LKB-1 / STK-11
... Yoo LI, Chung DC, Yuan J. LKB1- A Master Tumor Suppressor of the Small Intestine and Beyond. Nature Reviews; 2: 529-535. ...
... Yoo LI, Chung DC, Yuan J. LKB1- A Master Tumor Suppressor of the Small Intestine and Beyond. Nature Reviews; 2: 529-535. ...
Section D - Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Chromosome Structure
... tumor suppressor genes act in a genetically dominant manner. there are fewer tumor suppressor genes known than oncogenes. the retinoblastoma gene is a tumor suppressor gene. tumor suppressor genes normally become oncogenic by mutations that eliminate their normal activity. E tumor suppressor genes c ...
... tumor suppressor genes act in a genetically dominant manner. there are fewer tumor suppressor genes known than oncogenes. the retinoblastoma gene is a tumor suppressor gene. tumor suppressor genes normally become oncogenic by mutations that eliminate their normal activity. E tumor suppressor genes c ...
Discussion Questions for first 2 weeks.
... 12. How do the major and minor grooves of DNA engage the proteins? 13. What are the contacts and their significance of the PPAR LBD? 14. When DBD to DBD association constants are measured with DNA, the binding is weaker that found in the full-length protein. Why? 15. Structures are shown for two hor ...
... 12. How do the major and minor grooves of DNA engage the proteins? 13. What are the contacts and their significance of the PPAR LBD? 14. When DBD to DBD association constants are measured with DNA, the binding is weaker that found in the full-length protein. Why? 15. Structures are shown for two hor ...
Read Jan 9, Discussion on Jan 11, two papers
... 12. How do the major and minor grooves of DNA engage the proteins? 13. What are the contacts and their significance of the PPAR LBD? 14. When DBD to DBD association constants are measured with DNA, the binding is weaker that found in the full-length protein. Why? 15. Structures are shown for two hor ...
... 12. How do the major and minor grooves of DNA engage the proteins? 13. What are the contacts and their significance of the PPAR LBD? 14. When DBD to DBD association constants are measured with DNA, the binding is weaker that found in the full-length protein. Why? 15. Structures are shown for two hor ...
A G-protein-coupled receptor
... Amplification of an external signal downstream from a cell-surface receptor. ...
... Amplification of an external signal downstream from a cell-surface receptor. ...
BACTERIAL CATALASE AND CYTOCHROME OXIDASE TESTS
... Respiratory metabolism results in the conversion of glucose into energy in the form of ATP by the processes of glycolysis, Kreb’s cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. In the process of respiratory metabolism, most of the ATP is generated as a result of the activity of the electron transport system. ...
... Respiratory metabolism results in the conversion of glucose into energy in the form of ATP by the processes of glycolysis, Kreb’s cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. In the process of respiratory metabolism, most of the ATP is generated as a result of the activity of the electron transport system. ...
Exam Cell Biolog + Answers (V10
... A) Only target cells are exposed to aldosterone B) Only target cells contain receptors for aldosterone C) Aldosterone is unable to enter nontarget cells D) Nontarget cells destroy aldosterone before it can produce its effect E) Nontarget cells convert aldosterone to a hormone to which they do respon ...
... A) Only target cells are exposed to aldosterone B) Only target cells contain receptors for aldosterone C) Aldosterone is unable to enter nontarget cells D) Nontarget cells destroy aldosterone before it can produce its effect E) Nontarget cells convert aldosterone to a hormone to which they do respon ...
Outline 4.2 (M)
... • Compare active transport with passive transport. • Describe the importance of the sodium-potassium pump. • Distinguish between endocytosis and exocytosis. • Identify three ways that receptor proteins can change the activity of a cell. Movement Against a Concentration Gradient • The transport of a ...
... • Compare active transport with passive transport. • Describe the importance of the sodium-potassium pump. • Distinguish between endocytosis and exocytosis. • Identify three ways that receptor proteins can change the activity of a cell. Movement Against a Concentration Gradient • The transport of a ...
Cellular defense mechanisms against the biological effects of
... Induced by Chronic and Acute Doses ...
... Induced by Chronic and Acute Doses ...
Lizzie Yasewicz Date: 2/23/12 Student Conference Abstract
... therapeutic approaches and effective new strategies are desperately needed (Shukla et al.). cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) is a cellular transcription factor which has previously been linked to cell proliferation, fibrogenesis and cell transformation in other cancers (Shukla et al.). S ...
