Title Goes Here - Binus Repository
... Allocative efficiency (or efficiency) occurs when no possible reorganization of production can make anyone better off without making someone else worse off. Under condition all allocative efficiency, one person’s satisfaction or utility can be increased only by lowering someone else’s utility. ...
... Allocative efficiency (or efficiency) occurs when no possible reorganization of production can make anyone better off without making someone else worse off. Under condition all allocative efficiency, one person’s satisfaction or utility can be increased only by lowering someone else’s utility. ...
Monopolistic Competition
... variation meets societies needs. Nonprice Competition (product differentiation and advertising) may result in sustained profits for some firms. Ex: Nike might continue to make above normal profit because they are a well known brand. ...
... variation meets societies needs. Nonprice Competition (product differentiation and advertising) may result in sustained profits for some firms. Ex: Nike might continue to make above normal profit because they are a well known brand. ...
Chapter 17
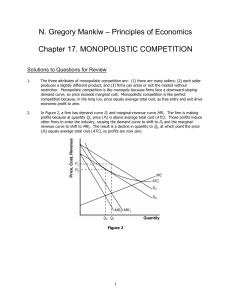
... producing at the point where average total cost is minimized, which is the efficient scale. • There is excess capacity in monopolistic competition in the long run. • In monopolistic competition, output is less than the efficient scale of perfect competition. ...
... producing at the point where average total cost is minimized, which is the efficient scale. • There is excess capacity in monopolistic competition in the long run. • In monopolistic competition, output is less than the efficient scale of perfect competition. ...
Powerpoint Presenation of Notes
... reduce competition, and exclusive sales contracts. The Federal Trade Commission Act (1914) created the Federal Trade Commission to investigate charges of unfair methods of competition and commerce. The Parens Patriae Act (1976) gave states the right to sue companies accused of antitrust activity; re ...
... reduce competition, and exclusive sales contracts. The Federal Trade Commission Act (1914) created the Federal Trade Commission to investigate charges of unfair methods of competition and commerce. The Parens Patriae Act (1976) gave states the right to sue companies accused of antitrust activity; re ...
Monopolistic Competition: The Chamberlin Model
... firm controls the entire supply of a product which has no close substitutes. • Distinction between firm and industry is irrelevant in the case of monopoly • It has power to control price of its products • If demand is the same, firm can rise the price as much as it wishes by reducing out ...
... firm controls the entire supply of a product which has no close substitutes. • Distinction between firm and industry is irrelevant in the case of monopoly • It has power to control price of its products • If demand is the same, firm can rise the price as much as it wishes by reducing out ...
The fine line between market dominance and abuse
... believe that the applicants have discharged the obligation to show harm to competition”. In this sense, the Tribunal placed great store on the promotional opportunities available to the BATSA’s rivals; the complainant’s own resources, including international brands and experience; and alternative me ...
... believe that the applicants have discharged the obligation to show harm to competition”. In this sense, the Tribunal placed great store on the promotional opportunities available to the BATSA’s rivals; the complainant’s own resources, including international brands and experience; and alternative me ...
Document
... Profit maximization under perfect competition How much economic profit will the profit-maximizing competitive firm make? Zero!! – Zero economic profit (or normal profit): Revenues are just sufficient to compensate for the use of labor, materials, and other physical inputs, financial and physical ca ...
... Profit maximization under perfect competition How much economic profit will the profit-maximizing competitive firm make? Zero!! – Zero economic profit (or normal profit): Revenues are just sufficient to compensate for the use of labor, materials, and other physical inputs, financial and physical ca ...
N. Gregory Mankiw – Principles of Economics Chapter 17
... The three attributes of monopolistic competition are: (1) there are many sellers; (2) each seller produces a slightly different product; and (3) firms can enter or exit the market without restriction. Monopolistic competition is like monopoly because firms face a downward-sloping demand curve, so pr ...
... The three attributes of monopolistic competition are: (1) there are many sellers; (2) each seller produces a slightly different product; and (3) firms can enter or exit the market without restriction. Monopolistic competition is like monopoly because firms face a downward-sloping demand curve, so pr ...
No Slide Title - Binus Repository
... Kenmore and Whirlpool • Location -- hard to jointly produce • Does the decline in profits stifle innovation? • Is there too much product differentiation? ...
... Kenmore and Whirlpool • Location -- hard to jointly produce • Does the decline in profits stifle innovation? • Is there too much product differentiation? ...
Micro ch 21- presentation 1 Market Structures
... Product that differs slightly from competitors’ versions--- preferences exist Buyers are not indifferent about the seller when the price of the product is the same Ex- Shoes, dresses, retail ...
... Product that differs slightly from competitors’ versions--- preferences exist Buyers are not indifferent about the seller when the price of the product is the same Ex- Shoes, dresses, retail ...
ECONOMICS Ch - cloudfront.net
... Describe how monopolies are formed, including government monopolies. Explain how a firm with a monopoly sets output and price. Describe characteristics of monopolistic competition. Explain how firms compete without lowering prices. Describe an oligopoly and give examples of one. Explain market pract ...
... Describe how monopolies are formed, including government monopolies. Explain how a firm with a monopoly sets output and price. Describe characteristics of monopolistic competition. Explain how firms compete without lowering prices. Describe an oligopoly and give examples of one. Explain market pract ...
File
... • Capitalism: An economic system where prices and production is determined by the mutual consent of buyers and sellers through the laws of supply and demand. Very little gov’t involvement and lots of private ownership. ...
