Constraint Satisfaction Complexity and Logic Phokion G. Kolaitis
... Boolean Non-Uniform CSP Definition: Boolean Non-Uniform CSP CSP(B) with B = ({0, 1}, R1B , . . . , R1B ) Fact: Boolean Non-Uniform CSP problems are Generalized Satisfiability Problems, i.e., variants of Boolean satisfiability in CNF. Examples: Each of the following problems is a CSP(B) problem for ...
... Boolean Non-Uniform CSP Definition: Boolean Non-Uniform CSP CSP(B) with B = ({0, 1}, R1B , . . . , R1B ) Fact: Boolean Non-Uniform CSP problems are Generalized Satisfiability Problems, i.e., variants of Boolean satisfiability in CNF. Examples: Each of the following problems is a CSP(B) problem for ...
pse14 VanLong 19108260 en
... problem is a standard optimal control problem. Necessary conditions for the existence (and unicity) of an optimal control are notoriously elusive. Eventually, one has to decipher the necessary conditions for a differential equation to have a (unique) solution, a question about which little is known w ...
... problem is a standard optimal control problem. Necessary conditions for the existence (and unicity) of an optimal control are notoriously elusive. Eventually, one has to decipher the necessary conditions for a differential equation to have a (unique) solution, a question about which little is known w ...
properties of some weak forms of continuity
... under the operations like compositions, restrictions, graph functions, and generalized ...
... under the operations like compositions, restrictions, graph functions, and generalized ...
The Theory of Economy Efficiency. Organizational, Institutional and
... yield more effective result with the same funds and manpower. Summing up, it is necessary to conclude that X-efficiency is not efficiency in its original sense but, more likely, untapped reserve which actually builds underproduced product (income) in the system’s functioning. In other words, if all ...
... yield more effective result with the same funds and manpower. Summing up, it is necessary to conclude that X-efficiency is not efficiency in its original sense but, more likely, untapped reserve which actually builds underproduced product (income) in the system’s functioning. In other words, if all ...
Constructions with ruler and compass
... At every stage, the next layer consists of those obtained as intersections of lines and circles constructed from points of the previous layers. The points of the previous layers have constructible co-ordinates by induction. Therefore the equations of the lines and circles have constructible coeffici ...
... At every stage, the next layer consists of those obtained as intersections of lines and circles constructed from points of the previous layers. The points of the previous layers have constructible co-ordinates by induction. Therefore the equations of the lines and circles have constructible coeffici ...
Constructions with ruler and compass
... All points so obtained as intersections are called constructible: the original two points are by definition constructible. It is also convenient to apply the term constructible to the lines and circles that we can draw by this process. We will extend the term further to other objects as well: a tria ...
... All points so obtained as intersections are called constructible: the original two points are by definition constructible. It is also convenient to apply the term constructible to the lines and circles that we can draw by this process. We will extend the term further to other objects as well: a tria ...
Document
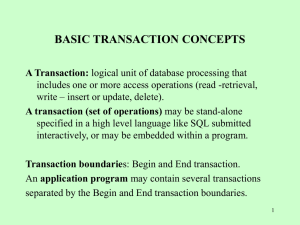
... This occurs when two transactions that access the same database items have their operations interleaved in a way that makes the value of some database item incorrect. The Temporary Update (or Dirty Read) Problem. This occurs when one transaction updates a database item and then the transaction fails ...
... This occurs when two transactions that access the same database items have their operations interleaved in a way that makes the value of some database item incorrect. The Temporary Update (or Dirty Read) Problem. This occurs when one transaction updates a database item and then the transaction fails ...
X - Information Theory Society
... An important mathematical theory can provide some insights which cannot be obtained from other means. Problems involve random variables taking values from countably infinite alphabets. Finite alphabet is the special case. Benefits: tighter bounds, faster convergent rates, etc. In source co ...
... An important mathematical theory can provide some insights which cannot be obtained from other means. Problems involve random variables taking values from countably infinite alphabets. Finite alphabet is the special case. Benefits: tighter bounds, faster convergent rates, etc. In source co ...
