Presentation
... chains, such as Taj hotels, ITC welcomgroup, etc.with close to 50% market share. It also has installa4ons in Sri Lanka, Maldives, Belfast and Dubai. In most of these hotels Microsense has provided t ...
... chains, such as Taj hotels, ITC welcomgroup, etc.with close to 50% market share. It also has installa4ons in Sri Lanka, Maldives, Belfast and Dubai. In most of these hotels Microsense has provided t ...
Managing Telecommunications
... “Infrastructure of old” is the telephone network, Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) – Built on twisted-pair copper wires and was intended for voice communications – Uses analog technology and circuit switching – Based on “dumb voice telephones” ...
... “Infrastructure of old” is the telephone network, Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) – Built on twisted-pair copper wires and was intended for voice communications – Uses analog technology and circuit switching – Based on “dumb voice telephones” ...
Alice and Bob Get Physical: Insights into Physical Layer Security
... channel probing techniques can verify the authenticity of a transmitter (thus thwarting spoofing attacks), as well as provide a means to ensure that a transmitter claims a single identity (thus thwarting Sybil attacks). Similarly, for confidentiality, we examine several strategies for establishing s ...
... channel probing techniques can verify the authenticity of a transmitter (thus thwarting spoofing attacks), as well as provide a means to ensure that a transmitter claims a single identity (thus thwarting Sybil attacks). Similarly, for confidentiality, we examine several strategies for establishing s ...
Wireless Multi-Client Bridge/AP 2611CB3 PLUS (Deluxe) 2.4 GHz
... No driver needed, easy and quick to connect your Ethernet device to Wireless ...
... No driver needed, easy and quick to connect your Ethernet device to Wireless ...
The Internet is a global communication network which acts as a
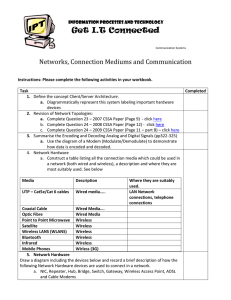
... Draw a diagram including the devices below and record a brief description of how the following Network Hardware devices are used to connect in a network. a. NIC, Repeater, Hub, Bridge, Switch, Gateway, Wireless Access Point, ADSL and Cable Modems ...
... Draw a diagram including the devices below and record a brief description of how the following Network Hardware devices are used to connect in a network. a. NIC, Repeater, Hub, Bridge, Switch, Gateway, Wireless Access Point, ADSL and Cable Modems ...
research and evaluate ubnt wifi antenna for a 5 km
... There is no need for an Ethernet cable to connect computers to each other. ...
... There is no need for an Ethernet cable to connect computers to each other. ...
Wireless Multi-Client Bridge/AP 2611CB3 PLUS (Deluxe)
... No driver needed, easy and quick to connect your Ethernet device to Wireless ...
... No driver needed, easy and quick to connect your Ethernet device to Wireless ...
Wireless Network Security
... • Use longer WEP encryption keys, which makes the data analysis task more difficult. If your WLAN equipment supports 128-bit WEP keys. • Change your WEP keys frequently. There are devices that support "dynamic WEP" which is off the standard but allows different WEP keys to be assigned to each user. ...
... • Use longer WEP encryption keys, which makes the data analysis task more difficult. If your WLAN equipment supports 128-bit WEP keys. • Change your WEP keys frequently. There are devices that support "dynamic WEP" which is off the standard but allows different WEP keys to be assigned to each user. ...
Wireless Security
... The packets sent over the network can then be decrypted with the key. About 250,000 IVs needed to crack a 64-bit WEP key, 500,000 to 1 million for a 128-bit (WEP2) key ...
... The packets sent over the network can then be decrypted with the key. About 250,000 IVs needed to crack a 64-bit WEP key, 500,000 to 1 million for a 128-bit (WEP2) key ...
A threat can be any person, object, or event that, if realized, could
... wireless base stations are relatively powerful, and residential neighbors or adjacent businesses may connect to each other's wireless networks. Many APs are initially configured to openly broadcast SSIDs of authorized users. SSIDs can be incorrectly used as passwords to verify authorised users, whic ...
... wireless base stations are relatively powerful, and residential neighbors or adjacent businesses may connect to each other's wireless networks. Many APs are initially configured to openly broadcast SSIDs of authorized users. SSIDs can be incorrectly used as passwords to verify authorised users, whic ...
Network Forensics Tracking Hackers Through Cyberspace.
... • An attacker sets up a WAP with the same SSID as a legitimate WLAN • Man-in-the-middle attack ...
... • An attacker sets up a WAP with the same SSID as a legitimate WLAN • Man-in-the-middle attack ...
Document
... 1. Unauthorized or “rogue” access points on trusted networks 2. Access to network by unauthorized clients (theft of service, "war driving") ...
... 1. Unauthorized or “rogue” access points on trusted networks 2. Access to network by unauthorized clients (theft of service, "war driving") ...
Network Tomography Based on Flow Level Measurements
... Introduction Security Criteria Vulnerabilities ...
... Introduction Security Criteria Vulnerabilities ...
