Accruals, cash flows, and operating profitability in the cross section
... profitability factor contains more information than the combination of the accruals and operating profitability factors. Sloan (1996) shows that the accrual component of earnings is less persistent than the cash flow component. He posits that the accrual anomaly arises because investors do not unde ...
... profitability factor contains more information than the combination of the accruals and operating profitability factors. Sloan (1996) shows that the accrual component of earnings is less persistent than the cash flow component. He posits that the accrual anomaly arises because investors do not unde ...
Computational Methods in Finance
... Customers choose them if they offer low risk, high profit and small premium ...
... Customers choose them if they offer low risk, high profit and small premium ...
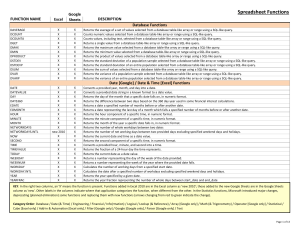
Spreadsheet Functions
... Calculates the accrued interest of a security that has periodic payments. Calculates the accrued interest of a security that pays interest at maturity. Returns the depreciation for each accounting period by using a depreciation coefficient Returns the depreciation for each accounting period Calculat ...
... Calculates the accrued interest of a security that has periodic payments. Calculates the accrued interest of a security that pays interest at maturity. Returns the depreciation for each accounting period by using a depreciation coefficient Returns the depreciation for each accounting period Calculat ...
Generating South African Volatility Surface
... Traders say volatilities are “skewed” when options of a given asset trade at increasing or decreasing levels of implied volatility as you move through the strikes. The volatility skew (smile) was first observed and mentioned by Black and Scholes in a paper that appeared in 1972 [BS 72]. It was then ...
... Traders say volatilities are “skewed” when options of a given asset trade at increasing or decreasing levels of implied volatility as you move through the strikes. The volatility skew (smile) was first observed and mentioned by Black and Scholes in a paper that appeared in 1972 [BS 72]. It was then ...
Volatility Markets Consistent modeling, hedging and practical
... these models, a parsimonious description of the dynamics of both the stock price and its instantaneous variance is the starting point. Such a model is based on “structural” assumptions on the underlying stock price. For example, Heston’s popular model [H93] assumes that the instantaneous variance of ...
... these models, a parsimonious description of the dynamics of both the stock price and its instantaneous variance is the starting point. Such a model is based on “structural” assumptions on the underlying stock price. For example, Heston’s popular model [H93] assumes that the instantaneous variance of ...
Earnings Surprises, Growth Expectations, and Stock
... between growth and value stocks is the same regardless of the sign of the earnings surprise. Thus, this table presents exactly the relation that would be expected if the two effects are completely unrelated. The table in figure 2 (a) contains the abnormal return behavior predicted by Basu (1977) and ...
... between growth and value stocks is the same regardless of the sign of the earnings surprise. Thus, this table presents exactly the relation that would be expected if the two effects are completely unrelated. The table in figure 2 (a) contains the abnormal return behavior predicted by Basu (1977) and ...
Earnings Seasonality and Stock Returns
... The nature of the earnings seasonality measure makes it unlikely that these returns are driven by seasonal firms having different fixed loadings on risk factors. In the first place, the portfolio of highly seasonal firms does not show higher volatility than the portfolio of negative seasonal firms. ...
... The nature of the earnings seasonality measure makes it unlikely that these returns are driven by seasonal firms having different fixed loadings on risk factors. In the first place, the portfolio of highly seasonal firms does not show higher volatility than the portfolio of negative seasonal firms. ...
Scotia Dividend Fund
... Suitability. Before purchasing a Scotia Dividend Fund GIC you should consider its suitability in relation to your investment objectives. Rate of return. The return payable, if any, is based on the performance of the Scotia Canadian Dividend Fund, which is a mutual fund. Mutual Funds have, in the pas ...
... Suitability. Before purchasing a Scotia Dividend Fund GIC you should consider its suitability in relation to your investment objectives. Rate of return. The return payable, if any, is based on the performance of the Scotia Canadian Dividend Fund, which is a mutual fund. Mutual Funds have, in the pas ...