Lecture - Department of Computing
... Two-phase locking protocol 1.before operating on an object a transaction must acquire a lock on that object 2.after releasing a lock a transaction must not go on to acquire any more locks • phase1 (growing): acquire locks (not simultaneously) • phase2 (shrinking): release locks (no further acquisiti ...
... Two-phase locking protocol 1.before operating on an object a transaction must acquire a lock on that object 2.after releasing a lock a transaction must not go on to acquire any more locks • phase1 (growing): acquire locks (not simultaneously) • phase2 (shrinking): release locks (no further acquisiti ...
Automated Theorem Proving in Loop Theory
... no automatically generated proof was found to be incorrect during translation. In some cases, the main results weren’t obtained directly with automated theorem provers. Instead, provers were used to prove key technical lemmas, or even just special cases, which in turn helped mathematicians find proo ...
... no automatically generated proof was found to be incorrect during translation. In some cases, the main results weren’t obtained directly with automated theorem provers. Instead, provers were used to prove key technical lemmas, or even just special cases, which in turn helped mathematicians find proo ...
the nekhoroshev theorem and long–term stabilities in the solar system
... normal forms considered in the proof of the Nekhoroshev’s theorem (see Section 4). In fact, for small values of perturbation parameter ε, the resonances of the system are organized as a web, the so– called Arnold web, which occupies a small measure set of the phase–space. Only a small fraction of in ...
... normal forms considered in the proof of the Nekhoroshev’s theorem (see Section 4). In fact, for small values of perturbation parameter ε, the resonances of the system are organized as a web, the so– called Arnold web, which occupies a small measure set of the phase–space. Only a small fraction of in ...
Database overview
... If read_TS(X) > TS(T) or if write_TS(X) > TS(T), then an younger transaction has already read the data item so abort and roll-back T and reject the operation. If the condition in part (a) does not exist, then execute write_item(X) of T and set write_TS(X) to TS(T). 2. Transaction T issues a read ...
... If read_TS(X) > TS(T) or if write_TS(X) > TS(T), then an younger transaction has already read the data item so abort and roll-back T and reject the operation. If the condition in part (a) does not exist, then execute write_item(X) of T and set write_TS(X) to TS(T). 2. Transaction T issues a read ...
pdf file
... and by commutativity, x · a = 1 ∈ G. But certainly, ax + ny = 1 implies that xa + ny = 1, so gcd(x, n) = 1 by Lemma 2.3, and x ∈ G. Q.E.D. ...
... and by commutativity, x · a = 1 ∈ G. But certainly, ax + ny = 1 implies that xa + ny = 1, so gcd(x, n) = 1 by Lemma 2.3, and x ∈ G. Q.E.D. ...
Transforms on Time Scales - Institute for Mathematics and its
... what is meant by a transform. All integral transforms can be expressed as integration against some function and all series transforms can be expressed as summing against some function. The theory of time scales presents itself as a potential way for defining what we mean as a transform. One might be ...
... what is meant by a transform. All integral transforms can be expressed as integration against some function and all series transforms can be expressed as summing against some function. The theory of time scales presents itself as a potential way for defining what we mean as a transform. One might be ...
externalities (new window)
... Private Property and Optimal Conservation Prices determine the timing of resource consumption The expected future price, PF, of a resource reflects the expected value of consuming one more unit of the resource in the future. The current price, PC, reflects the value of consuming one more unit of t ...
... Private Property and Optimal Conservation Prices determine the timing of resource consumption The expected future price, PF, of a resource reflects the expected value of consuming one more unit of the resource in the future. The current price, PC, reflects the value of consuming one more unit of t ...
Automated Theorem Proving - Home ANU
... To solve problem instances a constraint solver is usually much more efficient than a theorem prover (e.g. use a SAT solver) Theorem provers are not even guaranteed to terminate, in general Other tasks where theorem proving is more appropriate? Automated Theorem Proving – Peter Baumgartner – p.8 ...
