Chapter 5
... Chapter Outline and Learning Objectives 5.1 Externalities and Economic Efficiency Identify examples of positive and negative externalities and use graphs to show how externalities affect economic efficiency. 5.2 Private Solutions to Externalities: The Coase Theorem Discuss the Coase theorem and expl ...
... Chapter Outline and Learning Objectives 5.1 Externalities and Economic Efficiency Identify examples of positive and negative externalities and use graphs to show how externalities affect economic efficiency. 5.2 Private Solutions to Externalities: The Coase Theorem Discuss the Coase theorem and expl ...
Mathematical Induction
... To prove a theorem holds true for every natural number, n, you can use induction. 1. Prove it is true for n = 1 (or some specific number.) This is called the “base” case. 2. Assuming the theorem is true for n = k (this is called the “induction hypothesis”.) 3. Now do the work to show the next case f ...
... To prove a theorem holds true for every natural number, n, you can use induction. 1. Prove it is true for n = 1 (or some specific number.) This is called the “base” case. 2. Assuming the theorem is true for n = k (this is called the “induction hypothesis”.) 3. Now do the work to show the next case f ...
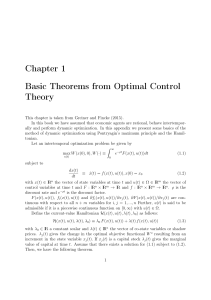
Chapter 1 Basic Theorems from Optimal Control Theory
... with λ0 = 1 is concave in x(t) and if the transversality condition limt→∞ e−ρt λ(t)(x(t) − xo (t)) ≥ 0 holds, conditions (a) and (b) from Theorem 1 are also sufficient for an optimum. If the maximized Hamiltonian Ho (x(t), λ(t), λ0 ) is strictly concave in x(t) for all t, xo (t) is unique (but not n ...
... with λ0 = 1 is concave in x(t) and if the transversality condition limt→∞ e−ρt λ(t)(x(t) − xo (t)) ≥ 0 holds, conditions (a) and (b) from Theorem 1 are also sufficient for an optimum. If the maximized Hamiltonian Ho (x(t), λ(t), λ0 ) is strictly concave in x(t) for all t, xo (t) is unique (but not n ...
Here is the final list of topics for the final exam.
... For roughly 80 percent of the exam, the focus will be on the definitions, theorems (and their proofs), and examples we have done in class (listed below). The remaining 20 percent will ask you to build on these to prove some new results or define some new concepts (much like the Inquiries we have don ...
... For roughly 80 percent of the exam, the focus will be on the definitions, theorems (and their proofs), and examples we have done in class (listed below). The remaining 20 percent will ask you to build on these to prove some new results or define some new concepts (much like the Inquiries we have don ...
Law and Economics – Hsu
... It does not matter to which party you assign property rights. Either way, they’re going to get together and bargain it out. 3. This makes the property right flow to the party that values it the most. The societally economic outcome will be obtained, even with externalities, without government interv ...
... It does not matter to which party you assign property rights. Either way, they’re going to get together and bargain it out. 3. This makes the property right flow to the party that values it the most. The societally economic outcome will be obtained, even with externalities, without government interv ...
environmental-natural-resources-economics-9th-edition
... seeking price supports or consumer groups seeking subsidies are examples of rent seeking. B. Incomplete information is other source of inefficient government policies. IX. The Pursuit of Efficiency Several solutions to the above problems should be covered. It is likely that you will already have cov ...
... seeking price supports or consumer groups seeking subsidies are examples of rent seeking. B. Incomplete information is other source of inefficient government policies. IX. The Pursuit of Efficiency Several solutions to the above problems should be covered. It is likely that you will already have cov ...
Natural-Resource-Economics-10th-Edition-Tietenberg
... seeking price supports or consumer groups seeking subsidies are examples of rent seeking. B. Incomplete information is other source of inefficient government policies. X. The Pursuit of Efficiency Several solutions to the above problems should be covered. It is likely that you will already have cove ...
... seeking price supports or consumer groups seeking subsidies are examples of rent seeking. B. Incomplete information is other source of inefficient government policies. X. The Pursuit of Efficiency Several solutions to the above problems should be covered. It is likely that you will already have cove ...
Sec 1 Cont: Mean Value Theorem (MVT)
... Review: Rolle’s Theorem For Rolle’s Theorem to work the function must be ...
... Review: Rolle’s Theorem For Rolle’s Theorem to work the function must be ...
Lecture 3
... Externality implies there is another cost (for negative externalities) or another benefit (for positive externalities) that is not counted by the market! Label market counted benefits and costs - “private” Label component not counted as “social” ...
... Externality implies there is another cost (for negative externalities) or another benefit (for positive externalities) that is not counted by the market! Label market counted benefits and costs - “private” Label component not counted as “social” ...
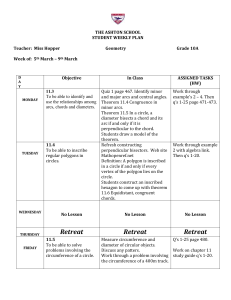
THE ASHTON SCHOOL STUDENT WEEKLY PLAN Teacher: Miss
... and major arcs and central angles. Theorem 11.4 Congruence in minor arcs. Theorem 11.5 In a circle, a diameter bisects a chord and its arc if and only if it is perpendicular to the chord. Students draw a model of the theorem. Refresh constructing perpendicular bisectors. Web site Mathopenref.net Def ...
