Degree Applicable - Glendale Community College
... Upon successful completion of the required coursework in Principles of Microeconomics, the student will be able to: 1. identify the key elements of the demand and supply market mechanism model and use the model to critically analyze real world examples; 2. explain how prices and quantities are deter ...
... Upon successful completion of the required coursework in Principles of Microeconomics, the student will be able to: 1. identify the key elements of the demand and supply market mechanism model and use the model to critically analyze real world examples; 2. explain how prices and quantities are deter ...
Sample Test: US Economic System 1. Under which economic
... 20. The government cuts taxes, hoping that having more money will result in people buying more goods and services. Which term best describes this type of policy? a. monetary policy b. fiscal policy c. labor policy d. income policy 21. What is the government most likely to use to keep track of infla ...
... 20. The government cuts taxes, hoping that having more money will result in people buying more goods and services. Which term best describes this type of policy? a. monetary policy b. fiscal policy c. labor policy d. income policy 21. What is the government most likely to use to keep track of infla ...
Lecture 19
... – Perfect competition, in which the market consists of a very large number of firms producing a homogeneous product. – Monopolistic competition, also called competitive market, where there are a large number of independent firms which have a very small proportion of the market share. – Oligopoly, in ...
... – Perfect competition, in which the market consists of a very large number of firms producing a homogeneous product. – Monopolistic competition, also called competitive market, where there are a large number of independent firms which have a very small proportion of the market share. – Oligopoly, in ...
Midterm 2 Summary Notes
... • Cournot: All firms set quantities at the same time • Calculate residual demand for a given firm and solve its profit maximization problem to find its best response function to other firms’ output decisions. • Solution is a set of quantities (one for each firm) that solves this system of equatio ...
... • Cournot: All firms set quantities at the same time • Calculate residual demand for a given firm and solve its profit maximization problem to find its best response function to other firms’ output decisions. • Solution is a set of quantities (one for each firm) that solves this system of equatio ...
Slides - Competition Policy International
... in the level of prices and profits before and after the imposition of the practice can be used to assess the change in market power. It is important to control for the impact on market power of changes in relevant competitive factors, such as costs or the extent of competition from other firms, that ...
... in the level of prices and profits before and after the imposition of the practice can be used to assess the change in market power. It is important to control for the impact on market power of changes in relevant competitive factors, such as costs or the extent of competition from other firms, that ...
Neoclassical School
... horizontal marginal cost curve In input market, companies can buy any number of input at a certain price. ...
... horizontal marginal cost curve In input market, companies can buy any number of input at a certain price. ...
Monopoly and Antitrust Policy
... Perfect Price Discrimination – firm charges maximum amount a buyer is willing to pay for each unit produced. Show that with perfect price discrimination the MR curve is the Demand curve. Total revenue is then calculated by TR = Σ MR. Antitrust Laws Sherman Act – 1890, declared every contract or cons ...
... Perfect Price Discrimination – firm charges maximum amount a buyer is willing to pay for each unit produced. Show that with perfect price discrimination the MR curve is the Demand curve. Total revenue is then calculated by TR = Σ MR. Antitrust Laws Sherman Act – 1890, declared every contract or cons ...
Battle of the Toms: Corbett v. Wolf
... • Sum of squared market shares of all firms • (% Share of Firm 1)2 + (% Share of Firm ...
... • Sum of squared market shares of all firms • (% Share of Firm 1)2 + (% Share of Firm ...
EFL Lesson 4
... Prices send signals and provide incentives to buyers and sellers. When supply or demand changes, market prices adjust, affecting incentives. Higher prices for a good or service provide incentives for buyers to purchase less of that good or service and for producers to make or sell more of it. Lowe ...
... Prices send signals and provide incentives to buyers and sellers. When supply or demand changes, market prices adjust, affecting incentives. Higher prices for a good or service provide incentives for buyers to purchase less of that good or service and for producers to make or sell more of it. Lowe ...
ECO 335 Economics of Regulation and Antitrust Dr. David Loomis Department of Economics
... concentrated industries - it is not. ...
... concentrated industries - it is not. ...
232handout mono comp +
... 2. A market or industry demand curve is not very informative. It would be downward sloping say for “all athletic shoes” but you are adding together very different products: e.g. Nike, Adidas, etc. For practical purposes we’ll say there is no industry demand curve. 3. MR
... 2. A market or industry demand curve is not very informative. It would be downward sloping say for “all athletic shoes” but you are adding together very different products: e.g. Nike, Adidas, etc. For practical purposes we’ll say there is no industry demand curve. 3. MR
Prices and Decision Making
... few large sellers dominate An individual firm can change output, sales, and prices in the industry Examples of Oligopolistic Markets Interdependent ...