Asset Liquidity and Stock Liquidity
... to measuring asset liquidity is similar to that of Berger and Bouwman (2009). Using this approach we come up with 4 alternative measures of asset liquidity that vary based on the liquidity scores assigned to the different assets. In our 1st set of tests we estimate the time-series and cross-sectiona ...
... to measuring asset liquidity is similar to that of Berger and Bouwman (2009). Using this approach we come up with 4 alternative measures of asset liquidity that vary based on the liquidity scores assigned to the different assets. In our 1st set of tests we estimate the time-series and cross-sectiona ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES THE EQUITY PREMIUM AND STRUCTURAL BREAKS Lubos Pastor
... (the expected "excess return"). It is well known that estimates of the equity premium based on historical data can vary widely, depending on the methodology and the sample period, and the imprecision in such estimates can figure prominently in inference and decision making. Pastor and Stambaugh (199 ...
... (the expected "excess return"). It is well known that estimates of the equity premium based on historical data can vary widely, depending on the methodology and the sample period, and the imprecision in such estimates can figure prominently in inference and decision making. Pastor and Stambaugh (199 ...
Strategic IPOs and product market competition
... Finally, shares of all publicly traded firms are infinitely divisible, and all investors are able to borrow and lend at the risk-free rate, rf. Under these assumptions, each investor maximizes expected utility by holding a certain combination of the risk-free asset and the market portfolio, and the ex ...
... Finally, shares of all publicly traded firms are infinitely divisible, and all investors are able to borrow and lend at the risk-free rate, rf. Under these assumptions, each investor maximizes expected utility by holding a certain combination of the risk-free asset and the market portfolio, and the ex ...
Mind the gap: the arms length principle and MNE value
... Multinational enterprises (MNEs) operating by way of wholly owned subsidiaries are responsible for an increasing percentage of global trade. This paper looks at how the existing rules based on the arm’s length principle allocate a MNE’s profit between the taxing jurisdictions in which it operates. I ...
... Multinational enterprises (MNEs) operating by way of wholly owned subsidiaries are responsible for an increasing percentage of global trade. This paper looks at how the existing rules based on the arm’s length principle allocate a MNE’s profit between the taxing jurisdictions in which it operates. I ...
Sentiment Dynamics and Stock Returns: The Case of
... information beyond the informational content of past and contemporaneous stock prices and returns themselves. This is also in harmony with the theoretical arguments laid out above as predictability of the noise component would evoke straightforward arbitrage arguments. Using sentiment data and retur ...
... information beyond the informational content of past and contemporaneous stock prices and returns themselves. This is also in harmony with the theoretical arguments laid out above as predictability of the noise component would evoke straightforward arbitrage arguments. Using sentiment data and retur ...
High Idiosyncratic Volatility and Low Returns
... and is also observed in the larger sample of 23 developed markets. Second and perhaps most interesting, the negative spread in returns between stocks with high and low idiosyncratic volatility in international markets strongly comoves with the difference in returns between U.S. stocks with high and ...
... and is also observed in the larger sample of 23 developed markets. Second and perhaps most interesting, the negative spread in returns between stocks with high and low idiosyncratic volatility in international markets strongly comoves with the difference in returns between U.S. stocks with high and ...
Entropy Measures in Finance and Risk Neutral Densities
... EPT Framework Consider a risky asset on time interval [0, T ]. Let YT be asset price process of ST at future time T . G as state space, a subset of real line R, g ST the probability densities on P H g the index of market uncertainty about YT . The H g is defined on the set of ...
... EPT Framework Consider a risky asset on time interval [0, T ]. Let YT be asset price process of ST at future time T . G as state space, a subset of real line R, g ST the probability densities on P H g the index of market uncertainty about YT . The H g is defined on the set of ...
The Misguided Beliefs of Financial Advisors
... These behavioral patterns have been studied extensively. See, for example, Nofsinger and Sias (1999), Grinblatt and Keloharju (2001b), Barber and Odean (2008), and Kaniel, Saar, and Titman (2008) for analyses of how investors trade in response to past price movements; Odean (1999), Barber and Odean ...
... These behavioral patterns have been studied extensively. See, for example, Nofsinger and Sias (1999), Grinblatt and Keloharju (2001b), Barber and Odean (2008), and Kaniel, Saar, and Titman (2008) for analyses of how investors trade in response to past price movements; Odean (1999), Barber and Odean ...