What is a species?
... ___________________________________ = no nucleus or membrane bound organelles; simple cells ___________________________________ = nucleus & membrane bound organelles (cells are more complex). ___________________________________ = organism made up of 1 cell ___________________________________ = organ ...
... ___________________________________ = no nucleus or membrane bound organelles; simple cells ___________________________________ = nucleus & membrane bound organelles (cells are more complex). ___________________________________ = organism made up of 1 cell ___________________________________ = organ ...
Ecology is the study of interactions among and with their environment
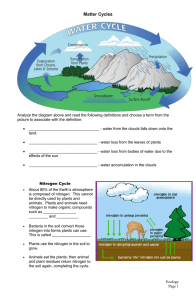
... Animals eat the plants; then animal and plant residues return nitrogen to the soil again, completing the cycle. ...
... Animals eat the plants; then animal and plant residues return nitrogen to the soil again, completing the cycle. ...
WINTER ANNUAL LEGUMES AS A NITROGEN SOURCE
... rainfall. The soil will be saturated for a depth of about 12". On coarser textured soil, moistureholding capacity will be less and leaching will be greater. On finer textured soil, moistureholding capacity will be greater and leaching will be less. The use of a rain gauge is strongly recommended so ...
... rainfall. The soil will be saturated for a depth of about 12". On coarser textured soil, moistureholding capacity will be less and leaching will be greater. On finer textured soil, moistureholding capacity will be greater and leaching will be less. The use of a rain gauge is strongly recommended so ...
Paleozoic Era
... increases as the frequency of the electromagnetic wave increases. a plant’s response to the lengths of daylight and darkness each day. lowest layer of the Sun’s atmosphere; gives off light and has temperatures of about 6,000 K. process by which plants and many other producers use light energy to pro ...
... increases as the frequency of the electromagnetic wave increases. a plant’s response to the lengths of daylight and darkness each day. lowest layer of the Sun’s atmosphere; gives off light and has temperatures of about 6,000 K. process by which plants and many other producers use light energy to pro ...
powerpoint
... soils. Softer, sedimentary rocks (eg: shale) weather more quickly. Chemical composition & soil colour: minerals derived from quartzite and granite have a relatively high silica content and are acidic; soils on chalk and limestone are alkaline. The darker the parent material the darker the soil. ...
... soils. Softer, sedimentary rocks (eg: shale) weather more quickly. Chemical composition & soil colour: minerals derived from quartzite and granite have a relatively high silica content and are acidic; soils on chalk and limestone are alkaline. The darker the parent material the darker the soil. ...
Topic 5.3 Soil Degradation
... a. Identify the given situation as a positive or negative feedback mechanism (it is an example of positive feedback), using examples from the scenario to justify your answer. ...
... a. Identify the given situation as a positive or negative feedback mechanism (it is an example of positive feedback), using examples from the scenario to justify your answer. ...
37_LectureOutline_LO
... For example, many plants acquire nitrogen in the form of nitrate ions (NO3−). However, as van Helmont’s data suggested, mineral nutrients from the soil contribute little to the overall mass of a plant. ...
... For example, many plants acquire nitrogen in the form of nitrate ions (NO3−). However, as van Helmont’s data suggested, mineral nutrients from the soil contribute little to the overall mass of a plant. ...
Parent materials
... deciduous-hardwood forests. Soils in these areas are referred to as prairie soils and timber soils. ...
... deciduous-hardwood forests. Soils in these areas are referred to as prairie soils and timber soils. ...
Chapter 1 – The Scope of Biology
... – If a particular variation is helpful, individual with the variation may live longer and produce more offspring than those that do not have it. (this is called natural selection) ...
... – If a particular variation is helpful, individual with the variation may live longer and produce more offspring than those that do not have it. (this is called natural selection) ...
KEY______KEY_____KEY__ Earth`s Changing - Parkway C-2
... dead organisms into smaller pieces and digest them with chemicals. ...
... dead organisms into smaller pieces and digest them with chemicals. ...
LOTL 10 Soils
... three of these types of particles in relatively equal amounts. Loamy soil is ideal for most garden plants because it holds plenty of moisture but also drains well so that sufficient air can reach the roots. ...
... three of these types of particles in relatively equal amounts. Loamy soil is ideal for most garden plants because it holds plenty of moisture but also drains well so that sufficient air can reach the roots. ...
