Example 1 - ClassZone
... back and forth, higher and higher, until it goes over the top and around in a circular motion. In the diagram below, AD and BC represent two of the swinging arms, and DC is parallel to the ground (line l). Explain why the moving platform AB is always parallel to the ground. ...
... back and forth, higher and higher, until it goes over the top and around in a circular motion. In the diagram below, AD and BC represent two of the swinging arms, and DC is parallel to the ground (line l). Explain why the moving platform AB is always parallel to the ground. ...
Note An elementary proof of Blackwell`s theorem
... Blackwell, 195 1, 1953, and Marschak and Miyasawa, 1968). In this paper we present a more compact and simpler proof of the theorem. A simpler proof was given also by Cremer (1982) and Ponssard (1975). We present here a proof of Blackwell’s theorem which is shorter than all of the above-mentioned pro ...
... Blackwell, 195 1, 1953, and Marschak and Miyasawa, 1968). In this paper we present a more compact and simpler proof of the theorem. A simpler proof was given also by Cremer (1982) and Ponssard (1975). We present here a proof of Blackwell’s theorem which is shorter than all of the above-mentioned pro ...
Homework Read carefully chapter 5 of Dunham`s book and
... b) Prove that the area S of the quadrilateral is given by 2S = ef sin α. Hint: Add areas of the triangles AF B, BF C, CF D, DF A. c) Show that 4(p − a)(p − c) = b2 + d2 − a2 − c2 + 2(ac + bd) and 4(p − b)(p − d) = ...
... b) Prove that the area S of the quadrilateral is given by 2S = ef sin α. Hint: Add areas of the triangles AF B, BF C, CF D, DF A. c) Show that 4(p − a)(p − c) = b2 + d2 − a2 − c2 + 2(ac + bd) and 4(p − b)(p − d) = ...
Warm-Up: 1. What are the three things that need to be true to apply
... Objective: Students will be able to understand and use Rolle’s Theorem. Rolle’s Theorem: Let f be continuous on the closed interval [a,b] and differentiable on the open interval (a,b). If f(a)=f(b) then there is at least one number c in (a,b) such that f’(c)=0. How does it work? ...
... Objective: Students will be able to understand and use Rolle’s Theorem. Rolle’s Theorem: Let f be continuous on the closed interval [a,b] and differentiable on the open interval (a,b). If f(a)=f(b) then there is at least one number c in (a,b) such that f’(c)=0. How does it work? ...
Slides - SIGMOBILE
... μ[n] = full-size gradient ascent o Else μ[n] = halved-size gradient ascent ...
... μ[n] = full-size gradient ascent o Else μ[n] = halved-size gradient ascent ...
four color theorem
... a mathematical theorem. The idea is to use a computer program to perform lengthy computations, and to provide a proof that the result of these computations implies the given theorem. In 1976, the four color theorem was the first major theorem to be verified using a computer program; the Kepler conje ...
... a mathematical theorem. The idea is to use a computer program to perform lengthy computations, and to provide a proof that the result of these computations implies the given theorem. In 1976, the four color theorem was the first major theorem to be verified using a computer program; the Kepler conje ...
c. - Phi Delta Phi
... long as the property is alienbility (can sell it), and as long as there are no/low transaction costs to sell/alienate, the resource will wind up with the most efficient user (no matter what the initial allocation of property rights were…it will move to the most efficient user…let market system do it ...
... long as the property is alienbility (can sell it), and as long as there are no/low transaction costs to sell/alienate, the resource will wind up with the most efficient user (no matter what the initial allocation of property rights were…it will move to the most efficient user…let market system do it ...
Review Sheet for Last Third of the Class
... 1. Concepts of rivalry and excludability. 2. Distinction between private goods, natural monopolies, common resources, and public goods on the basis of whether they are rival and/or excludable. 3. Public goods are neither rival nor excludable. a. Examples of public goods are national defence, basic r ...
... 1. Concepts of rivalry and excludability. 2. Distinction between private goods, natural monopolies, common resources, and public goods on the basis of whether they are rival and/or excludable. 3. Public goods are neither rival nor excludable. a. Examples of public goods are national defence, basic r ...
