2. Predictability of asset returns Deterministic and Random Walk
... in a portfolio with several different assets. A third step was the Arbitrage pricing theory (APT) of Ross (1976), being a generalization of the latter. ...
... in a portfolio with several different assets. A third step was the Arbitrage pricing theory (APT) of Ross (1976), being a generalization of the latter. ...
Ch797
... What Is The Risk Premium? • Required to Compensate Investors for Risk • Higher the Variance or Standard Deviation, the Higher the Required Risk Premium • Degree of Dependency Affects the Risk Premium – The more negative the degree of dependency – The lower the risk of the portfolio – The lower the ...
... What Is The Risk Premium? • Required to Compensate Investors for Risk • Higher the Variance or Standard Deviation, the Higher the Required Risk Premium • Degree of Dependency Affects the Risk Premium – The more negative the degree of dependency – The lower the risk of the portfolio – The lower the ...
Guide
... 15% standard deviation on the horizontal axis). Recall that the efficient frontier is constructed by combining risky securities so that the risk is minimized for every return. The parabolic shape of the frontier comes from this minimization process. The risk free asset is the (red) dot on the vertic ...
... 15% standard deviation on the horizontal axis). Recall that the efficient frontier is constructed by combining risky securities so that the risk is minimized for every return. The parabolic shape of the frontier comes from this minimization process. The risk free asset is the (red) dot on the vertic ...
Week Four Review Questions and Problems
... 8-5. Systematic risk is the variability in a security’s total returns that is directly associated with overall movements in the general market or economy. Nonsystematic risk is firm-specific, meaning that it only affects one firm or a small number of firms. Proper diversification cannot reduce syste ...
... 8-5. Systematic risk is the variability in a security’s total returns that is directly associated with overall movements in the general market or economy. Nonsystematic risk is firm-specific, meaning that it only affects one firm or a small number of firms. Proper diversification cannot reduce syste ...
EDITOR`S CORNER Managing Investments for
... about extended shortfalls on any single metric. Imagine two strategies, each of which is “perfect” for one of the first two objectives. ■ Model Portfolio 1. The first strategy begins with an assumption that 15-year strips provide a nearly perfect fit with liabilities. Suppose we found a way in 1988 ...
... about extended shortfalls on any single metric. Imagine two strategies, each of which is “perfect” for one of the first two objectives. ■ Model Portfolio 1. The first strategy begins with an assumption that 15-year strips provide a nearly perfect fit with liabilities. Suppose we found a way in 1988 ...
Investments, Chapter 5
... If you require a risk premium of 10 percent, then you will invest in X only if E[rX ] − rF ≥ 10%, i.e. only if 100, 000 − p 100, 000 − p ...
... If you require a risk premium of 10 percent, then you will invest in X only if E[rX ] − rF ≥ 10%, i.e. only if 100, 000 − p 100, 000 − p ...
Oregon State University
... asset class and a U.S. corporate fixed income asset class, that your firm invests their clients’ money in. This analysis will compliment analyses performed by other analysts to develop portfolios for your firm’s clients. Your firm uses a multifactor model approach to develop these expectations. Mult ...
... asset class and a U.S. corporate fixed income asset class, that your firm invests their clients’ money in. This analysis will compliment analyses performed by other analysts to develop portfolios for your firm’s clients. Your firm uses a multifactor model approach to develop these expectations. Mult ...
Investment Analysis and Portfolio Management
... adjust so that the demand and supply of assets are equal Many modifications/extensions can be made ...
... adjust so that the demand and supply of assets are equal Many modifications/extensions can be made ...
1 Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)
... We now assume an idealized framework for an open market place, where all the risky assets refer to (say) all the tradeable stocks available to all. In addition we have a risk-free asset (for borrowing and/or lending in unlimited quantities) with interest rate rf . We assume that all information is a ...
... We now assume an idealized framework for an open market place, where all the risky assets refer to (say) all the tradeable stocks available to all. In addition we have a risk-free asset (for borrowing and/or lending in unlimited quantities) with interest rate rf . We assume that all information is a ...
Expected Return Standard Deviation Increasing Utility
... Investor’s preferences toward the exp. return and risk may be expressed by the utility function that is higher for higher exp. returns and lower for higher risks. More risk-averse investors will apply greater penalties for risk. The greater the risk, the larger the penalty. We can formalize the risk ...
