Exam 2 Study Guide
... Marginal Social Cost Pigovian Tax Tradable Pollution Permits Coase Theorem Private market can solve externality problem if side payments can be made without cost ...
... Marginal Social Cost Pigovian Tax Tradable Pollution Permits Coase Theorem Private market can solve externality problem if side payments can be made without cost ...
CHAPTER 1
... large fixed costs that present a potentially insurmountable economic barrier to entry. Having more than one firm bearing these fixed costs is not cost efficient. Therefore, these types of firms are considered “necessary monopolies.” ...
... large fixed costs that present a potentially insurmountable economic barrier to entry. Having more than one firm bearing these fixed costs is not cost efficient. Therefore, these types of firms are considered “necessary monopolies.” ...
Chapter 1: Human Misery
... Degree of Market Power Concentration Ratio – percentage of the market sale by the largest four (or eight) firms – CR > 0.70 indicates significant market power ...
... Degree of Market Power Concentration Ratio – percentage of the market sale by the largest four (or eight) firms – CR > 0.70 indicates significant market power ...
Market Structures
... Government was laissez-faire with business until close to the 20th century. ...
... Government was laissez-faire with business until close to the 20th century. ...
AQA Theory of the firm topic list
... The formal diagrammatic analysis of the monopoly model. That monopoly power is influenced by factors such as barriers to entry, the number of competitors, advertising and the degree of product differentiation. The advantages and disadvantages of monopoly. ...
... The formal diagrammatic analysis of the monopoly model. That monopoly power is influenced by factors such as barriers to entry, the number of competitors, advertising and the degree of product differentiation. The advantages and disadvantages of monopoly. ...
antitrust checklist
... 1. Current Law—Must be in interstate commerce antitrust laws to apply 2. Analysis Factors: Focus on defendant’s conduct (Summit) Manufacture not commerce Effects must be felt within United States B. Patent Law 1. Patent May assign rights (i.e. through license) 2. Patent Pools are legitimate Se ...
... 1. Current Law—Must be in interstate commerce antitrust laws to apply 2. Analysis Factors: Focus on defendant’s conduct (Summit) Manufacture not commerce Effects must be felt within United States B. Patent Law 1. Patent May assign rights (i.e. through license) 2. Patent Pools are legitimate Se ...
Market Equilibrium
... Demand curve DD represents the case when all oligopolists move prices together and share the market. ...
... Demand curve DD represents the case when all oligopolists move prices together and share the market. ...
Principles of Microeconomics_CLEP Exam
... of economics that apply to the analysis of the behavior of individual consumers and businesses in the economy. Questions on this exam require candidates to apply analytical techniques to hypothetical as well as real-world situations and to analyze and evaluate economic decisions. Candidates are expe ...
... of economics that apply to the analysis of the behavior of individual consumers and businesses in the economy. Questions on this exam require candidates to apply analytical techniques to hypothetical as well as real-world situations and to analyze and evaluate economic decisions. Candidates are expe ...
6-MarketStructu res
... dominated by not more than half-a-dozen firms, including Avis, Budget, Europcar/National and Hertz. These firms have demonstrated extreme sensitivity to competitive activity from each other, and consequently end up with very similar product lines and tariff rates; this ensures market stability. ...
... dominated by not more than half-a-dozen firms, including Avis, Budget, Europcar/National and Hertz. These firms have demonstrated extreme sensitivity to competitive activity from each other, and consequently end up with very similar product lines and tariff rates; this ensures market stability. ...
GOAL 8: Features of the United States Economic System
... decisions of what, how, and for whom to produce are based on custom or habit An economic system in which the major Command Economics economic decisions are made by the central government Market Economy aka Capitalism Adam System in which individuals own the factors of production and make economic Sm ...
... decisions of what, how, and for whom to produce are based on custom or habit An economic system in which the major Command Economics economic decisions are made by the central government Market Economy aka Capitalism Adam System in which individuals own the factors of production and make economic Sm ...
Final Exam Review Sheet
... 24. Calculating economic profits. 25. Perfect competition, using market and firm graphs and illustrating changes in demand or costs of production. 26. Short run and long run. 27. Labor markets, marginal revenue product of labor, minimum wages 28. Profit maximization using the marginal principle 29. ...
... 24. Calculating economic profits. 25. Perfect competition, using market and firm graphs and illustrating changes in demand or costs of production. 26. Short run and long run. 27. Labor markets, marginal revenue product of labor, minimum wages 28. Profit maximization using the marginal principle 29. ...
Chapter 5 The Nature of Market
... Product differentiation leads to higher prices by raising per-unit costs and enhancing an individual business’s market power. However, consumers will likely have more choices because of businesses efforts to differentiate their products ...
