Unit 1: Going Into Business For Yourself
... organization and ownership of a business. He or she also accepts the risks and responsibilities Venture: A new business undertaking that involves risk Entrepreneurship: the process of recognizing an opportunity, testing it on the market, and gathering the necessary resources to go into business More ...
... organization and ownership of a business. He or she also accepts the risks and responsibilities Venture: A new business undertaking that involves risk Entrepreneurship: the process of recognizing an opportunity, testing it on the market, and gathering the necessary resources to go into business More ...
economics unit #2 study guide
... SSEMI3 The student will explain how markets, prices, and competition influence economic behavior. a. Identify and illustrate on a graph factors that cause changes in market supply and demand. b. Explain and illustrate on a graph how price floors create surpluses and price ceilings create shortages. ...
... SSEMI3 The student will explain how markets, prices, and competition influence economic behavior. a. Identify and illustrate on a graph factors that cause changes in market supply and demand. b. Explain and illustrate on a graph how price floors create surpluses and price ceilings create shortages. ...
1.3 Choosing to spend
... • When buyers and sellers come together, a market is formed. • For most goods and services, the market price is determined by the amount buyers are willing to pay and the price that businesses need to be paid to cover their costs. • Eventually, the price will settle at a point where supply equals de ...
... • When buyers and sellers come together, a market is formed. • For most goods and services, the market price is determined by the amount buyers are willing to pay and the price that businesses need to be paid to cover their costs. • Eventually, the price will settle at a point where supply equals de ...
Competition and Market Structures
... Further from pure competition than a monopolistic competition ...
... Further from pure competition than a monopolistic competition ...
Print › Economics wt Reading | Quizlet
... ways to convince buyers that the product is unique or better than others by advertising, giveaways, or other promotions ...
... ways to convince buyers that the product is unique or better than others by advertising, giveaways, or other promotions ...
Monopolistic Competition
... Price exceeds marginal cost in LR P=ATC b/c entry/exit Possesses excess capacity Evaluate based upon deadweight loss, consumer surplus ...
... Price exceeds marginal cost in LR P=ATC b/c entry/exit Possesses excess capacity Evaluate based upon deadweight loss, consumer surplus ...
Monopolistic Competition - Royal Order of Tanstaafl
... • The value of advertising is that it tells you the exact opposite of what the advertiser actually thinks. … If Coke and Pepsi spend billions of dollars to convince you that there are significant differences between these products, both companies realize that Pepsi and Coke are virtually identical. ...
... • The value of advertising is that it tells you the exact opposite of what the advertiser actually thinks. … If Coke and Pepsi spend billions of dollars to convince you that there are significant differences between these products, both companies realize that Pepsi and Coke are virtually identical. ...
Imperfect Competition
... 1. There are many buyers in the industry • An individual buyer, by his/her own actions cannot influence the market price of the goods. • If one person decides not to buy the good it will make no difference to the price of the good. ...
... 1. There are many buyers in the industry • An individual buyer, by his/her own actions cannot influence the market price of the goods. • If one person decides not to buy the good it will make no difference to the price of the good. ...
ECO 481
... 1. The more sellers, the harder it is to form a cartel. 2. The more non-homogeneous the product, the harder it is to form a cartel. 3. The more excess capacity, the harder it is to form a cartel. ...
... 1. The more sellers, the harder it is to form a cartel. 2. The more non-homogeneous the product, the harder it is to form a cartel. 3. The more excess capacity, the harder it is to form a cartel. ...
Unit 3 Reviewsheet
... 12. Industry--group of firms producing similar or identical products 13. Market structure--market classification according to number and size of firms, type of product, and type of competition; nature and degree of competition among firms in the same industry 14. Monopolistic competition--market str ...
... 12. Industry--group of firms producing similar or identical products 13. Market structure--market classification according to number and size of firms, type of product, and type of competition; nature and degree of competition among firms in the same industry 14. Monopolistic competition--market str ...
Word Doc
... Courts have generally interpreted antitrust laws based on a balancing of the anticompetitive and pro-competitive effects of a targeted practice. This standard is referred to as a “rule of reason” test. This is in contrast to a “per se rule,” which forbids a prohibited practice, regardless of any pos ...
... Courts have generally interpreted antitrust laws based on a balancing of the anticompetitive and pro-competitive effects of a targeted practice. This standard is referred to as a “rule of reason” test. This is in contrast to a “per se rule,” which forbids a prohibited practice, regardless of any pos ...