... Investor’s preferences toward the exp. return and risk may be expressed by the utility function that is higher for higher exp. returns and lower for higher risks. More risk-averse investors will apply greater penalties for risk. The greater the risk, the larger the penalty. We can formalize the risk ...
Lecture 10
... Expectation, variance, standard error (deviation), covariance, and correlation of returns may be based on ...
... Expectation, variance, standard error (deviation), covariance, and correlation of returns may be based on ...
Fin 331, Exam 2, Spring 2009
... 19. Most evidence indicates that U.S. stock markets are _______________________, A) Reasonably weak form and semi-strong form efficient B) Strong form efficient C) Reasonably weak form but not semi- or strong form efficient D) Neither weak form, semi- or strong form efficient 20. Which of the follo ...
... 19. Most evidence indicates that U.S. stock markets are _______________________, A) Reasonably weak form and semi-strong form efficient B) Strong form efficient C) Reasonably weak form but not semi- or strong form efficient D) Neither weak form, semi- or strong form efficient 20. Which of the follo ...
Finance - Mathematics
... Mathematical Finance Presentation Handout Abstract This presentation will give a broad overview of financial mathematics with topics including, measuring risk and return, methods of valuation for various assets, and portfolio optimization. I will discuss the background of how these concepts are deri ...
... Mathematical Finance Presentation Handout Abstract This presentation will give a broad overview of financial mathematics with topics including, measuring risk and return, methods of valuation for various assets, and portfolio optimization. I will discuss the background of how these concepts are deri ...
Actuarial Science Meets Financial Economics
... Incorporate risk into calculations Use specialized languages ...
... Incorporate risk into calculations Use specialized languages ...
Ch.5 part2
... • Risk aversion implies that investors will accept a lower reward (portfolio expected return) in exchange for a sufficient reduction in risk (std dev of portfolio return) • A statistic commonly used to rank portfolios in terms of the risk-return trade-off is the Sharpe measure (also reward-to-volati ...
... • Risk aversion implies that investors will accept a lower reward (portfolio expected return) in exchange for a sufficient reduction in risk (std dev of portfolio return) • A statistic commonly used to rank portfolios in terms of the risk-return trade-off is the Sharpe measure (also reward-to-volati ...
Key Concepts and Skills Expected Returns
... • Portfolio diversification is the investment in several different asset classes or sectors • Diversification is not just holding a lot of assets • For example, if you own 50 Internet stocks, then you are not diversified • However, if you own 50 stocks that span 20 different industries, then you are ...
... • Portfolio diversification is the investment in several different asset classes or sectors • Diversification is not just holding a lot of assets • For example, if you own 50 Internet stocks, then you are not diversified • However, if you own 50 stocks that span 20 different industries, then you are ...
Finance 332
... a. that all investors hold the same market portfolio regardless of risk aversion b. that only risk neutral investors will hold the same market portfolio c. that investors hold different stocks based on their risk aversion d. that investors hold different market portfolios when the lending rate is eq ...
... a. that all investors hold the same market portfolio regardless of risk aversion b. that only risk neutral investors will hold the same market portfolio c. that investors hold different stocks based on their risk aversion d. that investors hold different market portfolios when the lending rate is eq ...
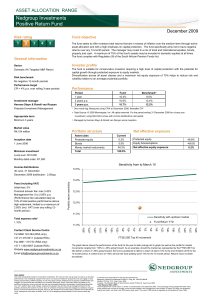
Nedgroup Investments Positive Return Fund
... The fund seeks to offer investors total returns that are in excess of inflation over the medium-term through active asset allocation and with a high emphasis on capital protection. The fund specifically aims not to have negative returns over any 12-month period. The manager may invest in a mix of lo ...
... The fund seeks to offer investors total returns that are in excess of inflation over the medium-term through active asset allocation and with a high emphasis on capital protection. The fund specifically aims not to have negative returns over any 12-month period. The manager may invest in a mix of lo ...
Regulation of credit and maximum rates: an analysis of their effects
... Since the promulgation of Financial System Law No. 393, the social function was introduced into the activity of Bolivian financial intermediation. In this direction, the regulation established maximum limits for the active interest rates and minimum levels of portfolio destined to sectors considered ...
... Since the promulgation of Financial System Law No. 393, the social function was introduced into the activity of Bolivian financial intermediation. In this direction, the regulation established maximum limits for the active interest rates and minimum levels of portfolio destined to sectors considered ...