Lecture 7
... We use ERi because it reflects the riskiness of the firm’s new investment project – provided the ‘new’ investment project has the same ‘business risk’ characteristics as the firm’s existing project. This is because ERi reflects the return required by investors to hold this share as part of their por ...
... We use ERi because it reflects the riskiness of the firm’s new investment project – provided the ‘new’ investment project has the same ‘business risk’ characteristics as the firm’s existing project. This is because ERi reflects the return required by investors to hold this share as part of their por ...
Exam 2
... a. Calculate the expected returns and the standard deviations of the two securities. E(Ra)=.6*4+.4*16=8.8%; E(Rb)=.6*3+.4*3=3% Variance(Alpha) = .6(4-8.8)2+.4(16-8.8)2=13.824+20.736=34.56 Standard Dev.(Alpha)=5.87%; Variance(Beta)=0 b. You have $10,000 to invest. Calculate the expected return and st ...
... a. Calculate the expected returns and the standard deviations of the two securities. E(Ra)=.6*4+.4*16=8.8%; E(Rb)=.6*3+.4*3=3% Variance(Alpha) = .6(4-8.8)2+.4(16-8.8)2=13.824+20.736=34.56 Standard Dev.(Alpha)=5.87%; Variance(Beta)=0 b. You have $10,000 to invest. Calculate the expected return and st ...
Long-term Investing as asset prices rise
... safety and invest for the long-term The factors that influence whether management of these companies achieve good long term returns are numerous and complicated. While macro-economic and geopolitical factors are an important input, our thinking on such matters is much ...
... safety and invest for the long-term The factors that influence whether management of these companies achieve good long term returns are numerous and complicated. While macro-economic and geopolitical factors are an important input, our thinking on such matters is much ...
US Fed finally raises rates and sends bond prices down
... Federal Reserve. The Fed raised US interest rates in December by 0.25%, for only the second time in nearly a decade. However, it also indicated that it cannot—as the phrase goes— “Eat Just One” and predicted at least three more hikes in 2017. While the fixed income securities within the fund’s portf ...
... Federal Reserve. The Fed raised US interest rates in December by 0.25%, for only the second time in nearly a decade. However, it also indicated that it cannot—as the phrase goes— “Eat Just One” and predicted at least three more hikes in 2017. While the fixed income securities within the fund’s portf ...
Lecture 1
... • Taking values from the table in the previous slide, CDF is .59 with the 20% return level • It means that there is 59% probability that return on POL will be less than 20% • An investor has Rs.100,000 investment in POL and he wants that he does not lose more than Rs.30000 of his investment, what is ...
... • Taking values from the table in the previous slide, CDF is .59 with the 20% return level • It means that there is 59% probability that return on POL will be less than 20% • An investor has Rs.100,000 investment in POL and he wants that he does not lose more than Rs.30000 of his investment, what is ...
Capital Asset Pricing Model
... portfolios based on their standard deviations, whereas the security market line depicts the relation between the required return and market risk, as measured by beta. An efficient market is a market in which asset prices reflect available information quickly and accurately. The EMH is commonly broke ...
... portfolios based on their standard deviations, whereas the security market line depicts the relation between the required return and market risk, as measured by beta. An efficient market is a market in which asset prices reflect available information quickly and accurately. The EMH is commonly broke ...
Reinvestment Risk
... Assuming credit risk requires that additional resources be devoted to the investment program ...
... Assuming credit risk requires that additional resources be devoted to the investment program ...
TopicsInAnalysis
... (This could get deep. We’ll look at the standard heat equation and Kolmogorov equation related to Brownian motion. Main point: If we set up the problem correctly, the Black-Scholes differential equation is exactly the standard heat equation.) 20. Option pricing and oil-property evaluation FIFTH TOPI ...
... (This could get deep. We’ll look at the standard heat equation and Kolmogorov equation related to Brownian motion. Main point: If we set up the problem correctly, the Black-Scholes differential equation is exactly the standard heat equation.) 20. Option pricing and oil-property evaluation FIFTH TOPI ...
Lecture Presentation to accompany Investment
... Portfolio Management • What is the relationship between covariance and correlation? • What is the formula for the standard deviation for a portfolio of risky assets and how does it differ from the standard deviation of an individual risky asset? • Given the formula for the standard deviation of a po ...
... Portfolio Management • What is the relationship between covariance and correlation? • What is the formula for the standard deviation for a portfolio of risky assets and how does it differ from the standard deviation of an individual risky asset? • Given the formula for the standard deviation of a po ...
Expected Return Standard Deviation
... Their risk will be determined by the industry sector and gearing. Some shares will be more risky and some less. ...
... Their risk will be determined by the industry sector and gearing. Some shares will be more risky and some less. ...
