Perfect Competition
... The Super Normal Profits from the Short Run attract more firms into the market. They know about these profits, and there is nothing to stop them entering the industry. As a result, the supply increases (from S1 to S2 in the graph below). This causes the prevailing market price to fall (from P1 to P2 ...
... The Super Normal Profits from the Short Run attract more firms into the market. They know about these profits, and there is nothing to stop them entering the industry. As a result, the supply increases (from S1 to S2 in the graph below). This causes the prevailing market price to fall (from P1 to P2 ...
Document
... The fall in the marginal cost of production causes a favorable shift in supply and a lower price accompanied by greater output. ...
... The fall in the marginal cost of production causes a favorable shift in supply and a lower price accompanied by greater output. ...
Monopolistic Competition Notes
... produce at the lowest costs (minimum ATC) but they decide not to. • The gap between the minimum ATC output and the profit maximizing output. ...
... produce at the lowest costs (minimum ATC) but they decide not to. • The gap between the minimum ATC output and the profit maximizing output. ...
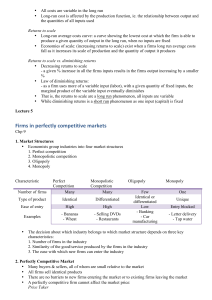
Firms in perfectly competitive markets
... In economics, implicit opportunity costs are included with explicit costs ...
... In economics, implicit opportunity costs are included with explicit costs ...
MONOPOLY
... • A monopoly firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve for its product. As a result, it must reduce price to sell a larger quantity, which causes marginal revenue to fall below price. • Monopoly firms maximize profits by producing the quantity ...
... • A monopoly firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve for its product. As a result, it must reduce price to sell a larger quantity, which causes marginal revenue to fall below price. • Monopoly firms maximize profits by producing the quantity ...
Microeconomic Concepts Describe how households, businesses
... Disadvantages- unlimited liability, difficulty in raising financial capital, amount of work, limited life. Partnership – a business jointly owned by two or more people. Advantages- ease of start-up, each partner brings a skill, larger pool of capital, lack of special taxes on partnerships. Disadvant ...
... Disadvantages- unlimited liability, difficulty in raising financial capital, amount of work, limited life. Partnership – a business jointly owned by two or more people. Advantages- ease of start-up, each partner brings a skill, larger pool of capital, lack of special taxes on partnerships. Disadvant ...
EOCT Study Guide
... Disadvantages- unlimited liability, difficulty in raising financial capital, amount of work, limited life. Partnership – a business jointly owned by two or more people. Advantages- ease of start-up, each partner brings a skill, larger pool of capital, lack of special taxes on partnerships. Disadvant ...
... Disadvantages- unlimited liability, difficulty in raising financial capital, amount of work, limited life. Partnership – a business jointly owned by two or more people. Advantages- ease of start-up, each partner brings a skill, larger pool of capital, lack of special taxes on partnerships. Disadvant ...
Perfect Competition Continued*
... supply is perfectly elastic. Fig 9-10 • Most industries have increasing costs, which means that firms entering the industry increase resource costs for the others. Fig 9-11 • Higher costs shift the ATC upwards. • Some industries have decreasing costs. ...
... supply is perfectly elastic. Fig 9-10 • Most industries have increasing costs, which means that firms entering the industry increase resource costs for the others. Fig 9-11 • Higher costs shift the ATC upwards. • Some industries have decreasing costs. ...
PANEL II Criteria Used to Assess The Durability of Market
... • Dangers of over-enforcement and chilling effects? - matters greatly how dominance was established • A firm’s dominant position may be entrenched because of previous/ongoing state support, even though firm’s inefficiency and/or exercise of market power may mean there are some fringe competitors • D ...
... • Dangers of over-enforcement and chilling effects? - matters greatly how dominance was established • A firm’s dominant position may be entrenched because of previous/ongoing state support, even though firm’s inefficiency and/or exercise of market power may mean there are some fringe competitors • D ...
CONSIDERATIONS ON THE CONCEPT OF COMPETITION
... Competition functions are the following3: 1. Facilitate autonomous adjustment of supply and demand in all areas of economic activity. The competition stimulates concerns for the growth, diversification, and quality improvement supply of goods, to adapt it to dynamic market requirements. On offer d ...
... Competition functions are the following3: 1. Facilitate autonomous adjustment of supply and demand in all areas of economic activity. The competition stimulates concerns for the growth, diversification, and quality improvement supply of goods, to adapt it to dynamic market requirements. On offer d ...
Topic Priority Checklist
... equilibria of the purely competitive firm. 33. In words and using graphical analysis, show the profit scenario of a single price monopolist and a perfectly price-discriminating monopolist. 34. Identify the government policies employed when a firm exercises monopoly power or is a natural monopoly. 35 ...
... equilibria of the purely competitive firm. 33. In words and using graphical analysis, show the profit scenario of a single price monopolist and a perfectly price-discriminating monopolist. 34. Identify the government policies employed when a firm exercises monopoly power or is a natural monopoly. 35 ...
Oligopoly
... Entry is not impossible, but it is difficult. These barriers include high start-up costs, such as in the banking industry the cost advantage of existing firms, such as in the airline industry limit pricing (existing firms lower the prices to make it harder for new firms to compete), such as pr ...
... Entry is not impossible, but it is difficult. These barriers include high start-up costs, such as in the banking industry the cost advantage of existing firms, such as in the airline industry limit pricing (existing firms lower the prices to make it harder for new firms to compete), such as pr ...
