y,z) space points defined by hit sensor location Collect secondary charges from gas ionizations by passing charged particles on wires ...
Revisiting moving electric charges
... Revisiting moving electric charges A 20 μF parallel plate capacitor stores 300 μC of charge. The plates are 6 cm apart. An electron enters the region between the plates along the midpoint with a speed of 1 x 106 m/s as shown. What is the magnitude and direction of the force that acts on the electron ...
... Revisiting moving electric charges A 20 μF parallel plate capacitor stores 300 μC of charge. The plates are 6 cm apart. An electron enters the region between the plates along the midpoint with a speed of 1 x 106 m/s as shown. What is the magnitude and direction of the force that acts on the electron ...
The Structure of Matter: The Basic Particle Model - ag
... The particle-wave duality, which is the principle pile of quantum mechanics (within the so called 'Copenhagen interpretation') can, following Louis de Broglie, be classically understood in the view of the basic particle model. This is explained (in this case qualitatively) in the context of SPECIAL ...
... The particle-wave duality, which is the principle pile of quantum mechanics (within the so called 'Copenhagen interpretation') can, following Louis de Broglie, be classically understood in the view of the basic particle model. This is explained (in this case qualitatively) in the context of SPECIAL ...
John Dalton
... Henri Becquerel - discovered radiation emitted by Uranium Marie Curie - discovered two other elements that emitted radiation (Polonium and Radium) Niels Bohr - Proposed energy levels and the Planetary model of the Atom Louis de Broglie - Proposed the wave particle duality of nature Werner Heisenberg ...
... Henri Becquerel - discovered radiation emitted by Uranium Marie Curie - discovered two other elements that emitted radiation (Polonium and Radium) Niels Bohr - Proposed energy levels and the Planetary model of the Atom Louis de Broglie - Proposed the wave particle duality of nature Werner Heisenberg ...
Chapter 30
... • Leptons are particles like electrons and neutrinos. • Other particles carry or transmit forces between particles. ...
... • Leptons are particles like electrons and neutrinos. • Other particles carry or transmit forces between particles. ...
Neutrino Oscillation - Stony Brook NN Group
... Summer: 4 Jul. 156 million km Winter : 3 Jan. 146 million km ...
... Summer: 4 Jul. 156 million km Winter : 3 Jan. 146 million km ...
Document
... • Anything that has volume and mass • Everything that exists is matter, and is made of ATOMS ...
... • Anything that has volume and mass • Everything that exists is matter, and is made of ATOMS ...
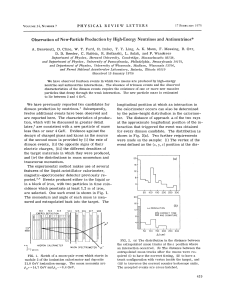
Observation of New-Particle Production by High
... No events with three muons in the final state have been observed. The estimated detection efficiency for trimuon events is approximately one half that for dimuon events. We have examined the characteristics of the observed dimuon events against the possibility' that they arise from a neutrino-induce ...
... No events with three muons in the final state have been observed. The estimated detection efficiency for trimuon events is approximately one half that for dimuon events. We have examined the characteristics of the observed dimuon events against the possibility' that they arise from a neutrino-induce ...
When Symmetry Breaks Down - School of Natural Sciences
... detect the effects of what we now call the electromagnetic interactions. Light is pretty obvious in everyday life, and other electromagnetic effects, such as static electricity, lightning bolts and the magnetic properties of some rocks, such as lodestone, were well known in ancient days. But it take ...
... detect the effects of what we now call the electromagnetic interactions. Light is pretty obvious in everyday life, and other electromagnetic effects, such as static electricity, lightning bolts and the magnetic properties of some rocks, such as lodestone, were well known in ancient days. But it take ...
Chapter 30
... Forces between particles are often described in terms of the actions of field particles or quanta For electromagnetic force, the photon is the field particle The electromagnetic force is mediated, or carried, by photons ...
... Forces between particles are often described in terms of the actions of field particles or quanta For electromagnetic force, the photon is the field particle The electromagnetic force is mediated, or carried, by photons ...
Chapter28ReadingQuiz..
... electrons have a wave nature. light has a particle nature. a photon can be converted into an electron. electrons are the conductors in metals. ...
... electrons have a wave nature. light has a particle nature. a photon can be converted into an electron. electrons are the conductors in metals. ...
Lepton
A lepton is an elementary, half-integer spin (spin 1⁄2) particle that does not undergo strong interactions, but is subject to the Pauli exclusion principle. The best known of all leptons is the electron, which is directly tied to all chemical properties. Two main classes of leptons exist: charged leptons (also known as the electron-like leptons), and neutral leptons (better known as neutrinos). Charged leptons can combine with other particles to form various composite particles such as atoms and positronium, while neutrinos rarely interact with anything, and are consequently rarely observed.There are six types of leptons, known as flavours, forming three generations. The first generation is the electronic leptons, comprising the electron (e−) and electron neutrino (νe); the second is the muonic leptons, comprising the muon (μ−) and muon neutrino (νμ); and the third is the tauonic leptons, comprising the tau (τ−) and the tau neutrino (ντ). Electrons have the least mass of all the charged leptons. The heavier muons and taus will rapidly change into electrons through a process of particle decay: the transformation from a higher mass state to a lower mass state. Thus electrons are stable and the most common charged lepton in the universe, whereas muons and taus can only be produced in high energy collisions (such as those involving cosmic rays and those carried out in particle accelerators).Leptons have various intrinsic properties, including electric charge, spin, and mass. Unlike quarks however, leptons are not subject to the strong interaction, but they are subject to the other three fundamental interactions: gravitation, electromagnetism (excluding neutrinos, which are electrically neutral), and the weak interaction. For every lepton flavor there is a corresponding type of antiparticle, known as antilepton, that differs from the lepton only in that some of its properties have equal magnitude but opposite sign. However, according to certain theories, neutrinos may be their own antiparticle, but it is not currently known whether this is the case or not.The first charged lepton, the electron, was theorized in the mid-19th century by several scientists and was discovered in 1897 by J. J. Thomson. The next lepton to be observed was the muon, discovered by Carl D. Anderson in 1936, which was classified as a meson at the time. After investigation, it was realized that the muon did not have the expected properties of a meson, but rather behaved like an electron, only with higher mass. It took until 1947 for the concept of ""leptons"" as a family of particle to be proposed. The first neutrino, the electron neutrino, was proposed by Wolfgang Pauli in 1930 to explain certain characteristics of beta decay. It was first observed in the Cowan–Reines neutrino experiment conducted by Clyde Cowan and Frederick Reines in 1956. The muon neutrino was discovered in 1962 by Leon M. Lederman, Melvin Schwartz and Jack Steinberger, and the tau discovered between 1974 and 1977 by Martin Lewis Perl and his colleagues from the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. The tau neutrino remained elusive until July 2000, when the DONUT collaboration from Fermilab announced its discovery.Leptons are an important part of the Standard Model. Electrons are one of the components of atoms, alongside protons and neutrons. Exotic atoms with muons and taus instead of electrons can also be synthesized, as well as lepton–antilepton particles such as positronium.