Chapter 13
... • For example, if you own 50 Internet stocks, you are not diversified • However, if you own 50 stocks that span 20 different industries, then you are diversified ...
... • For example, if you own 50 Internet stocks, you are not diversified • However, if you own 50 stocks that span 20 different industries, then you are diversified ...
Lecture 27: CAPM and Risk Premium
... less risky investment, or the amount a risk-averse agent will pay to avoid taking a risk. i. If the expected payoff of a risky investment (say, venture capitalism) is $10 million and the expected payoff of a safe investment (say, government bonds) is $9 million, then the risk premium is $1 million. ...
... less risky investment, or the amount a risk-averse agent will pay to avoid taking a risk. i. If the expected payoff of a risky investment (say, venture capitalism) is $10 million and the expected payoff of a safe investment (say, government bonds) is $9 million, then the risk premium is $1 million. ...
Merrill Finch Inc
... Note that the estimated returns of U.S. Rubber do not always move in the same direction as the overall economy. For example, when the economy is below average, consumers purchase fewer tires than they would if the economy was stronger. However, if the economy is in a flat-out recession, a large numb ...
... Note that the estimated returns of U.S. Rubber do not always move in the same direction as the overall economy. For example, when the economy is below average, consumers purchase fewer tires than they would if the economy was stronger. However, if the economy is in a flat-out recession, a large numb ...
Introduction to Financial Management
... risk without an equivalent reduction in expected returns – Reduces the variability of returns – Caused by the offset of worse-thanexpected returns from one asset by betterthan-expected returns from another ...
... risk without an equivalent reduction in expected returns – Reduces the variability of returns – Caused by the offset of worse-thanexpected returns from one asset by betterthan-expected returns from another ...
Market Risk
... An intuitive example for Beta Turbo Charged Seafood has the following % returns on its stock, relative to the listed changes in the % return on the market portfolio. The beta of Turbo Charged Seafood can be derived from ...
... An intuitive example for Beta Turbo Charged Seafood has the following % returns on its stock, relative to the listed changes in the % return on the market portfolio. The beta of Turbo Charged Seafood can be derived from ...
Answers
... 3. The same three stocks as above are being considered for purchase. An investor has determined the following information: Stock A B C ...
... 3. The same three stocks as above are being considered for purchase. An investor has determined the following information: Stock A B C ...
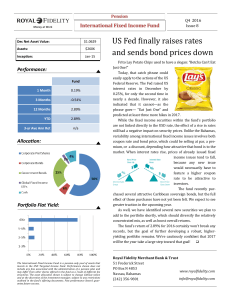
Schroder Fixed Income Fund - Wholesale Class Fund Summary Overview
... Security selection is carried out in a manner aiming to exploit those areas with the most potential for adding value. Independent fundamental credit research and active management at the security level are essential elements of our approach which focuses on the avoidance of default and identifying v ...
... Security selection is carried out in a manner aiming to exploit those areas with the most potential for adding value. Independent fundamental credit research and active management at the security level are essential elements of our approach which focuses on the avoidance of default and identifying v ...
Pioneers: Better be smart
... the pitfalls can be avoided by diversifying the holdings and rebalancing. The idea was first espoused in a seminal paper in 1982 published by Dr E Robert Fernholz, the founder of the firm and a creator of the enhanced equity portfolio construction method. “In the beginning, these findings were very ...
... the pitfalls can be avoided by diversifying the holdings and rebalancing. The idea was first espoused in a seminal paper in 1982 published by Dr E Robert Fernholz, the founder of the firm and a creator of the enhanced equity portfolio construction method. “In the beginning, these findings were very ...
top fund fortissimo - (c)
... The Correlation Coefficient indicates the strength and direction of a linear relationship between fund performance and benchmark. The coefficient is an element of [-1,1], where 1 equals a perfectly correlated increasing linear relationship, -1 equals a perfectly correlated decreasing linear relation ...
... The Correlation Coefficient indicates the strength and direction of a linear relationship between fund performance and benchmark. The coefficient is an element of [-1,1], where 1 equals a perfectly correlated increasing linear relationship, -1 equals a perfectly correlated decreasing linear relation ...
Investing During a Non-Normal Market Environment
... Contributing to the problem is the notion that ‘buy and hold’ investors are taking unlimited downside risks. This is not intuitive for most people who believe in this approach. While ‘buy and hold’ has had a glorious twenty-year reign, the advent of ETF’s, supersized mutual funds, leveraged investor ...
... Contributing to the problem is the notion that ‘buy and hold’ investors are taking unlimited downside risks. This is not intuitive for most people who believe in this approach. While ‘buy and hold’ has had a glorious twenty-year reign, the advent of ETF’s, supersized mutual funds, leveraged investor ...