Perfect Competition
... No individual firm or buyer, no matter how large their sales or purchases, can influence market quantity. ...
... No individual firm or buyer, no matter how large their sales or purchases, can influence market quantity. ...
AP Micro 4-3 Monopolistic Competition
... competitive firm in long-run equilibrium. If this firm were to realize productive efficiency, it would: A) have more economic profit. B) have a loss. C) also achieve allocative efficiency. D) be under producing. E) be in long-run equilibrium. ...
... competitive firm in long-run equilibrium. If this firm were to realize productive efficiency, it would: A) have more economic profit. B) have a loss. C) also achieve allocative efficiency. D) be under producing. E) be in long-run equilibrium. ...
The Free Enterprise System
... or color that identifies a good or service and that cannot be used by anyone but the owner. • Copyright – Involves anything that is authored by an individual, such as writings, music, and artwork. ...
... or color that identifies a good or service and that cannot be used by anyone but the owner. • Copyright – Involves anything that is authored by an individual, such as writings, music, and artwork. ...
ECO352_13.pdf
... Each firm's average cost curve downward-sloping as its own output increases Market structure must be imperfectly competitive, oligopoly if only a few (2-3) firms survive: aircraft monopolistic competition if several (10 or more) survive, free entry: autos In principle, scale economies are an added r ...
... Each firm's average cost curve downward-sloping as its own output increases Market structure must be imperfectly competitive, oligopoly if only a few (2-3) firms survive: aircraft monopolistic competition if several (10 or more) survive, free entry: autos In principle, scale economies are an added r ...
Theory of Markets
... results in an inward shift of the supply curve. • Subsidies - reduce costs and cause outward shift in supply curve Prices of other Goods- ...
... results in an inward shift of the supply curve. • Subsidies - reduce costs and cause outward shift in supply curve Prices of other Goods- ...
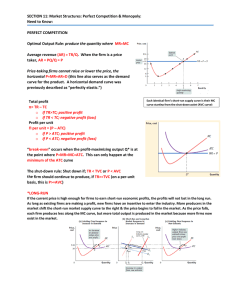
SECTION 11: Market Structures: Perfect Competition & Monopoly: Need to Know: PERFECT COMPETITION
... “break‐even” occurs when the profit‐maximizing output Q* is at the point where P=MR=MC=ATC. This can only happen at the minimum of the ATC curve ...
... “break‐even” occurs when the profit‐maximizing output Q* is at the point where P=MR=MC=ATC. This can only happen at the minimum of the ATC curve ...
Monopolistic Competition
... barriers to entry. Barriers to entry – Obstacles that make it difficult or impossible for wouldbe producers to enter a particular market, such as patents. ...
... barriers to entry. Barriers to entry – Obstacles that make it difficult or impossible for wouldbe producers to enter a particular market, such as patents. ...
Answers to Workshop 5
... Durashine now faces competition from firms other than Supasheen. It thus decides to consider some alternative strategies to adopt. It examines four options. The first is to a 10 per cent price cut. The second is to introduce a new brand of high gloss durable emulsion paint. The third is to launch a ...
... Durashine now faces competition from firms other than Supasheen. It thus decides to consider some alternative strategies to adopt. It examines four options. The first is to a 10 per cent price cut. The second is to introduce a new brand of high gloss durable emulsion paint. The third is to launch a ...
Monopolistic Competition
... Monopolistic Competition • A mixture of Perfect Competition and Monopoly • Many firms sell similar but not identical products. • Relatively large # of sellers (not nearly as much as perfect competition) • Firms determine their own output are price makers. • Slightly differentiated products (disting ...
... Monopolistic Competition • A mixture of Perfect Competition and Monopoly • Many firms sell similar but not identical products. • Relatively large # of sellers (not nearly as much as perfect competition) • Firms determine their own output are price makers. • Slightly differentiated products (disting ...
File
... market regulation costs both consumers and producers. Enduring Understanding: Markets arise in order to allow people and institutions to trade items of perceived value for something else of perceived value. Markets are most efficient when they are unrestricted. The prices in a market send signals to ...
... market regulation costs both consumers and producers. Enduring Understanding: Markets arise in order to allow people and institutions to trade items of perceived value for something else of perceived value. Markets are most efficient when they are unrestricted. The prices in a market send signals to ...
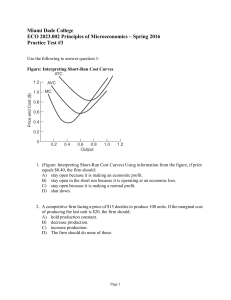
Spring 2016 Practice Test #3
... 32. Which of the following statements about trusts is NOT correct? A) The problems associated with the trust form of business organization led to the development of the antitrust acts. B) Trusts developed after the Civil War. C) Trusts acted like monopolies. D) The first antitrust act was passed aft ...
... 32. Which of the following statements about trusts is NOT correct? A) The problems associated with the trust form of business organization led to the development of the antitrust acts. B) Trusts developed after the Civil War. C) Trusts acted like monopolies. D) The first antitrust act was passed aft ...
How Does A Monopolistically Competitive Market Function?
... firms use NON-PRICE Competition. Examples of NON-PRICE Competition • Brand Names and Packaging • Product Attributes • Service • Location • Advertising (Two Goals) 1. Increase Demand 2. Make demand more INELASTIC ...
... firms use NON-PRICE Competition. Examples of NON-PRICE Competition • Brand Names and Packaging • Product Attributes • Service • Location • Advertising (Two Goals) 1. Increase Demand 2. Make demand more INELASTIC ...