Chpt 10 - 07 test.doc
... A network that covers a large campus or city A network that covers a large geographical area and is made up of many smaller networks A measure of how much data can travel over a given communication system in a given amount of time A pass-through and distribution point for every device connected to i ...
... A network that covers a large campus or city A network that covers a large geographical area and is made up of many smaller networks A measure of how much data can travel over a given communication system in a given amount of time A pass-through and distribution point for every device connected to i ...
Abstract for ITU seminar on BWA for rural & remote... In order to bridge the digital divide between urban and... rural wireless solution is envisaged in India, which offers mobility...
... existing rural wire-line systems, as well as any other switching systems using the standard interfaces. Along-with this they also support VOIP features for interfacing to a centralized soft-switch using an IP/MPLS network. This rural solution utilizes standard wireless broadband technologies (Wi-Fi ...
... existing rural wire-line systems, as well as any other switching systems using the standard interfaces. Along-with this they also support VOIP features for interfacing to a centralized soft-switch using an IP/MPLS network. This rural solution utilizes standard wireless broadband technologies (Wi-Fi ...
man-in-the-middle - Personal.kent.edu
... • Targets the Windows wireless stack • Possible to obtain the WEP key from a remote client • Sends flood of encrypted ARP requests • Attacker can obtain the WEP key within minutes ...
... • Targets the Windows wireless stack • Possible to obtain the WEP key from a remote client • Sends flood of encrypted ARP requests • Attacker can obtain the WEP key within minutes ...
Giuseppe Razzano , Neeli R. Prasad , Roberto De Paolis
... ·Dynamic keys: allows per-session and per-packet dynamic ciphering keys. ·Message integrity checking (MIC): ensures that message have not been tampered during transmission. ·48-bit IV hashing provides longer IV (used in conjunction with a base key to encrypt and decrypt data) that avoids the weaknes ...
... ·Dynamic keys: allows per-session and per-packet dynamic ciphering keys. ·Message integrity checking (MIC): ensures that message have not been tampered during transmission. ·48-bit IV hashing provides longer IV (used in conjunction with a base key to encrypt and decrypt data) that avoids the weaknes ...
Wireless Networking & Security
... Standard 64 bit WEP uses 40 bit key. Other 24 bits is IV. Can also use 128/256 bit protocols. IV (Initialization Vector) - prepended onto packets and is based on pre-shared key. • Such short IVs in 64 bit caused reuse of IVs with same key, which significantly shortened key cracking times of WEP. • A ...
... Standard 64 bit WEP uses 40 bit key. Other 24 bits is IV. Can also use 128/256 bit protocols. IV (Initialization Vector) - prepended onto packets and is based on pre-shared key. • Such short IVs in 64 bit caused reuse of IVs with same key, which significantly shortened key cracking times of WEP. • A ...
Security challenges in the lighting use case
... Security challenges in Smart Lighting Paul Chilton NXP Semiconductors ...
... Security challenges in Smart Lighting Paul Chilton NXP Semiconductors ...
Wireless security
.jpg?width=300)
Wireless security is the prevention of unauthorized access or damage to computers using wireless networks. The most common types of wireless security are Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) and Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA). WEP is a notoriously weak security standard. The password it uses can often be cracked in a few minutes with a basic laptop computer and widely available software tools. WEP is an old IEEE 802.11 standard from 1999, which was outdated in 2003 by WPA, or Wi-Fi Protected Access. WPA was a quick alternative to improve security over WEP. The current standard is WPA2; some hardware cannot support WPA2 without firmware upgrade or replacement. WPA2 uses an encryption device that encrypts the network with a 256-bit key; the longer key length improves security over WEP.Many laptop computers have wireless cards pre-installed. The ability to enter a network while mobile has great benefits. However, wireless networking is prone to some security issues. Hackers have found wireless networks relatively easy to break into, and even use wireless technology to hack into wired networks. As a result, it is very important that enterprises define effective wireless security policies that guard against unauthorized access to important resources. Wireless Intrusion Prevention Systems (WIPS) or Wireless Intrusion Detection Systems (WIDS) are commonly used to enforce wireless security policies.The risks to users of wireless technology have increased as the service has become more popular. There were relatively few dangers when wireless technology was first introduced. Hackers had not yet had time to latch on to the new technology, and wireless networks were not commonly found in the work place. However, there are many security risks associated with the current wireless protocols and encryption methods, and in the carelessness and ignorance that exists at the user and corporate IT level. Hacking methods have become much more sophisticated and innovative with wireless access. Hacking has also become much easier and more accessible with easy-to-use Windows- or Linux-based tools being made available on the web at no charge.Some organizations that have no wireless access points installed do not feel that they need to address wireless security concerns. In-Stat MDR and META Group have estimated that 95% of all corporate laptop computers that were planned to be purchased in 2005 were equipped with wireless cards. Issues can arise in a supposedly non-wireless organization when a wireless laptop is plugged into the corporate network. A hacker could sit out in the parking lot and gather information from it through laptops and/or other devices, or even break in through this wireless card–equipped laptop and gain access to the wired network.