File
... ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM 14. A system of folded membranes in which proteins, lipids, and other materialsare made is the ______________________. 15. Two forms of endoplasmic reticulum are and ______________________. ...
... ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM 14. A system of folded membranes in which proteins, lipids, and other materialsare made is the ______________________. 15. Two forms of endoplasmic reticulum are and ______________________. ...
B Cell Receptor Complexes - Sigma
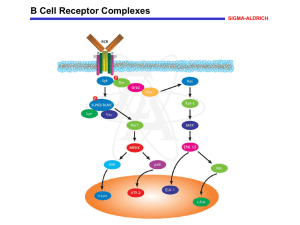
... family are activated initially and phosphorylate CD79 and CD79ß, thereby creating phosphotyrosine motifs that recruit downstream signaling molecules. In particular, phosphorylation of the BCR complex leads to the recruitment and activation of the protein tyrosine kinase Syk, which, in turn, promote ...
... family are activated initially and phosphorylate CD79 and CD79ß, thereby creating phosphotyrosine motifs that recruit downstream signaling molecules. In particular, phosphorylation of the BCR complex leads to the recruitment and activation of the protein tyrosine kinase Syk, which, in turn, promote ...
Cell Cycle
... Keep apoptotic pathway turned off by binding to a protein called Apaf-1 (apoptotic protease activating factor-1) Block release of cytochrome c by making it more difficult for the mitochondria to burst Internal damage to cell causes Bcl-2 protein to release Apaf-1 Apoptotic stimulus - Bcl-x (a relate ...
... Keep apoptotic pathway turned off by binding to a protein called Apaf-1 (apoptotic protease activating factor-1) Block release of cytochrome c by making it more difficult for the mitochondria to burst Internal damage to cell causes Bcl-2 protein to release Apaf-1 Apoptotic stimulus - Bcl-x (a relate ...
Cell Analogy Paper
... 6. Like a control room, the nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear envelope (controls what goes in and out) 7. Like a power plant, the mitochondria convert the energy in food to energy the cell can use. 8. Like an assembly line, the endoplasmic reticulum is where stuff is made. ...
... 6. Like a control room, the nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear envelope (controls what goes in and out) 7. Like a power plant, the mitochondria convert the energy in food to energy the cell can use. 8. Like an assembly line, the endoplasmic reticulum is where stuff is made. ...
Organelles
... Makes the essential proteins that are needed by the cell to carry out life processes The “transport system” of the cell. Once the protein is made, the E.R. takes it where it needs to go ...
... Makes the essential proteins that are needed by the cell to carry out life processes The “transport system” of the cell. Once the protein is made, the E.R. takes it where it needs to go ...
signal molecule
... retinoic acid) and bind to intracellular receptors The hormone-receptor complex has an exposed DNA binding site and can activate transcription directly (or, more typically as a homo- or hetero-dimer) This usually initiates a cascade of transcription events ...
... retinoic acid) and bind to intracellular receptors The hormone-receptor complex has an exposed DNA binding site and can activate transcription directly (or, more typically as a homo- or hetero-dimer) This usually initiates a cascade of transcription events ...
P. 64 looking Inside cells
... receive proteins and other newly formed materials and distribute them to other parts of the cell. 15. Organelles called capture energy from sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell. 16. The storage area of a cell is called a(n) ...
... receive proteins and other newly formed materials and distribute them to other parts of the cell. 15. Organelles called capture energy from sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell. 16. The storage area of a cell is called a(n) ...
Topic Report Cell Death: From Morphological to Molecular Definitions
... Programmed cell death =\= apoptosis =\= caspase activation =\= non-immunogenic cell death ...
... Programmed cell death =\= apoptosis =\= caspase activation =\= non-immunogenic cell death ...
What the Cell? - Effingham County Schools
... Cells! Who wants some?! Not that type, but this kind… ...
... Cells! Who wants some?! Not that type, but this kind… ...
Alphabodies – working inside the cell
... which limit their target space to about 10% of all human proteins; similarly, biologics, including antibodies, lack the ability to penetrate through cell membranes, and therefore can only address another 10%, that exist as extracellular proteins. It is therefore estimated that the vast majority of a ...
... which limit their target space to about 10% of all human proteins; similarly, biologics, including antibodies, lack the ability to penetrate through cell membranes, and therefore can only address another 10%, that exist as extracellular proteins. It is therefore estimated that the vast majority of a ...
Chapter 3 Section 3
... bound sacs that serve as the packaging and distribution center of the cell Enzymes inside the golgi modify the proteins, which then are enclosed in new Vesicles that bud from the surface of the golgi apparatus ...
... bound sacs that serve as the packaging and distribution center of the cell Enzymes inside the golgi modify the proteins, which then are enclosed in new Vesicles that bud from the surface of the golgi apparatus ...
Trends in Biotechnology
... The cell does not have many big spaces in it. The cell is really very crowded. ...
... The cell does not have many big spaces in it. The cell is really very crowded. ...
WHAT LIMITS CELL SIZE
... DIFFUSION: Diffusion is a fast and efficient process over short distances, however becomes slow and inefficient as distance increases Ex: mitochondria at center of very large cell – can’t get necessary nutrients from diffusion ...