... To solve problem instances a constraint solver is usually much more efficient than a theorem prover (e.g. use a SAT solver) Theorem provers are not even guaranteed to terminate, in general Other tasks where theorem proving is more appropriate? Automated Theorem Proving – Peter Baumgartner – p.8 ...
Three-dimensional Bonnesen type inequalities
... Let K be a convex body of R3 . How state a three-dimensional version of Problem 2.1? How to replace the constraints on perimeter and area? While the volume V is a natural substitute of the area, there are at least two possibilities for the other quantity. According to Kubota’s integral formula (see ...
... Let K be a convex body of R3 . How state a three-dimensional version of Problem 2.1? How to replace the constraints on perimeter and area? While the volume V is a natural substitute of the area, there are at least two possibilities for the other quantity. According to Kubota’s integral formula (see ...
View PDF - CiteSeerX
... imProof of Theorem 4.2: Notice that the condition , so we can use the first part of the proof plies that of Theorem 3.2. The notation used here is the same as that in the proof of Theorem 3.2. First, we have ...
... imProof of Theorem 4.2: Notice that the condition , so we can use the first part of the proof plies that of Theorem 3.2. The notation used here is the same as that in the proof of Theorem 3.2. First, we have ...
Full text
... Proof; We prove this theorem using Ehrlich's formulas: ®(2r -2s) = V®(2r-s -l) = 2s(2r-s -l) = n. D It can be shown that only for such an n does the length of the cycle of the basic-Duccisequence equal n. Theorem 9; If 2P(w) = n, then n = 2r -2\ where n > 2 and r > s > 0. Proof: Using properties (3) ...
... Proof; We prove this theorem using Ehrlich's formulas: ®(2r -2s) = V®(2r-s -l) = 2s(2r-s -l) = n. D It can be shown that only for such an n does the length of the cycle of the basic-Duccisequence equal n. Theorem 9; If 2P(w) = n, then n = 2r -2\ where n > 2 and r > s > 0. Proof: Using properties (3) ...
A transaction
... 3. [read_item,T,X]: Records that transaction T has read the value of database item X. 4. [commit,T]: Records that transaction T has completed successfully, and affirms that its effect can be committed (recorded permanently) to the database. 5. [abort,T]: Records that transaction T has been aborted. ...
... 3. [read_item,T,X]: Records that transaction T has read the value of database item X. 4. [commit,T]: Records that transaction T has completed successfully, and affirms that its effect can be committed (recorded permanently) to the database. 5. [abort,T]: Records that transaction T has been aborted. ...
Midsegments of Triangles
... 28. Given your answer to Exercise 27, is it possible for QP to equal 50? Explain. Answers may vary. Sample: The radii measure 61, since QO is one of the radii. QP is longer _______________________________________________________________________ than the radius of the circle. Therefore, its length ca ...
... 28. Given your answer to Exercise 27, is it possible for QP to equal 50? Explain. Answers may vary. Sample: The radii measure 61, since QO is one of the radii. QP is longer _______________________________________________________________________ than the radius of the circle. Therefore, its length ca ...
Equivalent and absolutely continuous measure
... jump-diffusions to be equivalent or absolutely continuous. The conditions consist of local bounds on the transformation of one generator into the other one and the assumption that the martingale problem for the second generator has for all initial distributions a unique solution. The formulation of ...
... jump-diffusions to be equivalent or absolutely continuous. The conditions consist of local bounds on the transformation of one generator into the other one and the assumption that the martingale problem for the second generator has for all initial distributions a unique solution. The formulation of ...
A79 INTEGERS 13 (2013) - RIMS, Kyoto University
... Emory REU in Number Theory and making valuable suggestions. We would also like to thank Robert Lemke Oliver for his guidance in both research and writing. ...
... Emory REU in Number Theory and making valuable suggestions. We would also like to thank Robert Lemke Oliver for his guidance in both research and writing. ...