... few large sellers dominate An individual firm can change output, sales, and prices in the industry Examples of Oligopolistic Markets Interdependent ...
Sept 19, 2012 - Competitors and Competition
... It is important to control for these extraneous factors if one needs to study the relation between concentration and price-cost margin Most studies focus on specific industries and compare geographically distinct markets ...
... It is important to control for these extraneous factors if one needs to study the relation between concentration and price-cost margin Most studies focus on specific industries and compare geographically distinct markets ...
EcN212EX3
... “As long as the marginal cost of production is greater than the average variable cost, then the average variable cost is increasing.” Is the preceding statement true or false? Use your knowledge of production and cost to justify your answer. ...
... “As long as the marginal cost of production is greater than the average variable cost, then the average variable cost is increasing.” Is the preceding statement true or false? Use your knowledge of production and cost to justify your answer. ...
Document
... to control the supply. Ethical issues involved with buying diamonds from warring African countries led to more problems for De Beers. Therefore, in July 2000, De Beers announced that it would no longer attempt to control the world’s supply of diamonds, and the monopoly officially ended. Although cas ...
... to control the supply. Ethical issues involved with buying diamonds from warring African countries led to more problems for De Beers. Therefore, in July 2000, De Beers announced that it would no longer attempt to control the world’s supply of diamonds, and the monopoly officially ended. Although cas ...
chapter 1: pro-competitve effect of trade
... 1A: Mechanism • Increase in the elasticity of the demand perceived by firms facing import competition • Effective entry of new (foreign) competitors displace low efficient (domestic) firms • Domestic producers are likely to face a fall in their domestic market share ...
... 1A: Mechanism • Increase in the elasticity of the demand perceived by firms facing import competition • Effective entry of new (foreign) competitors displace low efficient (domestic) firms • Domestic producers are likely to face a fall in their domestic market share ...
14_Finish-contestability-and-intro-to-govt
... Structural changes in costs in different industries can change the degree of contestability Contestability may force existing firms away from profit-maximising behaviour (e.g. towards sales-revenue maximisation) ...
... Structural changes in costs in different industries can change the degree of contestability Contestability may force existing firms away from profit-maximising behaviour (e.g. towards sales-revenue maximisation) ...
The Competitive Marketplace
... Oligopolistic Competition – occurs when relatively few sellers, or many small firms who follow the lead of a few larger firms, offer essentially homogeneous products and any action by one seller is expected to be noticed and reacted to by the other sellers. LO 1 ...
... Oligopolistic Competition – occurs when relatively few sellers, or many small firms who follow the lead of a few larger firms, offer essentially homogeneous products and any action by one seller is expected to be noticed and reacted to by the other sellers. LO 1 ...
File - Holtville FFA The Farmer in All of Us.
... b. a license that gives the inventor of a new product the exclusive right to sell it for a certain amount of time. c. an industry that runs best when one firm produces all the output. d. an industry where the government provides all the output. 48. Price discrimination is a. a factor that causes a ...
... b. a license that gives the inventor of a new product the exclusive right to sell it for a certain amount of time. c. an industry that runs best when one firm produces all the output. d. an industry where the government provides all the output. 48. Price discrimination is a. a factor that causes a ...
Jeopardy -- Final Exam Review (6/8)
... book have __________ What is greater? willingness to pay than those who wait for the cheaper softback ...
... book have __________ What is greater? willingness to pay than those who wait for the cheaper softback ...
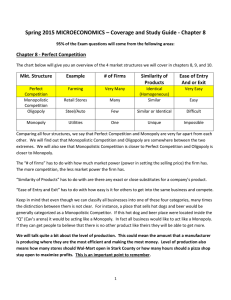
Chapter 8 - Perfect Competition
... extremes. We will also see that Monopolistic Competition is closer to Perfect Competition and Oligopoly is closer to Monopoly. The “# of firms” has to do with how much market power (power in setting the selling price) the firm has. The more competition, the less market power the firm has. “Similarit ...
... extremes. We will also see that Monopolistic Competition is closer to Perfect Competition and Oligopoly is closer to Monopoly. The “# of firms” has to do with how much market power (power in setting the selling price) the firm has. The more competition, the less market power the firm has. “Similarit ...