... • Capitalism: An economic system where prices and production is determined by the mutual consent of buyers and sellers through the laws of supply and demand. Very little gov’t involvement and lots of private ownership. ...
Monopolistic Competition
... MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION • Large number of firms and product variation meets societies needs. • Nonprice Competition (product differentiation and advertising) may result in sustained profits for some firms. Ex: Nike might continue to make above normal profit because they are a well known brand. ...
... MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION • Large number of firms and product variation meets societies needs. • Nonprice Competition (product differentiation and advertising) may result in sustained profits for some firms. Ex: Nike might continue to make above normal profit because they are a well known brand. ...
econ quiz 1- study guide
... 10. The Invisible Hand was Adam Smith’s theory that the free market should not be regulated by the government. 11. Individuals have the right to make economic choices about their property and how they are going to make money. 12. Competition between sellers keeps the cost of production low and the q ...
... 10. The Invisible Hand was Adam Smith’s theory that the free market should not be regulated by the government. 11. Individuals have the right to make economic choices about their property and how they are going to make money. 12. Competition between sellers keeps the cost of production low and the q ...
Chapter 8
... Activities Prohibited by the Clayton Act Price Discrimination – charging different customers different prices for the same good Tying Contracts – contracts requiring the buyer of a good to purchase another additional good Exclusive Dealing – requiring buyers of goods to agree not to purchase ...
... Activities Prohibited by the Clayton Act Price Discrimination – charging different customers different prices for the same good Tying Contracts – contracts requiring the buyer of a good to purchase another additional good Exclusive Dealing – requiring buyers of goods to agree not to purchase ...
File
... • Merging of two or more competing firms is beneficial in that it may increase their market share significantly, and thus achieve greater economies of scale. • The larger firm that results from a merger would have greater control over market supply and price. ...
... • Merging of two or more competing firms is beneficial in that it may increase their market share significantly, and thus achieve greater economies of scale. • The larger firm that results from a merger would have greater control over market supply and price. ...
03 - CANVAS- Environmental factors
... influence a firm’s acquisition and allocation of resources and its creation of products ...
... influence a firm’s acquisition and allocation of resources and its creation of products ...
Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly
... particular product is better and thus are willing to pay a higher price A very important characteristic of monopolistic competition Perfect competition – no differentiation Monopolies – have no incentive for differentiation ...
... particular product is better and thus are willing to pay a higher price A very important characteristic of monopolistic competition Perfect competition – no differentiation Monopolies – have no incentive for differentiation ...
Goal 8: Analyze features of the economic system of the US
... C. A shortage D. Elasticity 24. What is the name of laws that attempt to prevent monopolies from forming? A. Anti-trust laws B. Anti-monopoly laws C. Administrative laws D. Constitutional laws 25. What concept makes stockholders only responsible for a portion of the debts of a corporation? A. Absolu ...
... C. A shortage D. Elasticity 24. What is the name of laws that attempt to prevent monopolies from forming? A. Anti-trust laws B. Anti-monopoly laws C. Administrative laws D. Constitutional laws 25. What concept makes stockholders only responsible for a portion of the debts of a corporation? A. Absolu ...
Pure Competition
... Profit Maximization: TR – TC Approach • The competitive producer will ask three questions • Should the firm produce? • If so, in what amount? • What economic profit (loss) will be realized? ...
... Profit Maximization: TR – TC Approach • The competitive producer will ask three questions • Should the firm produce? • If so, in what amount? • What economic profit (loss) will be realized? ...
Antitrust Law
... • If a tie-in creates a monopoly when there are no or few good alternatives, it is likely illegal; if products or service are tied together when there are other competitors, the tie-in will likely pass the rule of reason test. • Supreme Court is likely to impose a per se illegality only when three c ...
... • If a tie-in creates a monopoly when there are no or few good alternatives, it is likely illegal; if products or service are tied together when there are other competitors, the tie-in will likely pass the rule of reason test. • Supreme Court is likely to impose a per se illegality only when three c ...
SECTION 12: Market Structures: Imperfect Competition Need to Know: : market structure with a few large producers that are interdependent and engage in strategic
... The payoff matrix is a diagram showing how the payoffs to each player in a game depend on the actions of both. A dominant strategy is an action that is a player’s best action regardless of what the other player does. A Nash equilibrium occurs when the game ends, and each player is happy with t ...
... The payoff matrix is a diagram showing how the payoffs to each player in a game depend on the actions of both. A dominant strategy is an action that is a player’s best action regardless of what the other player does. A Nash equilibrium occurs when the game ends, and each player is happy with t ...
United States v. EI Du Pont De Nemours & Co (1956)
... require mass to shift to substitute products. So cross-elasticity of demand for a product calculated on current price only defines the outer-limit of the monopolist’s punitive power. SSNIP of 1992 merger guidelines requires that cross-elasticity for substitute products be measured after “small, sign ...
... require mass to shift to substitute products. So cross-elasticity of demand for a product calculated on current price only defines the outer-limit of the monopolist’s punitive power. SSNIP of 1992 merger guidelines requires that cross-elasticity for substitute products be measured after “small, sign ...
Different Market Structures
... or use marketing and pricing strategies which will prevent new entrants gaining a foothold in their marketplace. They may even sell their goods or services at prices that do not maximize profits, but instead prevent profitable competition entering the market or discourages the government or competit ...
... or use marketing and pricing strategies which will prevent new entrants gaining a foothold in their marketplace. They may even sell their goods or services at prices that do not maximize profits, but instead prevent profitable competition entering the market or discourages the government or competit ...