... therapeutic approaches and effective new strategies are desperately needed (Shukla et al.). cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) is a cellular transcription factor which has previously been linked to cell proliferation, fibrogenesis and cell transformation in other cancers (Shukla et al.). S ...
SMART Notebook
... Includes: protozoans (animal-like), algae (plant-like), euglena (plant/animal), slime mold ...
... Includes: protozoans (animal-like), algae (plant-like), euglena (plant/animal), slime mold ...
Diapositivo 1 - Cell Biology Promotion
... Angiogenic activity Promoting cell growth, differentiation and motility ...
... Angiogenic activity Promoting cell growth, differentiation and motility ...
Section 18-3 - Pearson School
... The Tree of Life Evolves (pages 457-458) 1. Is the following sentence true or false? The scientific view of life was more complex in Linnaeus’s time. 2. What fundamental traits did Linnaeus use to separate plants from animals? ...
... The Tree of Life Evolves (pages 457-458) 1. Is the following sentence true or false? The scientific view of life was more complex in Linnaeus’s time. 2. What fundamental traits did Linnaeus use to separate plants from animals? ...
Section 18-3 Kingdoms and Domains (pages 457-461)
... The Tree of Life Evolves (pages 457-458) 1. Is the following sentence true or false? The scientific view of life was more complex in Linnaeus’s time. 2. What fundamental traits did Linnaeus use to separate plants from animals? ...
... The Tree of Life Evolves (pages 457-458) 1. Is the following sentence true or false? The scientific view of life was more complex in Linnaeus’s time. 2. What fundamental traits did Linnaeus use to separate plants from animals? ...
Lecture 23 - Signaling 2
... • TNF R1 receptor is activated by TNF-alpha • 80 amino acid structural motif in the cytoplasmic tail of receptor called a Death Domain (DD) interacts with DDs on other proteins • The fate of the cell rests in the relative abundance (and activities) of proteins in two separate, but inter-related, sig ...
... • TNF R1 receptor is activated by TNF-alpha • 80 amino acid structural motif in the cytoplasmic tail of receptor called a Death Domain (DD) interacts with DDs on other proteins • The fate of the cell rests in the relative abundance (and activities) of proteins in two separate, but inter-related, sig ...
Modeling dynamics of cell-to-cell variability in TRAIL
... verified by comparison with analytical results to be sufficient to reach the steady-state distribution. Sister cells were simply constructed by duplication of the mother cell state. Because in experiments from [13], the distribution of durations between division and treatment was not uniform (see Fi ...
... verified by comparison with analytical results to be sufficient to reach the steady-state distribution. Sister cells were simply constructed by duplication of the mother cell state. Because in experiments from [13], the distribution of durations between division and treatment was not uniform (see Fi ...
Protein Structure
... • Domains can be between 25 and 500 residues long. • Most are less than 200 residues. • Domains can be smaller than 50 residues, but these need to be stabilized. Examples are the zinc finger and a scorpion toxin. ...
... • Domains can be between 25 and 500 residues long. • Most are less than 200 residues. • Domains can be smaller than 50 residues, but these need to be stabilized. Examples are the zinc finger and a scorpion toxin. ...
Proteomics investigation into cardiac endothelial
... • Tat associated with neural cell death and probable agent of HIV associated dementia • 2849 proteins were identified from SILAC treated cells which were either phosphoenriched or phospho-depleted (therefore reduced complexity of sample) • 17 up regulated and 72 down regulated proteins identified f ...
... • Tat associated with neural cell death and probable agent of HIV associated dementia • 2849 proteins were identified from SILAC treated cells which were either phosphoenriched or phospho-depleted (therefore reduced complexity of sample) • 17 up regulated and 72 down regulated proteins identified f ...
Slide - Linked Science
... Q1: What are the potential interacting partners? What we know: It contains a protein domain called Hairy_orange We know Hairy_orange’s interacting domains ...
... Q1: What are the potential interacting partners? What we know: It contains a protein domain called Hairy_orange We know Hairy_orange’s interacting domains ...
