* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 30
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
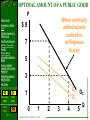
Public Goods Demand for a Public Good Optimal Amount of a Public Good Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits 30 C HAPTE R Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 1 Next Slide Government And Market Failure Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 PUBLIC GOODS Public Goods Demand for a Public Good Optimal Amount of a Public Good Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Private Goods Divisibility Demand Curve is Horizontal Summation Public Goods Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 2 Next Slide Indivisible Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 DEMAND FOR A PUBLIC GOOD Problems of Revealing Preferences Public Goods Demand for a Public Good Optimal Amount of a Public Good Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling Quantity 1 Adams’ Willingness to pay (price) Exclusion Principle does not apply Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 3 Benson’s Collective Willingness Willingness to pay (price) to pay (price) Next Slide Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 DEMAND FOR A PUBLIC GOOD Problems of Revealing Preferences Public Goods Demand for a Public Good Optimal Amount of a Public Good Quantity Adams’ Willingness to pay (price) 1 $4 Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 4 Next Slide Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 Benson’s Collective Willingness Willingness to pay (price) to pay (price) + $5 = $9 DEMAND FOR A PUBLIC GOOD Problems of Revealing Preferences Public Goods Demand for a Public Good Optimal Amount of a Public Good Quantity Adams’ Willingness to pay (price) 1 2 $4 3 Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 5 Next Slide Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 Benson’s Collective Willingness Willingness to pay (price) to pay (price) + $5 + 4 = $9 = 7 DEMAND FOR A PUBLIC GOOD Problems of Revealing Preferences Public Goods Demand for a Public Good Optimal Amount of a Public Good Quantity Adams’ Willingness to pay (price) 1 2 3 $4 3 2 Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 6 Next Slide Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 Benson’s Collective Willingness Willingness to pay (price) to pay (price) + $5 + 4 + 3 = $9 = 7 = 5 DEMAND FOR A PUBLIC GOOD Problems of Revealing Preferences Public Goods Demand for a Public Good Optimal Amount of a Public Good Quantity Adams’ Willingness to pay (price) 1 2 3 4 $4 3 2 1 Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 7 Next Slide Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 Benson’s Collective Willingness Willingness to pay (price) to pay (price) + $5 + 4 + 3 + 2 = $9 = 7 = 5 = 3 DEMAND FOR A PUBLIC GOOD Problems of Revealing Preferences Public Goods Demand for a Public Good Optimal Amount of a Public Good Quantity Adams’ Willingness to pay (price) 1 2 3 4 5 $4 3 2 1 0 Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 8 Next Slide Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 Benson’s Collective Willingness Willingness to pay (price) to pay (price) + $5 + 4 + 3 + 2 + 1 = $9 = 7 = 5 = 3 = 1 OPTIMAL AMOUNT OF A PUBLIC GOOD P Public Goods Demand for a Public Good $9 Optimal Amount of a Public Good Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights 7 5 Adams’ willingness to pay Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling 3 Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 9 Next Slide 1 D1 0 1 Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 2 3 4 5 Q OPTIMAL AMOUNT OF A PUBLIC GOOD P Public Goods Demand for a Public Good $9 Optimal Amount of a Public Good Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Benson’s willingness to pay 7 5 Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling 3 Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 10 Next Slide D2 D1 1 0 1 Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 2 3 4 5 Q Public Goods Demand for a Public Good Optimal Amount of a Public Good Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights OPTIMAL AMOUNT OF A PUBLIC GOOD P When vertically $9 added equals collective 7 willingness to pay 5 Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling 3 Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 11 Next Slide D2 D1 1 0 1 Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 2 3 4 DC 5 Q OPTIMAL AMOUNT OF A PUBLIC GOOD P Public Goods Demand for a Public Good $9 S Optimal Amount of a Public Good Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights 7 The public good’s marginal Cost as shown by S 5 Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling 3 Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 12 Next Slide DC 1 0 1 Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 2 3 4 5 Q OPTIMAL AMOUNT OF A PUBLIC GOOD P Public Goods Demand for a Public Good $9 S Optimal Amount of a Public Good Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Yields the optimum amount of the public good 7 5 Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling MB = MC 3 Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 13 Next Slide DC 1 0 1 Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 2 3 4 5 Q COST-BENEFIT ANALYSIS Public Goods Demand for a Public Good Optimal Amount of a Public Good Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Marginal Cost = Marginal Benefit Rule Externalities Spillover Costs Overallocation Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 14 Next