* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam 2 Study Guide
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
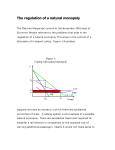
ECON 2106 Principles of Microeconomics Study Guide Outline Chapter 7: Production and Cost Accounting (Explicit) costs vs. Economic (Implicit) costs Law of diminishing Marginal Returns SR vs. LR o Fixed and variable costs Cost curves o MC o AVC o ATC LRATC o Economies of scale o Diseconomies of scale o Constant returns to scale Chapter 8: Profit-maximization Calculate profit: π = TR - TC Accounting π vs. Economic π Goal of firm Demand and cost constraints How to choose profit-maximizing output o TR TC approach: Calc 𝜋 = 𝑇𝑅 − 𝑇𝐶 at each output level and compare o MR MC approach: Choose q where MR=MC Shut-down rule o TR < TVC Shut down Chapter 9: Perfect Competition (Supplemental handouts available) Characteristics Goal of perfectly competitive firm How to choose output Shut-down rule o P < AVC Shut down SR vs. LR o SR: # firms is fixed o LR: # can change o EQM in SR o EQM in LR Profit/Loss and entry/exit Different cost industries Chapter 10: Monopoly (Supplemental handouts available) Characteristics Barriers to entry o Natural o Legal o Network Externalities Goal of monopolistic firm How to choose output SR vs. LR Monopoly vs. Perfect Competition o Generally PM>P* and QM<Q* Government involvement o Regulation o Rent-seeking behavior Price Discrimination o Conditions o Perfect Price Discrimination o Choosing Multiple Prices o In Everyday Life Chapter 14: Economic Efficiency Economic efficiency Pareto improvements Efficient quantity Measuring market gains (Consumer and Producer Surplus) Inefficient markets and Deadweight Loss o Price ceiling & Price floor o Significant market power (i.e. monopoly) o Excise taxes Chapter 15: Government’s Role in Economic Efficiency Market Failures and solutions o Monopoly Anti-trust Law Regulation (natural monopoly) Marginal Cost Pricing Average Cost Pricing o Externalities Positive Externality Marginal Social Benefit Subsidy Negative Externality Marginal Social Cost Pigovian Tax Tradable Pollution Permits Coase Theorem Private market can solve externality problem if side payments can be made without cost Chapter 15: Government’s Role in Economic Efficiency (cont) Market Failures and solutions (cont) o Public Goods Characteristics Nonrival Non-excludable Free-rider Problem Government Provision Tragedy of the Commons (overuse of common resources) o Asymmetric Information Adverse selection (quality) A good reputation can help Moral Hazard (future behavior) Higher rates for riskier behavior Principal-Agent Problem Incentives for agent to act in accordance with principal’s wishes o Government Policies Sometimes policies can be the cause of economic inefficiency