Bertrand Homogenous Competition with Exogenous Sunk Costs
... many firms in the industry. Prices are not high enough to sustain a normal rate of return on sunk costs incurred. This results in the forced exit of firms, or mergers/acquisitions – thereby reducing N and increasing concentration levels back up to (or above) the predicted lower bound ...
... many firms in the industry. Prices are not high enough to sustain a normal rate of return on sunk costs incurred. This results in the forced exit of firms, or mergers/acquisitions – thereby reducing N and increasing concentration levels back up to (or above) the predicted lower bound ...
1 - Studyit
... An oligopoly is when few very large firms dominate the market. Each sells a strongly differentiated product and has strong price control due to market share. The barriers to entry are very high, often in the form of capital costs as unless a start up was large, the other competitors could easily eli ...
... An oligopoly is when few very large firms dominate the market. Each sells a strongly differentiated product and has strong price control due to market share. The barriers to entry are very high, often in the form of capital costs as unless a start up was large, the other competitors could easily eli ...
Chpt. 9 -Perfect Competition Supplement (Man)
... firms which own more than 40% of the market share. ◦ Oligopsony, a market dominated by many sellers and a few buyers. ◦ Monopoly, where there is only one provider of a product or service. ◦ Natural monopoly, a monopoly in which economies of scale cause efficiency to increase continuously with the si ...
... firms which own more than 40% of the market share. ◦ Oligopsony, a market dominated by many sellers and a few buyers. ◦ Monopoly, where there is only one provider of a product or service. ◦ Natural monopoly, a monopoly in which economies of scale cause efficiency to increase continuously with the si ...
Chapter 6: The Role of Profit
... The effects of profit-maximizing behavior on consumers in each market structure The short-run and long-run outcomes of profit-maximizing behavior natural monopolies and how governments regulate them ...
... The effects of profit-maximizing behavior on consumers in each market structure The short-run and long-run outcomes of profit-maximizing behavior natural monopolies and how governments regulate them ...
Market Failures
... person = 0). Private provision -> underconsumption or undersupply o Non-excludability – it’s not feasible to exclude anyone from the benefits of the good (cost of exclusion is too high) -> free rider problem ...
... person = 0). Private provision -> underconsumption or undersupply o Non-excludability – it’s not feasible to exclude anyone from the benefits of the good (cost of exclusion is too high) -> free rider problem ...
Market Failures
... person = 0). Private provision -> underconsumption or undersupply o Non-excludability – it’s not feasible to exclude anyone from the benefits of the good (cost of exclusion is too high) -> free rider problem ...
... person = 0). Private provision -> underconsumption or undersupply o Non-excludability – it’s not feasible to exclude anyone from the benefits of the good (cost of exclusion is too high) -> free rider problem ...
The Role of Prices
... When people conduct business without regard for government controls on price or quantity. Black markets allow consumers to pay more so they can buy a good when rationing makes it otherwise unavailable. Such trade is illegal ...
... When people conduct business without regard for government controls on price or quantity. Black markets allow consumers to pay more so they can buy a good when rationing makes it otherwise unavailable. Such trade is illegal ...
Lecture 5 The Market Equilibrium
... ►Their efforts tend to push price up, enriching suppliers ■ Suppliers compete with each other ► Their efforts tend to push price down, enriching demanders ■ Demanders do NOT compete with suppliers, even thought it sometimes seems that way! ► What about bargaining? Each party tries to convince the ot ...
... ►Their efforts tend to push price up, enriching suppliers ■ Suppliers compete with each other ► Their efforts tend to push price down, enriching demanders ■ Demanders do NOT compete with suppliers, even thought it sometimes seems that way! ► What about bargaining? Each party tries to convince the ot ...
4. The model of Perfect Competition
... BFD Ch. 8. Sloman, J. Economics. Prentice Hall [library shelfmark: 330 SLO] ...
... BFD Ch. 8. Sloman, J. Economics. Prentice Hall [library shelfmark: 330 SLO] ...