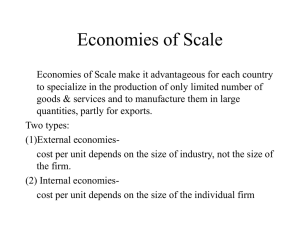
Economies of Scale and International Trade,a
... Economies of Scale Economies of Scale make it advantageous for each country to specialize in the production of only limited number of goods & services and to manufacture them in large quantities, partly for exports. Two types: (1)External economiescost per unit depends on the size of industry, not t ...
... Economies of Scale Economies of Scale make it advantageous for each country to specialize in the production of only limited number of goods & services and to manufacture them in large quantities, partly for exports. Two types: (1)External economiescost per unit depends on the size of industry, not t ...
Market economy test.
... — History. Anti-dumping and competition law have similar origins • US • 1890 Sherman Act (antitrust) prohibited any restraint of trade or attempt to monopolize by groups or individuals • 1914 Clayton Act (antitrust) first captured concept of predatory pricing and price discrimination. • 1916 Anti-Du ...
... — History. Anti-dumping and competition law have similar origins • US • 1890 Sherman Act (antitrust) prohibited any restraint of trade or attempt to monopolize by groups or individuals • 1914 Clayton Act (antitrust) first captured concept of predatory pricing and price discrimination. • 1916 Anti-Du ...
File
... restricted due to high costs or other impediments, which may be economic, social or political. For instance, a government can create a monopoly over an industry that it wants to control, such as electricity. ...
... restricted due to high costs or other impediments, which may be economic, social or political. For instance, a government can create a monopoly over an industry that it wants to control, such as electricity. ...
File use market structures ppt
... Big Challenge to Government due to price leadership, collusion and cartels. Collusion = an agreement to act together or behave in a cooperative manner. Cartels = a formal organization of producers that agree to fix prices and production (Most successful when limiting production and price) SWS 2006 ...
... Big Challenge to Government due to price leadership, collusion and cartels. Collusion = an agreement to act together or behave in a cooperative manner. Cartels = a formal organization of producers that agree to fix prices and production (Most successful when limiting production and price) SWS 2006 ...
Business Administration
... Partners in tender submit proposal for contract on certain products The purpose of tender is to obtain a larger number of offers and the most suitable is selected ...
... Partners in tender submit proposal for contract on certain products The purpose of tender is to obtain a larger number of offers and the most suitable is selected ...
Antitrust Policy
... o Break up monopolies into competing firms o Courts can also fine or imprison violators o Parties injured by illegal combinations and conspiracies can sue the perpetrators for treble damages o Sound foundation for positive government action against business monopolies Clayton Act of 1914 o Contain ...
... o Break up monopolies into competing firms o Courts can also fine or imprison violators o Parties injured by illegal combinations and conspiracies can sue the perpetrators for treble damages o Sound foundation for positive government action against business monopolies Clayton Act of 1914 o Contain ...
SpotNomics
... As an independent professional authority, the MCCAA plays a leading role in promoting and protecting consumer interests while ensuring that businesses are fair and competitive. What consumer and competition legislation is utilized by the Authority to carry out its work? The Authority has many differ ...
... As an independent professional authority, the MCCAA plays a leading role in promoting and protecting consumer interests while ensuring that businesses are fair and competitive. What consumer and competition legislation is utilized by the Authority to carry out its work? The Authority has many differ ...
What Are The Characteristics of A Monopoly?
... Pharmaceutical drugs, Rubics Cube… -Government allows monopoly for public benefits or to stimulate innovation. -The government issues patents to protect inventors and forbids others from using their invention. (They last 20 years) ...
... Pharmaceutical drugs, Rubics Cube… -Government allows monopoly for public benefits or to stimulate innovation. -The government issues patents to protect inventors and forbids others from using their invention. (They last 20 years) ...
Economics of Government Intervention Lynne Kiesling Cato University 2011
... “Secret recipe”, some particular skill or technology, ownership of a natural resource ...
... “Secret recipe”, some particular skill or technology, ownership of a natural resource ...
Market Structures - McEachern High School
... And fast food is all very similar. In selling a SIMILAR product, such businesses must highlight SMALL DIFFERENCES— In a process called PRODUCT DIFFERENTIATION— In order to attract customers. They do this through… Advertising. ...
... And fast food is all very similar. In selling a SIMILAR product, such businesses must highlight SMALL DIFFERENCES— In a process called PRODUCT DIFFERENTIATION— In order to attract customers. They do this through… Advertising. ...