Chapter 6
... Measuring Returns To measure the level of wealth created by an investment rather than the change in wealth, need to cumulate returns over time Cumulative Wealth Index, CWIn, over n periods, = WI (1 TR )(1 TR )...(1 TR ) ...
... Measuring Returns To measure the level of wealth created by an investment rather than the change in wealth, need to cumulate returns over time Cumulative Wealth Index, CWIn, over n periods, = WI (1 TR )(1 TR )...(1 TR ) ...
SFDCP Small Cap Value Equity Portfolio
... A risk-adjusted measure developed by Nobel Laureate William Sharpe. It is calculated by using standard deviation and excess return to determine reward per unit of risk. The higher the Sharpe Ratio, the better the fund's historical risk-adjusted performance. The Sharpe ratio is calculated for the pas ...
... A risk-adjusted measure developed by Nobel Laureate William Sharpe. It is calculated by using standard deviation and excess return to determine reward per unit of risk. The higher the Sharpe Ratio, the better the fund's historical risk-adjusted performance. The Sharpe ratio is calculated for the pas ...
Sanlam Investment Management Small Cap Fund
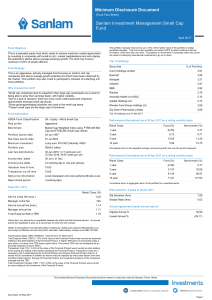
... -cap fund category of 1.12%. For the one year to 31 March 2017, the SIM Small Cap Fund generated a positive return of 5.84%, compared to the peer average return for the ASISA small- and mid-cap fund category of 8.45%. By contribution, taking into account total return (share price move and dividend r ...
... -cap fund category of 1.12%. For the one year to 31 March 2017, the SIM Small Cap Fund generated a positive return of 5.84%, compared to the peer average return for the ASISA small- and mid-cap fund category of 8.45%. By contribution, taking into account total return (share price move and dividend r ...
Governance, Transparency and Good Portfolio Management
... Easy to use and can customize their overall fund ...
... Easy to use and can customize their overall fund ...
The Three Biggest Risks to Successful Investing
... Profitability premium—high vs. low profitability companies ...
... Profitability premium—high vs. low profitability companies ...
Premier Multi-Asset Distribution Fund
... Box logistics assets will be let to institutional grade tenants on long-dated leases providing stable and growing revenue with the potential for capital appreciation, to achieve a target net return in excess of 9% per annum over the medium term. Tritax is a leading FCA-regulated, UK real estate fund ...
... Box logistics assets will be let to institutional grade tenants on long-dated leases providing stable and growing revenue with the potential for capital appreciation, to achieve a target net return in excess of 9% per annum over the medium term. Tritax is a leading FCA-regulated, UK real estate fund ...
Modeling Portfolios that Contain Risky Assets I: Risk and
... Given the complexity of the dynamics underlying such market fluctuations, we adopt a statistical approach to quantifying their trends and correlations. More specifically, we will choose an appropriate set of statistics that will be computed from selected return rate histories of the relevant assets ...
... Given the complexity of the dynamics underlying such market fluctuations, we adopt a statistical approach to quantifying their trends and correlations. More specifically, we will choose an appropriate set of statistics that will be computed from selected return rate histories of the relevant assets ...
30 June 2007 Balance Nature strives for balance. In the wild, lions
... Listed companies could be seeking to monetise their future earnings, raise capital or have other goals made possible by a public listing. Investors ...
... Listed companies could be seeking to monetise their future earnings, raise capital or have other goals made possible by a public listing. Investors ...
Chapter 1 A Brief History of Risk and Return
... The risk-free rate Rf = 8%. For a risk-free asset, = 0 by definition Note that if the investor borrows at the risk-free rate and invests the proceeds in asset A, the investment in asset A will exceed 100%. % of Portfolio in Asset A ...
... The risk-free rate Rf = 8%. For a risk-free asset, = 0 by definition Note that if the investor borrows at the risk-free rate and invests the proceeds in asset A, the investment in asset A will exceed 100%. % of Portfolio in Asset A ...