Imperfect competition
... • In an industry with monopolistic competition – there are many sellers producing products that are close substitutes for one another – each firm has only limited ability to influence its output price. ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, 2008 ...
... • In an industry with monopolistic competition – there are many sellers producing products that are close substitutes for one another – each firm has only limited ability to influence its output price. ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, 2008 ...
WHAT IS ECONOMICS?
... services cost and allow them to decide whether to consume more or less of a good or service (demand) given how much they value them (utility or preferences) and their budget constraints • Prices tell producers how much consumers are willing to pay for what they produce and how much revenue they will ...
... services cost and allow them to decide whether to consume more or less of a good or service (demand) given how much they value them (utility or preferences) and their budget constraints • Prices tell producers how much consumers are willing to pay for what they produce and how much revenue they will ...
MICRO SYL FALL11 RBW
... STUDENTS ARE RESPONSIBLE FOR DROPPING THE COURSE BY COMPLETING ALL NECESSARY PAPER WORK. FAILURE TO DO SO MAY RESULT IN AN “F” IN THE CLASS. PLEASE NOTE THAT DROPPING COURSES AND REPEATING THEM MORE THAN TWICE MAY RESULT IN INCREASED TUITION CHARGES. COUNSELING AND TUTORIALS ARE AVAILABLE. PLEASE CA ...
... STUDENTS ARE RESPONSIBLE FOR DROPPING THE COURSE BY COMPLETING ALL NECESSARY PAPER WORK. FAILURE TO DO SO MAY RESULT IN AN “F” IN THE CLASS. PLEASE NOTE THAT DROPPING COURSES AND REPEATING THEM MORE THAN TWICE MAY RESULT IN INCREASED TUITION CHARGES. COUNSELING AND TUTORIALS ARE AVAILABLE. PLEASE CA ...
Econ 201 Chpt 14: Perfect Competition 1
... – Perfect competition, in which the market consists of a very large number of firms producing a homogeneous product. – Monopolistic competition, also called competitive market, where there are a large number of independent firms which have a very small proportion of the market share. – Oligopoly, in ...
... – Perfect competition, in which the market consists of a very large number of firms producing a homogeneous product. – Monopolistic competition, also called competitive market, where there are a large number of independent firms which have a very small proportion of the market share. – Oligopoly, in ...
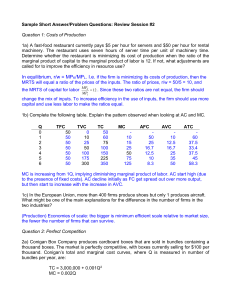
Review Session #2
... 4c) Define a natural monopoly, explaining what the size of the market has to do with whether an industry is a natural monopoly. Suppose that a natural monopolist were required by law to charge its average cost. Draw a diagram, label the price charged, and the deadweight loss to society relative to m ...
... 4c) Define a natural monopoly, explaining what the size of the market has to do with whether an industry is a natural monopoly. Suppose that a natural monopolist were required by law to charge its average cost. Draw a diagram, label the price charged, and the deadweight loss to society relative to m ...
Chapter 7 Practice Questions
... to join the market. Entry of new firms to the industry causes an increase in supply, which then decrease the equilibrium price. This means that firms that were previously making a profit would now be breaking even or making a smaller profit. Entry also causes an increase in competition so that the f ...
... to join the market. Entry of new firms to the industry causes an increase in supply, which then decrease the equilibrium price. This means that firms that were previously making a profit would now be breaking even or making a smaller profit. Entry also causes an increase in competition so that the f ...
Ch - PC
... American enterprise is not free; the man with only a little capital is finding it harder to get into the field, more...impossible to compete with the big fellow. Why? Because the laws of this country do not prevent the strong from crushing the weak...and because the strong have crushed the weak the ...
... American enterprise is not free; the man with only a little capital is finding it harder to get into the field, more...impossible to compete with the big fellow. Why? Because the laws of this country do not prevent the strong from crushing the weak...and because the strong have crushed the weak the ...