... Product differentiation leads to higher prices by raising per-unit costs and enhancing an individual business’s market power. However, consumers will likely have more choices because of businesses efforts to differentiate their products ...
4 bases for the majority of legal systems around the world
... Typically the government steps in for companies who are considered vital to the country or necessary for the public good (ex: health care, transportation) ...
... Typically the government steps in for companies who are considered vital to the country or necessary for the public good (ex: health care, transportation) ...
Monopolistic Competition
... there is more than one seller, but too few to create a perfectly competitive market products may not be standardized no free entry and exit ...
... there is more than one seller, but too few to create a perfectly competitive market products may not be standardized no free entry and exit ...
Economics, by R. Glenn Hubbard and Anthony Patrick
... In pure monopoly, because of the high barriers to entry, economic profits can be earned in the long-run as well. At the expense of competition ...
... In pure monopoly, because of the high barriers to entry, economic profits can be earned in the long-run as well. At the expense of competition ...
Oligopoly - Cornell University
... many firms, identical products Monopoly: single firm, no close substitutes Oligopoly: several firms, similar products, degree of product differentiation varies depending upon the market Monopolistic competition: many firms, similar products, slightly differentiated products ...
... many firms, identical products Monopoly: single firm, no close substitutes Oligopoly: several firms, similar products, degree of product differentiation varies depending upon the market Monopolistic competition: many firms, similar products, slightly differentiated products ...
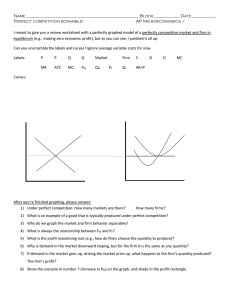
Perfect Competition
... There are no barriers to entry. Barriers to entry are social, political, or economic impediments that prevent other firms from entering the market. Barriers sometimes take the form of patents granted to produce a certain ...
... There are no barriers to entry. Barriers to entry are social, political, or economic impediments that prevent other firms from entering the market. Barriers sometimes take the form of patents granted to produce a certain ...
INFLUENCE OF GOVERNMENT ON MARKETING
... needs to be taken into consideration when decisions are being made. Consumers would be unhappy if they purchased products that didn’t work or didn’t do what it was supposed to. Feeling of being conned by advertising. Need to protect consumers against rogue businesses. Unit 5 - Slide 6 ...
... needs to be taken into consideration when decisions are being made. Consumers would be unhappy if they purchased products that didn’t work or didn’t do what it was supposed to. Feeling of being conned by advertising. Need to protect consumers against rogue businesses. Unit 5 - Slide 6 ...
AP Microeconomics Review #4
... • Circle Test: use to find dom. strategy: circle your opponents best move based on your move; if player gets two circles in same decision, then it is a dominant strategy ...
... • Circle Test: use to find dom. strategy: circle your opponents best move based on your move; if player gets two circles in same decision, then it is a dominant strategy ...
Market Structures
... Other—non price competition (use product differentiation and advertising to compete) Result—some control over price ...
... Other—non price competition (use product differentiation and advertising to compete) Result—some control over price ...
Chapter 1 What Is Economics?
... Perfect (pure) competition is a market structure in which buyers and sellers each compete directly and completely under the laws of supply and demand making the same products. Monopolistic competition is different as producers attempt to make different products than their competition or make sim ...
... Perfect (pure) competition is a market structure in which buyers and sellers each compete directly and completely under the laws of supply and demand making the same products. Monopolistic competition is different as producers attempt to make different products than their competition or make sim ...
Capitalism
... Markets Economic Freedom Private Property Rights Competition Profit Motive Voluntary Exchange ...
... Markets Economic Freedom Private Property Rights Competition Profit Motive Voluntary Exchange ...
Revision_Market_Power
... Anti-competitive behaviour: Anti-competitive practices are strategies operated by firms that are deliberately behaviour designed to limit the degree of competition inside a market. Such actions can be taken by one firm in isolation or a number of firms engaged in some form of explicit or implicit co ...
... Anti-competitive behaviour: Anti-competitive practices are strategies operated by firms that are deliberately behaviour designed to limit the degree of competition inside a market. Such actions can be taken by one firm in isolation or a number of firms engaged in some form of explicit or implicit co ...
What are prices and output like in a perfectly competitive market?
... Government policies keep firms from controlling the prices and supply of important goods. Antitrust laws are laws that encourage competition in the marketplace. 1. Regulating Business Practices The government has the power to regulate business practices if these practices give too much power to a co ...
... Government policies keep firms from controlling the prices and supply of important goods. Antitrust laws are laws that encourage competition in the marketplace. 1. Regulating Business Practices The government has the power to regulate business practices if these practices give too much power to a co ...