Slide Spillover Benefits Underallocation Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 SPILLOVER COSTS AND BENEFITS P Public Goods Demand for a Public Good St Spillover costs Optimal Amount of a Public Good S Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 15 Overallocation Next Slide 0 Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 Q0 Qe D Q SPILLOVER COSTS AND BENEFITS P St Public Goods Demand for a Public Good Optimal Amount of a Public Good Spillover Benefits Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Dt Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 16 Underallocation Next Slide 0 Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 Qe Q0 D Q SPILLOVER COSTS AND BENEFITS Public Goods Demand for a Public Good Optimal Amount of a Public Good Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 17 Next Slide Individual Bargaining Coase Theorem Liability Rules and Lawsuits Government Intervention Direct Controls Specific Taxes Subsidies and Government Provision Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 CORRECTING SPILLOVER COSTS P Public Goods Demand for a Public Good St Spillover costs Optimal Amount of a Public Good S Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling TAX Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 18 Overallocation Corrected Next Slide 0 Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 Q0 Qe D Q CORRECTING SPILLOVER BENFITS P Public Goods Demand for a Public Good S Optimal Amount of a Public Good Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Spillover Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Dt Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling Key Terms D Underallocation Previous Slide End Show 30 - 19 Next Slide 0 Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 Qe Q0 Q CORRECTING SPILLOVER BENFITS P Correcting by Subsidy to Consumers Public Goods Demand for a Public Good S Optimal Amount of a Public Good Cost-Benefit Analysis Subsidy to consumer increases demand Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Dt Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 20 D Underallocation Corrected Next Slide 0 Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 Qe Q0 Q CORRECTING SPILLOVER BENFITS Public Goods Demand for a Public Good P Correcting by Subsidy to Producers St Subsidy to producers increases supply Optimal Amount of a Public Good Cost-Benefit Analysis S’t Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 21 Underallocation Corrected Next Slide 0 Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 Qe Q0 D Q Demand for a Public Good Optimal Amount of a Public Good Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 22 Next Slide Price per pollution right Public Goods A MARKET-BASED APPROACH TO SPILLOVER COSTS The Tragedy of the Commons A Market for Externality Rights •Operation of the Market •Advantages S = Supply of pollution rights D 2002 $200 $100 D 2012 500 750 1000 Quantity of pollution rights Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 SOCIETY’S OPTIMAL AMOUNT OF EXTERNALITY REDUCTION Public Goods Demand for a Public Good Optimal Amount of a Public Good Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling End Show 30 - 23 MC – MB Equilibrium Optimal Reduction of an Externality Shifts in the Curves Key Terms Previous Slide Application of MC = MB Rule Graphically… Next Slide Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 Public Goods Demand for a Public Good Optimal Amount of a Public Good Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 24 Next Slide Society’s marginal benefit and marginal cost of pollution abatement SOCIETY’S OPTIMAL AMOUNT OF EXTERNALITY REDUCTION MC Socially optimum amount of pollution abatement MB 0 Q1 Amount of pollution abatement Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 Public Goods Demand for a Public Good Optimal Amount of a Public Good Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 25 Next Slide SOLID-WASTE DISPOSAL AND RECYCLING The Law of Conservation of Matter and Energy Market for Recyclable Inputs Policy •Demand Incentives •Supply Incentives Global Warming Theory Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 Public Goods Demand for a Public Good Optimal Amount of a Public Good Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 26 Next Slide SOLID-WASTE DISPOSAL AND RECYCLING Information Failures Asymmetric Information Inadequate information about sellers Inadequate information about buyers Moral Hazard Problem Adverse Selection Problem •Workplace Safety Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 Chapter Conclusions Public Goods Demand for a Public Good Optimal Amount of a Public Good Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 27 Next Slide Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002 cost-benefit analysis Marginal-cost – marginal-benefit rule externalities Coase theorem tragedy of the commons market for externality rights optimal reduction of an externality law of conservation of matter and energy asymmetric information moral hazard problem adverse selection problem Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin 2002 BACK END Public Goods Demand for a Public Good Optimal Amount of a Public Good Cost-Benefit Analysis Spillover Costs and Benefits Market-Based Approach to Spillover Rights Society’s Optimal Amount of Externality Reduction Solid-Waste Disposal and Recycling Key Terms Previous Slide End Show 30 - 29 Next Slide Public Choice Theory And The Economics of Taxation Chapter 31 Copyright McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2002