Chpt 14 Supplement
... – Perfect competition, in which the market consists of a very large number of firms producing a homogeneous product. – Monopolistic competition, also called competitive market, where there are a large number of independent firms which have a very small proportion of the market share. – Oligopoly, in ...
... – Perfect competition, in which the market consists of a very large number of firms producing a homogeneous product. – Monopolistic competition, also called competitive market, where there are a large number of independent firms which have a very small proportion of the market share. – Oligopoly, in ...
Exam 3 Version B
... 21. Which of the following would make cheating on a collusive agreement more likely? a. greater ease of observing other firms’ prices b. a reduction in the number of sellers in the market c. more frequent shifts in market demand d. all of the above would make cheating on a collusive agreement less l ...
... 21. Which of the following would make cheating on a collusive agreement more likely? a. greater ease of observing other firms’ prices b. a reduction in the number of sellers in the market c. more frequent shifts in market demand d. all of the above would make cheating on a collusive agreement less l ...
economics and the constitution free markets mix economy
... The validity of the public debt of the United States, authorized by law, including debts incurred for payment of pensions and bounties for services in suppressing insurrection or rebellion, shall not be questioned. But neither the United States nor any State shall assume or pay any debt or obligatio ...
... The validity of the public debt of the United States, authorized by law, including debts incurred for payment of pensions and bounties for services in suppressing insurrection or rebellion, shall not be questioned. But neither the United States nor any State shall assume or pay any debt or obligatio ...
Chapter 16
... • Resources for which property rights are absent or poorly defined • No one can effectively be excluded from such resources • Without government intervention, these resources are generally overexploited & undersupplied ...
... • Resources for which property rights are absent or poorly defined • No one can effectively be excluded from such resources • Without government intervention, these resources are generally overexploited & undersupplied ...
Perfect Competition & Monopoly
... g. Making above-normal profits by existing firms will result in new entries into the industry. Firms that have losses shut down and leave the industry in the long run. ...
... g. Making above-normal profits by existing firms will result in new entries into the industry. Firms that have losses shut down and leave the industry in the long run. ...
Monopolistic Competition
... In a monopolistically competitive market, if firms are making profit, new firms enter, and the demand curves for the incumbent firms shift to the left. Similarly, if firms are making losses, old firms exit, and the demand curves of the remaining firms shift to the right. Because of these shifts in d ...
... In a monopolistically competitive market, if firms are making profit, new firms enter, and the demand curves for the incumbent firms shift to the left. Similarly, if firms are making losses, old firms exit, and the demand curves of the remaining firms shift to the right. Because of these shifts in d ...
Chap 16 Monopolistic Competition
... In a monopolistically competitive market, if firms are making profit, new firms enter, and the demand curves for the incumbent firms shift to the left. Similarly, if firms are making losses, old firms exit, and the demand curves of the remaining firms shift to the right. Because of these shifts in d ...
... In a monopolistically competitive market, if firms are making profit, new firms enter, and the demand curves for the incumbent firms shift to the left. Similarly, if firms are making losses, old firms exit, and the demand curves of the remaining firms shift to the right. Because of these shifts in d ...
Chapter 4The Firm and Market Structures
... - The quantity sold is highest in perfect competition, and the price in perfect competition is usually lowest (but this depends on such factors as demand elasticity and increasing returns to scale). - Monopolists, oligopolists, and producers in monopolistic competition attempt to differentiate their ...
... - The quantity sold is highest in perfect competition, and the price in perfect competition is usually lowest (but this depends on such factors as demand elasticity and increasing returns to scale). - Monopolists, oligopolists, and producers in monopolistic competition attempt to differentiate their ...
Oligopolies and monopolistic competition
... More “powerful” models in that they correspond better to the real world Unfortunately, this means that they are also more complex These models have required the development of new tools ...
... More “powerful” models in that they correspond better to the real world Unfortunately, this means that they are also more complex These models have required the development of new tools ...