PPT
... Residing in the plasma membrane with seven transmembrane domains, GPCRs respond to extracellular stimuli that include catecholamine neurotransmitters, neuropeptides, larger protein hormones, lipids, nucleotides and other biological molecules. When a GPCR binds its extracellular ligand, it interacts ...
... Residing in the plasma membrane with seven transmembrane domains, GPCRs respond to extracellular stimuli that include catecholamine neurotransmitters, neuropeptides, larger protein hormones, lipids, nucleotides and other biological molecules. When a GPCR binds its extracellular ligand, it interacts ...
TYPES OF RECEPTORS
... Receptors that are kinases or bind kinases: When a signaling chemical binds to the membrane receptor protein on the outside of the cell, this triggers a change in the 3D conformation of that protein, which in turn, triggers a chemical reaction on the inside of the cell. ...
... Receptors that are kinases or bind kinases: When a signaling chemical binds to the membrane receptor protein on the outside of the cell, this triggers a change in the 3D conformation of that protein, which in turn, triggers a chemical reaction on the inside of the cell. ...
The Sonic Hedgehog
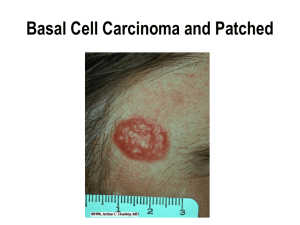
... • Like most skin cancers, BCC is primarily caused by sun exposure, specifically UVB rays • These rays cause mutations in DNA including deletions and substitutions ...
... • Like most skin cancers, BCC is primarily caused by sun exposure, specifically UVB rays • These rays cause mutations in DNA including deletions and substitutions ...
A7: Decoding genome encoded host-pathogen
... Previous work: We have identified GGDEF, EAL, HD and PilZ domain containing 16179 proteins in 779 completely sequenced bacterial genomes. We found that these domains cooccur with 124 other domains, which suggests their contribution in many biological processes. We also mapped their sequential order ...
... Previous work: We have identified GGDEF, EAL, HD and PilZ domain containing 16179 proteins in 779 completely sequenced bacterial genomes. We found that these domains cooccur with 124 other domains, which suggests their contribution in many biological processes. We also mapped their sequential order ...
Title: Synthetic Rigidin Analogues as Anticancer Agents, Salts, Solvates and... . Thereof, and Method of Producing Same
... chemotherapeutic. However, drugs that bind to the colchicine site tend to not be expunged by the Pgp drug efflux pump. Significant research efforts have focused on finding colchicine homologues that balance inhibition of mitosis in cancer cells while sparing other fast growing cells. Benefits: Rigid ...
... chemotherapeutic. However, drugs that bind to the colchicine site tend to not be expunged by the Pgp drug efflux pump. Significant research efforts have focused on finding colchicine homologues that balance inhibition of mitosis in cancer cells while sparing other fast growing cells. Benefits: Rigid ...
Apoptosome

The apoptosome is a large quaternary protein structure formed in the process of apoptosis. Its formation is triggered by the release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria in response to an internal (intrinsic) or external (extrinsic) cell death stimulus. Stimuli can vary from DNA damage and viral infection to developmental cues such as those leading to the degradation of a tadpole's tail.In mammalian cells, once cytochrome c is released, it binds to the cytosolic protein Apaf-1 to facilitate the formation of apoptosome. An early biochemical study suggests a two-to-one ratio of cytochrome c to apaf-1 for apoptosome formation. However, recent structural studies suggest the cytochrome c to apaf-1 ratio is one-to-one. It has also been shown that the nucleotide dATP as third component binds to apaf-1, however its exact role is still debated. The mammalian apoptosome had never been crystallized, but a human APAF-1/cytochrome-c apoptosome has been imaged at lower (2 nm) resolution by cryogenic transmission electron microscopy 10 years ago, revealing a wheel-like particle with 7-fold symmetry. Recently, a medium resolution (9.5 Ångström) structure of human apoptosome was also solved by cryo-electron microscopy, which allows unambiguous inference for positions of all the APAF-1 domains (CARD, NBARC and WD40) and cytochrome c. There is also now a crystal structure of the monomeric, inactive Apaf-1 subunit (PDB 3SFZ). Once formed, the apoptosome can then recruit and activate the inactive pro-caspase-9. Once activated, this initiator caspase can then activate effector caspases and trigger a cascade of events leading to apoptosis.