Chapter 13 Study Guide
... producers -organisms that make their own food (Ex: plants and some bacteria) consumers-organisms that obtain energy by feeding on other organisms (Ex: animals) Carnivores-type of consumers that eat only animals. Scavenger-type of carnivore that feeds on dead organisms Herbivore-type of consumers tha ...
... producers -organisms that make their own food (Ex: plants and some bacteria) consumers-organisms that obtain energy by feeding on other organisms (Ex: animals) Carnivores-type of consumers that eat only animals. Scavenger-type of carnivore that feeds on dead organisms Herbivore-type of consumers tha ...
Nutrient Cycles - drakepond8thgradescience
... Importance: needed for many biological compounds such as DNA and for bone formation. ...
... Importance: needed for many biological compounds such as DNA and for bone formation. ...
Soil Notes
... erodible land out of production and replanting it with soil-saving plants for 1015 years ...
... erodible land out of production and replanting it with soil-saving plants for 1015 years ...
Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
... Roots are a sink – provide place for sugar to be used for cellular activities (respiration) Source to sink – leaves to roots or any place that needs sugar (new leaves…) ...
... Roots are a sink – provide place for sugar to be used for cellular activities (respiration) Source to sink – leaves to roots or any place that needs sugar (new leaves…) ...
Human Population Effects On Environment
... and nitrates by nitrifying bacteria. This is basically an intensification of the natural processes that take place during the nitrogen cycle. ...
... and nitrates by nitrifying bacteria. This is basically an intensification of the natural processes that take place during the nitrogen cycle. ...
Soil color – a window for public and educators to understands soils
... Soil color is one of the most visually striking properties recorded by soil scientists around the world. Soil color is an important characteristic related to soil properties such organic matter, parent materials, drainage. It is a simplified way for the public and educators alike to understand soils ...
... Soil color is one of the most visually striking properties recorded by soil scientists around the world. Soil color is an important characteristic related to soil properties such organic matter, parent materials, drainage. It is a simplified way for the public and educators alike to understand soils ...
Topic 543: Tetanus
... Introduction: Tetanus is caused by the bacteria Clostridium Tetani which can be found in soil, water, and dust. Tetanus can enter the body through minor cuts or skin abrasions, and is a serious and sometimes fatal disease that can attack the nervous system and cause severe uncontrollable muscle spas ...
... Introduction: Tetanus is caused by the bacteria Clostridium Tetani which can be found in soil, water, and dust. Tetanus can enter the body through minor cuts or skin abrasions, and is a serious and sometimes fatal disease that can attack the nervous system and cause severe uncontrollable muscle spas ...
Lesson Title: Soil Mapping the Schoolyard Grade levels: Grades 3
... discussion about types of soil occurs. Explain that maps are created to show the types of soil in an area. Show and discuss the sample soil map. Pay particular attention to the symbols on the map. Main Lesson: (may take several sessions of 30 to 45 minutes each) 1. Explain that the class will be cre ...
... discussion about types of soil occurs. Explain that maps are created to show the types of soil in an area. Show and discuss the sample soil map. Pay particular attention to the symbols on the map. Main Lesson: (may take several sessions of 30 to 45 minutes each) 1. Explain that the class will be cre ...
Biology Spring Final Bingo
... All viruses are made of proteins and The basic structure of a virus includes DNA or RNA surrounded by a These viruses infect bacteria only Bacteria that cause disease are called… A bacterial infection results when bacteria break down the body’s… This is caused by a virus not a bacterium… Viral disea ...
... All viruses are made of proteins and The basic structure of a virus includes DNA or RNA surrounded by a These viruses infect bacteria only Bacteria that cause disease are called… A bacterial infection results when bacteria break down the body’s… This is caused by a virus not a bacterium… Viral disea ...
Soil Exploration
... 1. Which type of soil drained the fastest? Which drained the slowest? What factors in the soil do you think resulted in the speed of percolation? 2. Which types of soils contained organic material? How do you know? How would that affect the number and type of organisms that live in and around the so ...
... 1. Which type of soil drained the fastest? Which drained the slowest? What factors in the soil do you think resulted in the speed of percolation? 2. Which types of soils contained organic material? How do you know? How would that affect the number and type of organisms that live in and around the so ...
SOIL FORMATION FACTORS
... inmost soil, high organic matter content and well-decomposed and acidic soil ...
... inmost soil, high organic matter content and well-decomposed and acidic soil ...