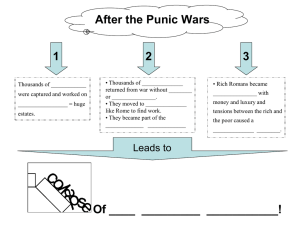
After the Punic Wars
... and Caesar defeated Pompey. After the civil war, Caesar was given more power. Senators didn't trust anyone who wanted to be a dictator and take their power. They thought he was trying to end the Republic. Caesar tried to get control of the senate by adding more senators who were loyal to him. Theref ...
... and Caesar defeated Pompey. After the civil war, Caesar was given more power. Senators didn't trust anyone who wanted to be a dictator and take their power. They thought he was trying to end the Republic. Caesar tried to get control of the senate by adding more senators who were loyal to him. Theref ...
Roman Numeral Outline (RNO)
... 1. Republic-government where citizens select their leaders 2. Consuls- two chief officials a. limited power b. powered divided equally between the two c. veto power d. beginning in 367 B.C. one had to be a plebeian 3. The senate = most powerful part of the Roman Republic a. initially, all senate mem ...
... 1. Republic-government where citizens select their leaders 2. Consuls- two chief officials a. limited power b. powered divided equally between the two c. veto power d. beginning in 367 B.C. one had to be a plebeian 3. The senate = most powerful part of the Roman Republic a. initially, all senate mem ...
WH 1 Lesson 28 Instructional Resource 1
... Pompey, and Marcus Crassus formed in 60 B.C. – Triumvirate is a ruling board or commission of three men. ...
... Pompey, and Marcus Crassus formed in 60 B.C. – Triumvirate is a ruling board or commission of three men. ...
fall of the roman republic: 133-27 bc
... The Rise of Popular Tribunes (brothers Gracchus) Reformers who tried to use their plebian tribune status to seize power and reform the Senate. Both murdered. The Rise of Private Armies Roman Generals Marius and Sulla recruited private armies more loyal to themselves than to the state. The two co ...
... The Rise of Popular Tribunes (brothers Gracchus) Reformers who tried to use their plebian tribune status to seize power and reform the Senate. Both murdered. The Rise of Private Armies Roman Generals Marius and Sulla recruited private armies more loyal to themselves than to the state. The two co ...
Roman Empire - Gilbert Public Schools
... – Romans borrowed their alphabet • Etruscans borrowed from Greeks ...
... – Romans borrowed their alphabet • Etruscans borrowed from Greeks ...
Government
... voted on some big issues, if the consuls asked them to. Things like whether to go to war. And they elected the consuls and prefects and the Senators. But the Assembly was set up so that richer people got more votes than poorer people. Which to me is unfair. ...
... voted on some big issues, if the consuls asked them to. Things like whether to go to war. And they elected the consuls and prefects and the Senators. But the Assembly was set up so that richer people got more votes than poorer people. Which to me is unfair. ...
Greek and Roman Government - Mr. Hudec and His Latin Stuff
... Judge; must be at least 39 years old Consul Two elected men at least 40 years old; executive power ...
... Judge; must be at least 39 years old Consul Two elected men at least 40 years old; executive power ...
1 CLAS 111 Final Exam Review sheet: I cannot guarantee
... Romans: effective end of struggle of orders 264-241 First Punic War 218-201 Second Punic War 149-146 Third Punic War 133 Tiberius Gracchus tribune of the plebs 107 Marius consul for first time 91-89 Social War (war between Rome and its Italian allies) 88 Sulla marches on Rome 83-81 Civil war between ...
... Romans: effective end of struggle of orders 264-241 First Punic War 218-201 Second Punic War 149-146 Third Punic War 133 Tiberius Gracchus tribune of the plebs 107 Marius consul for first time 91-89 Social War (war between Rome and its Italian allies) 88 Sulla marches on Rome 83-81 Civil war between ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... In 44 B.C., Caesar’s _____________gathered around him as he entered the senate and stabbed him to death. From Republic to Empire: After Caesar’s death _______ war broke out. Caesar’s nephew, (18 years old), ___________, Mark Antony, and Marcus Lepidus defeated those who killed _______. Then they fo ...
... In 44 B.C., Caesar’s _____________gathered around him as he entered the senate and stabbed him to death. From Republic to Empire: After Caesar’s death _______ war broke out. Caesar’s nephew, (18 years old), ___________, Mark Antony, and Marcus Lepidus defeated those who killed _______. Then they fo ...
The Collapse of the Republic
... full Roman citizenship • Augustus was probably the best, most capable of all the emperors (too bad he was the 1st) • In spite of a number of poor, lousy, malicious, and insane emperors, the empire would last another 400 years after his death due to the civil service he set up. • These paid workers w ...
... full Roman citizenship • Augustus was probably the best, most capable of all the emperors (too bad he was the 1st) • In spite of a number of poor, lousy, malicious, and insane emperors, the empire would last another 400 years after his death due to the civil service he set up. • These paid workers w ...