... and major arcs and central angles. Theorem 11.4 Congruence in minor arcs. Theorem 11.5 In a circle, a diameter bisects a chord and its arc if and only if it is perpendicular to the chord. Students draw a model of the theorem. Refresh constructing perpendicular bisectors. Web site Mathopenref.net Def ...
Market Failures
... • Private market does not provide insurance for many important risks that individuals face • Causes: transactions costs , asymmetries of information, enforcement costs • Solution: government undertake a number of initiatives, insurance programs, loans and ...
... • Private market does not provide insurance for many important risks that individuals face • Causes: transactions costs , asymmetries of information, enforcement costs • Solution: government undertake a number of initiatives, insurance programs, loans and ...
Market Failures
... • Private market does not provide insurance for many important risks that individuals face • Causes: transactions costs , asymmetries of information, enforcement costs • Solution: government undertake a number of initiatives, insurance programs, loans and ...
... • Private market does not provide insurance for many important risks that individuals face • Causes: transactions costs , asymmetries of information, enforcement costs • Solution: government undertake a number of initiatives, insurance programs, loans and ...
Externalities
... So … • Societal optimum dictates that each firm produce less than in an autarkical system. • Remedy, again, would be a tax. • Once again, a situation where ownership is not well-defined and one’s actions affect others. ...
... So … • Societal optimum dictates that each firm produce less than in an autarkical system. • Remedy, again, would be a tax. • Once again, a situation where ownership is not well-defined and one’s actions affect others. ...
Concepts For Micro Theory
... Taxes vs. Standards: who gets the money/efficiency Right amount of pollution: Between firms, between firms and consumers. Diagram read from both sides price of clean air/water is too low results in too much of polluting input (isoquant diagram) results in too much output private margin ...
... Taxes vs. Standards: who gets the money/efficiency Right amount of pollution: Between firms, between firms and consumers. Diagram read from both sides price of clean air/water is too low results in too much of polluting input (isoquant diagram) results in too much output private margin ...
Externalities, Environmental Policy, and Public Goods
... In England during the Middle Ages, each village had an area of pasture, known as a commons, on which any family in the village was allowed to graze its cows or sheep without charge. Since the grass that one cow ate was not available to another cow, consumption was rival. But every family in the vill ...
... In England during the Middle Ages, each village had an area of pasture, known as a commons, on which any family in the village was allowed to graze its cows or sheep without charge. Since the grass that one cow ate was not available to another cow, consumption was rival. But every family in the vill ...
Exam 2 Study Guide
... o Choosing Multiple Prices o In Everyday Life Chapter 14: Economic Efficiency Economic efficiency Pareto improvements Efficient quantity Measuring market gains (Consumer and Producer Surplus) Inefficient markets and Deadweight Loss o Price ceiling & Price floor o Significant market power ( ...
... o Choosing Multiple Prices o In Everyday Life Chapter 14: Economic Efficiency Economic efficiency Pareto improvements Efficient quantity Measuring market gains (Consumer and Producer Surplus) Inefficient markets and Deadweight Loss o Price ceiling & Price floor o Significant market power ( ...
Lecture 10: Theories of Market Failure
... "commons" (as in "Boston Common"). Everyone could graze as many sheep on the commons as they wanted. This created an externality problem: if you put a sheep on the commons, you got all the benefits (more and fatter sheep) while the costs (in terms of the impact on the other sheep and the land qualit ...
... "commons" (as in "Boston Common"). Everyone could graze as many sheep on the commons as they wanted. This created an externality problem: if you put a sheep on the commons, you got all the benefits (more and fatter sheep) while the costs (in terms of the impact on the other sheep and the land qualit ...
Taylor`s Theorem - Integral Remainder
... Remark In this version, the error term involves an integral. Because of this, we assume that f k+1 is continuous, whereas previously we only assumed this derivative exists. However, we get the valuable bonus that this integral version of Taylor’s theorem does not involve the essentially unknown cons ...
... Remark In this version, the error term involves an integral. Because of this, we assume that f k+1 is continuous, whereas previously we only assumed this derivative exists. However, we get the valuable bonus that this integral version of Taylor’s theorem does not involve the essentially unknown cons ...
, (), De- Vladimir I. GURARIY OH 44242, USA,
... OH 44242, USA, Linability and Spaceability of sets in Function Spaces. ABSTRACT. The set M in linear topological space X is said to be linable (corresp., spaceable) if there exists a inÞnitedimensional linear manifold (corresp. subspace) Y in X such that Y is subset in M . Report is devoted to revie ...
... OH 44242, USA, Linability and Spaceability of sets in Function Spaces. ABSTRACT. The set M in linear topological space X is said to be linable (corresp., spaceable) if there exists a inÞnitedimensional linear manifold (corresp. subspace) Y in X such that Y is subset in M . Report is devoted to revie ...