McDonalds use a wide range of both price and non-price
... changes the price of a product without changing it physically to compete with its competition. Non-price competition is where a firm makes its product or products seem different. Non-price competition can be broken up into two branches, product variation and product differentiation. Product variatio ...
... changes the price of a product without changing it physically to compete with its competition. Non-price competition is where a firm makes its product or products seem different. Non-price competition can be broken up into two branches, product variation and product differentiation. Product variatio ...
Perfect-Competition
... power) • Homogeneous product – no branding or differentiation • Perfect information – consumers always know what’s on offer for what prices • Freedom of entry & exit – no “barriers to entry” So… firms are price takers. ...
... power) • Homogeneous product – no branding or differentiation • Perfect information – consumers always know what’s on offer for what prices • Freedom of entry & exit – no “barriers to entry” So… firms are price takers. ...
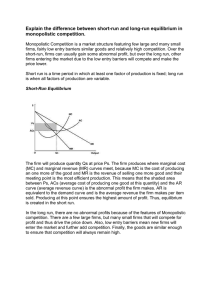
Explain the difference between short-run and long-run
... Monopolistic Competition is a market structure featuring few large and many small firms, fairly low entry barriers similar goods and relatively high competition. Over the short-run, firms can usually gain some abnormal profit, but over the long run, other firms entering the market due to the low ent ...
... Monopolistic Competition is a market structure featuring few large and many small firms, fairly low entry barriers similar goods and relatively high competition. Over the short-run, firms can usually gain some abnormal profit, but over the long run, other firms entering the market due to the low ent ...
Module on the basics of Competition policy and law
... effective competition policy advocates for the removal of obstacles and facilitates investment flows by providing a predictable legal and regulatory environment that reduces the scope of arbitrary decision-making, thereby instilling transparency in the system. (iii) Privatisation reform policy Gover ...
... effective competition policy advocates for the removal of obstacles and facilitates investment flows by providing a predictable legal and regulatory environment that reduces the scope of arbitrary decision-making, thereby instilling transparency in the system. (iii) Privatisation reform policy Gover ...
Peking University Industrial Organization, Spring 2013 Guanghua
... were imposed on each firm? (e) Calculate the equilibrium price, firm output, total output and number of firms in the industry if a technical innovation were to reduce unit production costs to $5? Question 5 In models of monopolistic competition, entry of comparable goods makes each competitor’s resi ...
... were imposed on each firm? (e) Calculate the equilibrium price, firm output, total output and number of firms in the industry if a technical innovation were to reduce unit production costs to $5? Question 5 In models of monopolistic competition, entry of comparable goods makes each competitor’s resi ...
CHAPTER OVERVIEW
... no single model that can portray this market structure due to the wide diversity of oligopolistic situations and mutual interdependence that makes predictions about pricing and output quantity precarious.) A. The kinked-demand model assumes a noncollusive oligopoly. (Figure 9.4) 1. The individual fi ...
... no single model that can portray this market structure due to the wide diversity of oligopolistic situations and mutual interdependence that makes predictions about pricing and output quantity precarious.) A. The kinked-demand model assumes a noncollusive oligopoly. (Figure 9.4) 1. The individual fi ...
Short Run
... The Law of Diminishing Returns states the benefits from adding extra units of input will decrease as the overall amount of input increases. Total Product is the total amount of product produced through the factors of production. Average Product is the amount of total output divided by the amount of ...
... The Law of Diminishing Returns states the benefits from adding extra units of input will decrease as the overall amount of input increases. Total Product is the total amount of product produced through the factors of production. Average Product is the amount of total output divided by the amount of ...
AP Economics Syllabus - Gilbert Public Schools
... Behavioral Expectations: We will follow all District policies as outlined in the Gilbert Public Schools District student handbook. Pay particular attention to policies on bullying and dress code. Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) As members of the Coyote family, we pride ourselve ...
... Behavioral Expectations: We will follow all District policies as outlined in the Gilbert Public Schools District student handbook. Pay particular attention to policies on bullying and dress code. Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) As members of the Coyote family, we pride ourselve ...
Principles of Economics, Case and Fair,8e
... federal regulatory group created by Congress in 1887 to oversee and correct abuses in the railroad industry. Sherman Act Passed by Congress in 1890, the act declared every contract or conspiracy to restrain trade among states or nations illegal and declared any attempt at monopoly, successful or not ...
... federal regulatory group created by Congress in 1887 to oversee and correct abuses in the railroad industry. Sherman Act Passed by Congress in 1890, the act declared every contract or conspiracy to restrain trade among states or nations illegal and declared any attempt at monopoly, successful or not ...
Lecture 13
... federal regulatory group created by Congress in 1887 to oversee and correct abuses in the railroad industry. Sherman Act Passed by Congress in 1890, the act declared every contract or conspiracy to restrain trade among states or nations illegal and declared any attempt at monopoly, successful or not ...
... federal regulatory group created by Congress in 1887 to oversee and correct abuses in the railroad industry. Sherman Act Passed by Congress in 1890, the act declared every contract or conspiracy to restrain trade among states or nations illegal and declared any attempt at monopoly, successful or not ...
2 reviews - David E. Harrington
... Each Chinese restaurant produces meals that are slightly different from those of other Chinese restaurants. Rather than being a price taker, each Chinese restaurant faces a downward-sloping demand curve. Free Entry or Exit Firms can enter or exit the market without restriction. ...