8. Over the past 75 years, we have observed that investments with
... 8. Over the past 75 years, we have observed that investments with higher average annual returns also tend to have the highest standard deviations in their annual returns. This observation supports the notion that there is a positive correlation between risk and return. Which of the following lists c ...
... 8. Over the past 75 years, we have observed that investments with higher average annual returns also tend to have the highest standard deviations in their annual returns. This observation supports the notion that there is a positive correlation between risk and return. Which of the following lists c ...
Chapter 1
... The Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH) says that the best valuation for an individual security is its current market price. A major conclusion of the EMH is that it will not be profitable to attempt to outperform the market. Even if there are those not fully informed or capable of appraising shares, ...
... The Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH) says that the best valuation for an individual security is its current market price. A major conclusion of the EMH is that it will not be profitable to attempt to outperform the market. Even if there are those not fully informed or capable of appraising shares, ...
How the Market Works… and What It Means for Your Portfolio
... about the suitability of investing in each emerging market, making considerations that include local market accessibility, government stability, and property rights, before making investments. For educational purposes; should not be used as investment advice. ...
... about the suitability of investing in each emerging market, making considerations that include local market accessibility, government stability, and property rights, before making investments. For educational purposes; should not be used as investment advice. ...
Making Diversification work for you With every
... inclined to reinvest any and all resources into his line of business. However, because this business-man has basically ‘put all of his eggs into one basket’, his resources are not diversified. Therefore, any event that adversely affects his line of business, presents the risk of a severe dent in his ...
... inclined to reinvest any and all resources into his line of business. However, because this business-man has basically ‘put all of his eggs into one basket’, his resources are not diversified. Therefore, any event that adversely affects his line of business, presents the risk of a severe dent in his ...
Financial Research Company
... Product2 – Portfolio analysis Main functions: 1. Analyze on return for investors 2. Analyze whether the BEST combination of assets that provides the most diversification benefit 3. Identify the assets that degraded portfolio’s performance 4. Ways to improve portfolio’s performance ...
... Product2 – Portfolio analysis Main functions: 1. Analyze on return for investors 2. Analyze whether the BEST combination of assets that provides the most diversification benefit 3. Identify the assets that degraded portfolio’s performance 4. Ways to improve portfolio’s performance ...
Lecture 4: Cost of capital and CAPM. First lecture
... • From the Markowitz Portfolio Selection model – Separation Theorem – All investors hold the same portfolio of risky assets ...
... • From the Markowitz Portfolio Selection model – Separation Theorem – All investors hold the same portfolio of risky assets ...
M.I.T. 15.460 Sloan School of Management Financial Engineering
... Financial Engineering Course Description This course provides an introduction to financial engineering. The course covers the following topics: asset pricing theory and its applications, financial optimization, market equilibrium, market frictions, dynamics trading strategies, risk management, and s ...
... Financial Engineering Course Description This course provides an introduction to financial engineering. The course covers the following topics: asset pricing theory and its applications, financial optimization, market equilibrium, market frictions, dynamics trading strategies, risk management, and s ...
CHAPTER 5 Risk and Rates of Return - Course ON-LINE
... Since every investor holds the tangency portfolio as the portfolio of risky assets, the tangency portfolio is the market portfolio (of risky assets). For A WM=50% WRf=50%, for B WM=125% WRf=-25%, All risky securities should have nonzero weight in the market portfolio. Demand should equal supply, oth ...
... Since every investor holds the tangency portfolio as the portfolio of risky assets, the tangency portfolio is the market portfolio (of risky assets). For A WM=50% WRf=50%, for B WM=125% WRf=-25%, All risky securities should have nonzero weight in the market portfolio. Demand should equal supply, oth ...
The Returns and Risks from Investing
... Measuring Returns • Total Return (TR) compares performance over time or across different securities • Total Return is a percentage relating all cash flows received during a given time period, denoted CFt +(PE - PB), to the start of period ...
... Measuring Returns • Total Return (TR) compares performance over time or across different securities • Total Return is a percentage relating all cash flows received during a given time period, denoted CFt +(PE - PB), to the start of period ...