Practice Problems: Module D, Waiting
... a) Determine the economic order quantity. b) How many orders per year will there be? c) Compute the total cost of ordering and carrying flour. d) If ordering costs were to increase by $1 per order, how much would that affect the minimum total annual cost? HINT – Find new EOQ. ...
... a) Determine the economic order quantity. b) How many orders per year will there be? c) Compute the total cost of ordering and carrying flour. d) If ordering costs were to increase by $1 per order, how much would that affect the minimum total annual cost? HINT – Find new EOQ. ...
20160425145340assignment_week_7
... USE THE AdventureWorks2012 database for the following: 1. Use sp_configure to grant the first parameter to all users by default, show advanced options and run reconfigure. Use sp_configure to change the maximum lock settings from 0 to 20000 using the locks option and run reconfigure. Copy and paste ...
... USE THE AdventureWorks2012 database for the following: 1. Use sp_configure to grant the first parameter to all users by default, show advanced options and run reconfigure. Use sp_configure to change the maximum lock settings from 0 to 20000 using the locks option and run reconfigure. Copy and paste ...
MN415 - GM-FB Case Summary
... executives having the skills required by GM; e.g. integrating FB was the natural way to convince the Fisher brothers, who where highly respected managers/industry leaders, to dedicate all of their time to GM Reported fallacies about the rational2 - The FB/GM story is not a case of market failure of ...
... executives having the skills required by GM; e.g. integrating FB was the natural way to convince the Fisher brothers, who where highly respected managers/industry leaders, to dedicate all of their time to GM Reported fallacies about the rational2 - The FB/GM story is not a case of market failure of ...
externality
... • Internalizing an externality involves altering incentives so that people take account of the external effects of their actions. • The government can internalize an externality by imposing a tax/subsidy to reduce/increase the equilibrium quantity to the socially desirable level. ...
... • Internalizing an externality involves altering incentives so that people take account of the external effects of their actions. • The government can internalize an externality by imposing a tax/subsidy to reduce/increase the equilibrium quantity to the socially desirable level. ...
CHAPTER OVERVIEW
... 2. Spillover benefits occur when the benefits of a good are received by others in the community although they did not pay for them. These benefits are not reflected in the individual demand curve. B. One approach to reducing the externality or misallocation problem is the market approach of individu ...
... 2. Spillover benefits occur when the benefits of a good are received by others in the community although they did not pay for them. These benefits are not reflected in the individual demand curve. B. One approach to reducing the externality or misallocation problem is the market approach of individu ...
Ramsey`s theorem for colors from a metric space
... compact but not metric, and where the statement of the theorem fails. Let K be any compact space where not every sequence has a convergent subsequence. For instance, K can be an uncountable product of unit intervals. Take some sequence a1 , a2 , . . . in K which does not have any convergent subseque ...
... compact but not metric, and where the statement of the theorem fails. Let K be any compact space where not every sequence has a convergent subsequence. For instance, K can be an uncountable product of unit intervals. Take some sequence a1 , a2 , . . . in K which does not have any convergent subseque ...
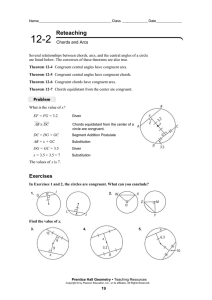
12.2 Reteaching
... In this problem, x is the radius. To find its value draw radius BD , which becomes the hypotenuse of right ∆BED. Then use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve. ED = CE = 3 ...
... In this problem, x is the radius. To find its value draw radius BD , which becomes the hypotenuse of right ∆BED. Then use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve. ED = CE = 3 ...
analytically smootidng effect for schrodinger equations
... Lemma 2.4. Let cp = x . E - iEx . E < E > - 1 and lEI small enough. Then I.., has the inverse 1:;; 1 = J' (D) -l I..,I!!.., = I!!.., I.., J(D)- l which maps continuously from Hp,o to Hp,o' if 8' < 8 - l E I and 181, W I < l . §3. Proof of Theorem In order to prove Theorem 1 it suffices to show the f ...