... DIFFUSION: Diffusion is a fast and efficient process over short distances, however becomes slow and inefficient as distance increases Ex: mitochondria at center of very large cell – can’t get necessary nutrients from diffusion ...
Lokeshwar et al: Supplemental Information Antibodies and
... cells were transfected with either vector or myr-Akt plasmid. Twenty-four hour following transfection, cells were treated with myr-Akt. A: total Akt and phospho-Akt expression in PC3ML transfectants after 24 h of 4-MU treatment (0.4 mM). B: Cell proliferation: PC3-ML transfectants were treated with ...
... cells were transfected with either vector or myr-Akt plasmid. Twenty-four hour following transfection, cells were treated with myr-Akt. A: total Akt and phospho-Akt expression in PC3ML transfectants after 24 h of 4-MU treatment (0.4 mM). B: Cell proliferation: PC3-ML transfectants were treated with ...
Prezentacja programu PowerPoint
... initial stage of the immune defense. They are cytotoxic without prior senitization or MHC restriction for transformed cells or cells infected with some viruses or bacteria. Our data indicate that level of NK activity correlates with a health status. Low NK cell function in elderly individuals is ass ...
... initial stage of the immune defense. They are cytotoxic without prior senitization or MHC restriction for transformed cells or cells infected with some viruses or bacteria. Our data indicate that level of NK activity correlates with a health status. Low NK cell function in elderly individuals is ass ...
Complete the following table to fully describe the various organelles
... Complete the following table to fully describe the various organelles Cell Structure ...
... Complete the following table to fully describe the various organelles Cell Structure ...
No Slide Title
... ATM/p53 Signaling Pathway The ataxia telangiectasia-mutated gene (ATM) encodes a protein kinase that acts as a tumor suppressor. ATM activation, via IR damage to DNA, stimulates DNA repair and blocks cell cycle progression. One mechanism through which this occurs is ATM dependent phosphorylation of ...
... ATM/p53 Signaling Pathway The ataxia telangiectasia-mutated gene (ATM) encodes a protein kinase that acts as a tumor suppressor. ATM activation, via IR damage to DNA, stimulates DNA repair and blocks cell cycle progression. One mechanism through which this occurs is ATM dependent phosphorylation of ...
END OF CHAPTER QUESTIONS
... Mitosis stages: In Prophase, chromosomes appear after chromatin coils; the nucleolus breaks down; elongated microtubules grow from centrioles; and the nuclear envelope disappears. In Metaphase, chromosomes align in the equatorial middle of the cell. In Anaphase, microtubule strands pull sister chrom ...
... Mitosis stages: In Prophase, chromosomes appear after chromatin coils; the nucleolus breaks down; elongated microtubules grow from centrioles; and the nuclear envelope disappears. In Metaphase, chromosomes align in the equatorial middle of the cell. In Anaphase, microtubule strands pull sister chrom ...
Marine Natural Products with Potential as Treatments for Pancreatic
... Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute at FAU ...
... Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute at FAU ...
Multiple Effects of Hymenocrater longiflorus on human colon cancer
... Immunoflourescence staining for γ-H2AX on RKO cell line at 4 hrs for 80 and 100µg ml-1 H. longiflorus plant extract in compares with CPT, UV and NT cells. Also during treatment with plant extract at different times and concentrations observe increasing in proteins like P21, P53, P53-P, γ-H2AX and cl ...
... Immunoflourescence staining for γ-H2AX on RKO cell line at 4 hrs for 80 and 100µg ml-1 H. longiflorus plant extract in compares with CPT, UV and NT cells. Also during treatment with plant extract at different times and concentrations observe increasing in proteins like P21, P53, P53-P, γ-H2AX and cl ...
PARTS OF THE CELL CELL ORGANELLES
... NUCLEUS: controls most cell processes and contains DNA (code for all proteins and other molecules made by cells) ...
... NUCLEUS: controls most cell processes and contains DNA (code for all proteins and other molecules made by cells) ...
Apoptosis

Apoptosis (/ˌæpəˈtoʊsɪs/; from Ancient Greek ἀπό apo, ""by, from, of, since, than"" and πτῶσις ptōsis, ""fall"") is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, chromosomal DNA fragmentation, and global mRNA decay.In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's lifecycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic bodies that phagocytic cells are able to engulf and quickly remove before the contents of the cell can spill out onto surrounding cells and cause damage.Between 50 and 70 billion cells die each day due to apoptosis in the average human adult. For an average child between the ages of 8 and 14, approximately 20 billion to 30 billion cells die a day.Research in and around apoptosis has increased substantially since the early 1990s. In addition to its importance as a biological phenomenon, defective apoptotic processes have been implicated in a wide variety of diseases. Excessive apoptosis causes atrophy, whereas an insufficient amount results in uncontrolled cell proliferation, such as cancer.Some factors like Fas receptor, caspases (C-cysteine rich, asp- aspartic acid moiety containing, ase – proteases) etc. promote apoptosis, while members of Bcl-2 inhibit apoptosis.