... Each Chinese restaurant produces meals that are slightly different from those of other Chinese restaurants. Rather than being a price taker, each Chinese restaurant faces a downward-sloping demand curve. Free Entry or Exit Firms can enter or exit the market without restriction. ...
Natural Monopolies
... average total cost. Therefore, if regulators require a natural monopoly to charge a price equal to marginal cost, regulator will have to subsidize the “loss” – difference between ATC and price ...
... average total cost. Therefore, if regulators require a natural monopoly to charge a price equal to marginal cost, regulator will have to subsidize the “loss” – difference between ATC and price ...
full powerpoint presentation - Iowa State University Department of
... A problem if there is uncertainty – i.e. if wage is fixed to performance and there is a bad year in chemical sales Could potentially turn off customers – i.e. annoying sales personnel ...
... A problem if there is uncertainty – i.e. if wage is fixed to performance and there is a bad year in chemical sales Could potentially turn off customers – i.e. annoying sales personnel ...
PRACTICE FOR PERFECT COMPETITION Fatma Nur Karaman
... 1) What is the difference between perfect competition and monopolistic competition? A) In monopolistic competition, firms produce identical goods, while in perfect competition, firms produce slightly different goods. B) Perfect competition has a large number of small firms while monopolistic competi ...
... 1) What is the difference between perfect competition and monopolistic competition? A) In monopolistic competition, firms produce identical goods, while in perfect competition, firms produce slightly different goods. B) Perfect competition has a large number of small firms while monopolistic competi ...
Advanced Microeconomic Theory II - Fall 2011 Outline – Short
... firms choose prices simultaneously and non-cooperatively; and that firms produce identical goods. 5.2.1 – The Edgeworth Solution Edgeworth introduced capacity constraints. With such constraints, Bertrand is no longer and equilibrium. 5.2.2 – The Temporal Dimension When the possibility of a reaction ...
... firms choose prices simultaneously and non-cooperatively; and that firms produce identical goods. 5.2.1 – The Edgeworth Solution Edgeworth introduced capacity constraints. With such constraints, Bertrand is no longer and equilibrium. 5.2.2 – The Temporal Dimension When the possibility of a reaction ...
CHAPTER OVERVIEW
... of paper with his or her name. Then leave the room for five minutes on some excuse while the students decide on their bids. This will give them the opportunity to “collude,” and the bright class will decide to have everyone except one person bid $.01 and the high bidder will submit $.02; then they’l ...
... of paper with his or her name. Then leave the room for five minutes on some excuse while the students decide on their bids. This will give them the opportunity to “collude,” and the bright class will decide to have everyone except one person bid $.01 and the high bidder will submit $.02; then they’l ...
Homework #5
... d. Is there a main dish and starter combination that makes both Al and Ben better off than their common dominant strategy pair? If yes name it, if no then show that none of the other pairs make both of them simultaneously better off. e. Now suppose the utilities of Al and Ben are just as before exce ...
... d. Is there a main dish and starter combination that makes both Al and Ben better off than their common dominant strategy pair? If yes name it, if no then show that none of the other pairs make both of them simultaneously better off. e. Now suppose the utilities of Al and Ben are just as before exce ...
Perfect Competition
... But no-where have we indicated or implied the willingness and ability of the producer to supply those goods. Where is the short-run supply curve in this model? For a purely competitive industry the short run market supply curve is the horizontal summation of the MC curves (above the level of AVC) fo ...
... But no-where have we indicated or implied the willingness and ability of the producer to supply those goods. Where is the short-run supply curve in this model? For a purely competitive industry the short run market supply curve is the horizontal summation of the MC curves (above the level of AVC) fo ...
Economics L-6 Monopoly and Monopolistic competition
... The slope of the MR curve is just double of the demand curve. This means the MR curve is twice as steep as the demand curve. This also means that the demand curve will always lie above the MR curve. ...
... The slope of the MR curve is just double of the demand curve. This means the MR curve is twice as steep as the demand curve. This also means that the demand curve will always lie above the MR curve. ...
Absolute Advantage vs. Comparative Advantage
... • Paul owns a custom clothing shop called Paul's Custom Clothes and Accessories. He specializes in creating women's clothing and accessories. He has found that he is able to produce his shirts at a lower production cost than his competitors can. However, he has also found that he has a greater oppor ...
... • Paul owns a custom clothing shop called Paul's Custom Clothes and Accessories. He specializes in creating women's clothing and accessories. He has found that he is able to produce his shirts at a lower production cost than his competitors can. However, he has also found that he has a greater oppor ...
Chapter Seventeen
... provides information to consumers They also argue that advertising increases competition by offering a greater variety of products and prices. The willingness of a firm to spend advertising dollars can be a signal to consumers about the quality of the ...
... provides information to consumers They also argue that advertising increases competition by offering a greater variety of products and prices. The willingness of a firm to spend advertising dollars can be a signal to consumers about the quality of the ...
Course Syllabus - California State University, Bakersfield
... particularly households and business firms. It contrasts with macroeconomics, which is the study of the behavior of the economic system as a whole. Successful study of economics requires an ability to engage in abstract thinking. The course will focus on the development of economic models used to an ...
... particularly households and business firms. It contrasts with macroeconomics, which is the study of the behavior of the economic system as a whole. Successful study of economics requires an ability to engage in abstract thinking. The course will focus on the development of economic models used to an ...