* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam 3 Version B
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
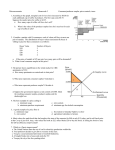
Exam 3 Version A Econ 202 Fall 2006 Dr. Claudia Strow Name__________________________ I. Game Theory (10 points) Bill and Wanda are trying to decide whether to eat at Applebees or BW3 for dinner. They are each trying to maximize their own individual utility, which is given below for each pair of choices. They may either eat at the same restaurant or at different restaurants and their happiness depends not only on their own decision but on where the other eats as well. Bill Applebees BW3 Applebees B: 12 B: 15 W: 10 W: 12 Wanda BW3 B: 7 B: 10 W: 8 W: 15 a. Does Bill have a dominant strategy, and if so what is it? b. Does Wanda have a dominant strategy, and if so what is it? c. What is/are the Nash equilibrium/equilibria? _______________________________________ II. Market Structures (24 points) Fill in the following chart with the correct answer for each market structure. Perfect Competition Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly Monopoly # of firms Standardized or Differentiated product Do significant barriers to entry exist (yes or no)? Can there be positive economic profit in the short run (yes or no)? Can there be positive economic profit in the long run (yes or no)? Will individual firms ever advertise (yes or no)? 1 1. The demand curve faced by a perfectly competitive firm is __________. A demand curve faced by a monopolistically competitive firm is ________________. a. horizontal; downward sloping b. downward sloping; downward sloping c. downward sloping; horizontal d. horizontal; horizontal 2. The difference between the value a buyer places on an item and the price they actually have to pay for the item is called a. economic profit b. deadweight loss c. producer surplus d. economic rent e. consumer surplus 3. Which of the following market structures generally supplies the lowest quantity to the market? a. monopolistic competition b. noncolluding oligopolies c. perfect competition d. monopoly 4. Which of the following market structures generally charges the highest price to the market? a. monopolistic competition b. noncolluding oligopolies c. perfect competition d. monopoly 5 Tommy’s Tires operates in a purely competitive market. If the price equals $100 per tire and average total costs equal $80 per tire at the profit-maximizing output level, then in the long run a. the market supply curve will shift to the left b. the equilibrium price per tire will rise c. more firms will enter the market d. average total costs will rise e. both a and b will occur 6. Based on the following long run total costs, what will be the long run price charged by a perfectly competitive firm? Q TC 0 0 1 40 2 60 3 75 4 120 5 200 6 300 a. 15 b. 25 c. 30 d. 20 2 e. We cannot tell from the information given 7. Suppose that the MR and MC of Wrist-Go-Round manufacturing bracelets is the following: Q MR MC 2 50 50 3 50 48 4 50 51 5 50 55 6 50 60 Wrist-Go-Round should produce ____ bracelets a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 5 e. 6 8. Using the information given in the problem above, if Wrist-Go-Round chooses to produce, what is their profit? a. $0 b. $2 c. $6 d. $5 e. we do not have enough information to determine their profit 9. If Carter’s Plumbing chooses to produce, then they maximize profits by fixing 10 leaky sinks a month. If they fix 10 sinks, then they can charge $10 for each sink. They must pay $160 in total cost, of which $90 is total fixed cost. Should Carter’s Plumbing fix sinks in the short run? a. yes since TR>TFC b. yes since TR>TVC c. yes since TR>MC d. no since TR<MC e. no since TR<TC 10. Q ATC 10 70 11 80 12 90 Above are the Average Total Costs for different quantities of sweaters produced at Granny’s Knitting. If Granny’s has already made and sold 11 sweaters, what is the minimum price for which she would be willing to produce and sell a 12th sweater? a. b. c. d. e. $200 $7.50 $1080 $90 $180 3 Use the following Graph for a perfectly competitive firm to answer questions 11-13. MC ATC AVC 60 40 30 20 10 30 35 40 43 55 60 Q 11. When the price is 10 and the firm maximizes its profit or minimizes its loss, the firm will in the short run a. experience a positive profit. b. experience a loss, but continues to operate. c. shut down and experience a zero profit. d shut down and experience a loss (a negative profit). 12. This firm makes a positive economic profit only if the price is greater than a. $10 b. $20 c. $30 d. $40 e. $60 13. When price is equal to 30, the profit-maximizing firm will produce what level of output? a. 30 b. 40 c. 43 d. 55 e. none of the above 14. Suppose that a single-price monopolist lowers its price from $80 to $75 in order to sell more output. Marginal revenue will a. equal $75 b. equal $80 c. be between $75 and $80 d. be less than $75 e. be greater than $80 4 Use the graph below to answer questions 15-18 $ 50 MC ATC 35 18 17 6 MR 10 15 20 23 26 15. A single-price monopoly would set the price at: a. $6 b. $17 c. $18 d. $35 e. $50 32 D 35 Q 16. The profit of a single price monopolist is a. $18 b. $15 c. $270 d. $525 e. none of the above 17. A purely competitive market would charge a market price of: a. $6 b. $17 c. $18 d. $35 e. $50 18. If this firm decides to charge two prices such that all individuals with blonde hair pay $18 and all other individuals pay the single price monopolist price, then a. deadweight loss will decrease while consumer surplus will increase b. deadweight loss will increase while consumer surplus will decrease c. both deadweight loss and consumer surplus will decrease d. both deadweight loss and consumer surplus will increase e. deadweight loss will not change but consumer surplus will decrease 5 19. Which of the following is a distinguishing characteristic of oligopolies a. a standardized product b. interdependence among firms c. product differentiation d. downward-sloping demand curves faced by firms e. the goal of profit maximization 20. The type of collusion where one firm sets its price for the good and all other firms in the industry matches that price is called a. Price leadership collusion b. Tit for Tat collusion c. Explicit collusion d. Cartel collusion 21. Which of the following would make cheating on a collusive agreement more likely? a. greater ease of observing other firms’ prices b. a reduction in the number of sellers in the market c. more frequent shifts in market demand d. all of the above would make cheating on a collusive agreement less likely 22. In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm has excess capacity because it is always producing where a. MR>MC b. the firm is in the portion of its ATC that exhibits diseconomies of scale. c. the firm is in the portion of its ATC that exhibits economies of scale. d. the firm is at the minimum point of the ATC. e. economic profit is greater than zero 6