... Lemma 2.4. Let cp = x . E - iEx . E < E > - 1 and lEI small enough. Then I.., has the inverse 1:;; 1 = J' (D) -l I..,I!!.., = I!!.., I.., J(D)- l which maps continuously from Hp,o to Hp,o' if 8' < 8 - l E I and 181, W I < l . §3. Proof of Theorem In order to prove Theorem 1 it suffices to show the f ...
Mechanized foundations of finite group theory
... occurrence of x, have immediate access to a proof of the associated property. Reasoning about these structures is also very convenient, providing a powerful extension to the notion of refinement types. This styles works very well in practice, allowing us, as described in [4], to build a development ...
... occurrence of x, have immediate access to a proof of the associated property. Reasoning about these structures is also very convenient, providing a powerful extension to the notion of refinement types. This styles works very well in practice, allowing us, as described in [4], to build a development ...
On the Uniqueness of the Decomposition of Manifolds, Polyhedra
... Let M3 and N3 be closed connected geometric prime and orientable 3-manifolds without decomposition into Cartesian product. Let X, Y be closed connected orientable surfaces. If M3 X ≈ N3 Y , then M3≈ N3 and X ≈ Y unless M3 and N3 are Seifert fibered 3-manifolds which are surface bundles over S1 wit ...
... Let M3 and N3 be closed connected geometric prime and orientable 3-manifolds without decomposition into Cartesian product. Let X, Y be closed connected orientable surfaces. If M3 X ≈ N3 Y , then M3≈ N3 and X ≈ Y unless M3 and N3 are Seifert fibered 3-manifolds which are surface bundles over S1 wit ...
Chapter 5
... Discuss the Coase theorem and explain how private bargaining can lead to economic efficiency in a market with an externality. 5.3 Government Policies to Deal with Externalities Analyze government policies to achieve economic efficiency in a market with an externality. 5.4 Four Categories of Goods Ex ...
... Discuss the Coase theorem and explain how private bargaining can lead to economic efficiency in a market with an externality. 5.3 Government Policies to Deal with Externalities Analyze government policies to achieve economic efficiency in a market with an externality. 5.4 Four Categories of Goods Ex ...
The Competition Syllabus - Mathematics Grade VII-XII
... 6. Orthogonal projections on a plane To the curriculum content are also added added: common perpendicular to two straight, three perpendicular reciprocal theorem; mediated plan; leap plan. Note: The Correct use in writing by students of the solution of some theorems (without demonstration): Steiner ...
... 6. Orthogonal projections on a plane To the curriculum content are also added added: common perpendicular to two straight, three perpendicular reciprocal theorem; mediated plan; leap plan. Note: The Correct use in writing by students of the solution of some theorems (without demonstration): Steiner ...
How to Solve an Equation: a topological approach
... Extend x(t) as much as possible, say to 0 < β < ∞. Take ti → β and f −1 ({ty + (1 − t)y0 ,t ∈ [0, 1]}) is compact. ...
... Extend x(t) as much as possible, say to 0 < β < ∞. Take ti → β and f −1 ({ty + (1 − t)y0 ,t ∈ [0, 1]}) is compact. ...
Econ160SQ6(Externalities, Public Goods)
... the locals will accept any offer above $8 million from the firm for the right to move from 100% cleanup to 50% cleanup. Therefore, any offer between $8 million and $10 million will make both parties better off. So we move from 100% to 50%. But trade stops at this point since the firm would only be w ...
... the locals will accept any offer above $8 million from the firm for the right to move from 100% cleanup to 50% cleanup. Therefore, any offer between $8 million and $10 million will make both parties better off. So we move from 100% to 50%. But trade stops at this point since the firm would only be w ...
Takehome final questons
... And that’s it. I’ve been scouring your textbook (and my brain) trying to come up with something that isn’t just duplicating a computation you’ve already performed on an assignment – I suppose I could have you go into Non-Euclid and construct and measure yet another figure or work out another hyperb ...
... And that’s it. I’ve been scouring your textbook (and my brain) trying to come up with something that isn’t just duplicating a computation you’ve already performed on an assignment – I suppose I could have you go into Non-Euclid and construct and measure yet another figure or work out another hyperb ...